Increased microparticle tissue factor activity in cancer patients with Venous Thromboembolism - PubMed (original) (raw)
Increased microparticle tissue factor activity in cancer patients with Venous Thromboembolism
David A Manly et al. Thromb Res. 2010 Jun.
Abstract
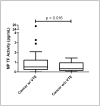
Cancer patients exhibit a high rate of thromboembolism (VTE). In this study, we analyzed levels of microparticle (MP) tissue factor (TF) activity in cancer patients with or without VTE. Blood was collected from cancer patients within 24 h of objectively diagnosed VTE (n=53) and from cancer patients without VTE (n=13). MPs were isolated from platelet poor plasma by centrifugation at 20,000g for 15 min. MP TF activity was measured using a two-stage chromogenic assay. Cancer patients with VTE had a significantly higher mean MP TF activity compared with cancer patients without VTE (1.7+/-3.8 pg/mL vs 0.6+/-0.4 pg/mL, p<0.05). Further prospective studies are required to determine if levels of MP TF activity may be a useful biomarker to identify patients at increased risk for VTE.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Figure
Comparison of MP TF activity between cancer patients with VTE (n=53) and cancer patients without VTE (n=13) (Median, Inter-quartile Range, 2 Standard Deviations). Dots represent MP TF activity levels beyond 2 standard deviations.
Similar articles
- High concentration of the plasma microparticles for venous thromboembolism associated with lung cancer.
Wang M, Huang X, Zhu M, Zhang S, Zhang Y. Wang M, et al. Clin Respir J. 2020 May;14(5):481-487. doi: 10.1111/crj.13158. Epub 2020 Feb 19. Clin Respir J. 2020. PMID: 32031323 - Tissue factor-bearing microparticles and inflammation: a potential mechanism for the development of venous thromboembolism in cancer.
Date K, Ettelaie C, Maraveyas A. Date K, et al. J Thromb Haemost. 2017 Dec;15(12):2289-2299. doi: 10.1111/jth.13871. Epub 2017 Nov 8. J Thromb Haemost. 2017. PMID: 29028284 Review. - Microparticle-associated tissue factor activity, venous thromboembolism and mortality in pancreatic, gastric, colorectal and brain cancer patients.
Thaler J, Ay C, Mackman N, Bertina RM, Kaider A, Marosi C, Key NS, Barcel DA, Scheithauer W, Kornek G, Zielinski C, Pabinger I. Thaler J, et al. J Thromb Haemost. 2012 Jul;10(7):1363-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2012.04754.x. J Thromb Haemost. 2012. PMID: 22520016 - Endothelial, platelet, and tissue factor-bearing microparticles in cancer patients with and without venous thromboembolism.
Campello E, Spiezia L, Radu CM, Bulato C, Castelli M, Gavasso S, Simioni P. Campello E, et al. Thromb Res. 2011 May;127(5):473-7. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2011.01.002. Epub 2011 Jan 22. Thromb Res. 2011. PMID: 21256535 - Measurement of microparticle tissue factor activity in clinical samples: A summary of two tissue factor-dependent FXa generation assays.
Hisada Y, Alexander W, Kasthuri R, Voorhees P, Mobarrez F, Taylor A, McNamara C, Wallen H, Witkowski M, Key NS, Rauch U, Mackman N. Hisada Y, et al. Thromb Res. 2016 Mar;139:90-7. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2016.01.011. Epub 2016 Jan 18. Thromb Res. 2016. PMID: 26916302 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Tumor-derived tissue factor-positive microparticles and venous thrombosis in cancer patients.
Geddings JE, Mackman N. Geddings JE, et al. Blood. 2013 Sep 12;122(11):1873-80. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-04-460139. Epub 2013 Jun 24. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23798713 Free PMC article. Review. - A novel pathway of cellular activation mediated by antiphospholipid antibody-induced extracellular vesicles.
Wu M, Barnard J, Kundu S, McCrae KR. Wu M, et al. J Thromb Haemost. 2015 Oct;13(10):1928-40. doi: 10.1111/jth.13072. Epub 2015 Sep 15. J Thromb Haemost. 2015. PMID: 26264622 Free PMC article. - Thrombin Generation and Cancer: Contributors and Consequences.
Reddel CJ, Tan CW, Chen VM. Reddel CJ, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jan 16;11(1):100. doi: 10.3390/cancers11010100. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30654498 Free PMC article. Review. - Microparticles: new light shed on the understanding of venous thromboembolism.
Zhou L, Qi XL, Xu MX, Mao Y, Liu ML, Song HM. Zhou L, et al. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014 Sep;35(9):1103-10. doi: 10.1038/aps.2014.73. Epub 2014 Aug 25. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014. PMID: 25152025 Free PMC article. Review. - Role of tissue factor in thrombosis in antiphospholipid antibody syndrome.
Boles J, Mackman N. Boles J, et al. Lupus. 2010 Apr;19(4):370-8. doi: 10.1177/0961203309360810. Lupus. 2010. PMID: 20353972 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Khorana AA, Francis CW, Culakova E, et al. Thromboembolism is a leading cause of death in cancer patients receiving outpatient chemotherapy. Thromb Haemost. 2007;5(3):632–4. - PubMed
- Kroger K, Weiland D, Ose C, et al. Risk factors for venous thromboembolic events in cancer patients. Ann Oncol. 2006 Feb;17(2):297–303. - PubMed
- Ay C, Simanek R, Vormittag R, et al. High plasma levels of soluble P-selectin are predictive of venous thromboembolism in cancer patients: results from the Vienna Cancer and Thrombosis Study (CATS) Blood. 2008 Oct 1;112(7):2703–8. - PubMed
- Cosmi B, Legnani C, Cini M, et al. The role of D-dimer and residual venous obstruction in recurrence of venous thromboembolism after anticoagulation withdrawal in cancer patients. Haematologica. 2005 May;90(5):713–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous