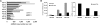Absolute quantification of microRNAs by using a universal reference - PubMed (original) (raw)
Absolute quantification of microRNAs by using a universal reference
Ute Bissels et al. RNA. 2009 Dec.
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a species of small RNAs approximately 21-23-nucleotides long that have been shown to play an important role in many different cellular, developmental, and physiological processes. Accordingly, numerous PCR-, sequencing-, or hybridization-based methods have been established to identify and quantify miRNAs. Their short length results in a high dynamic range of melting temperatures and therefore impedes a proper selection of detection probes or optimized PCR primers. While miRNA microarrays allow for massive parallel and accurate relative measurement of all known miRNAs, they have so far been less useful as an assay for absolute quantification. Here, we present a microarray-based approach for global and absolute quantification of miRNAs. The method relies on the parallel hybridization of the sample of interest labeled with Cy5 and a universal reference of 954 synthetic miRNAs in equimolar concentrations that are labeled with Cy3 on a microarray slide containing probes for all human, mouse, rat, and viral miRNAs (miRBase 12.0). Each single miRNA is quantified with respect to the universal reference canceling biases related to sequence, labeling, or hybridization. We demonstrate the accuracy of the method by various spike-in experiments. Furthermore, we quantified miRNA copy numbers in liver samples and CD34(+)/CD133(-) hematopoietic progenitor cells.
Figures
FIGURE 1.
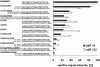
Relative signal intensities of different oligodeoxynucleotide probes for miR-16 and miR-122. The signal intensity of each different oligo variant is displayed in relation to the corresponding standard probe signal intensity, which is set to 100%. All oligodeoxynucleotide probes comprise the reverse complementary sequence of miR-16 and miR-122 and are covalently linked to the slide surface via a C6-amino linker except for the no linker controls. “a),” Standard probe: perfect match reverse complementary miRNA, C6-amino linker; “b)–d).” probe variants with an additional spacer of 6, 12, and 18 random nucleotides on the 5′-end; “e)” and “f),” dimer or trimer probe variants; “g)” and “h),” truncated probe variants; and “i)–l),” probe variants without linker.
FIGURE 2.
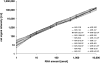
Dynamic range of the miRNA microarrays. An equimolar mixture of miRNAs was labeled and hybridized to microarrays in amounts of 1 amol to 10 fmol per miRNA. Net signal intensities (background subtracted signals) for 20 miRNAs are shown. The slope within the dlog-Plots was 1.004 (±0.05 SD) with a regression coefficient of >0.98.
FIGURE 3.
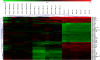
Average linkage cluster of miRNAs that are differently labeled by the three tested RNA-ligases. The universal reference (version 0.9) was labeled with Cy5 by three RNA ligases, Rnl1, Rnl2(1-249), and Rnl2(1-249)K227Q (n = 7 for each ligase). Discriminatory gene analysis of the microarray signal intensities by the SAM algorithm resulted in 51 miRNAs that are differentially labeled by the different ligases. These miRNAs were grouped according to similarities using two-dimensional hierarchical clustering (Euclidian distance, average linkage). Log2-transformed expression ratios are indicated from −3.0 (green) to 3.0 (red). (1-7) Sample 1-7 labeled by Rnl2(1-249)K227Q; (8-14) sample 8-14 labeled by Rnl2(1-249); (15-21) sample 15-21 labeled by Rnl1.
FIGURE 4.
Absolute quantification of miRNAs. (A) Liver total RNA was spiked with 75 synthetic miRNAs not detectable in liver in amounts ranging from 0.3125 to 20 fmol and hybridized versus the universal reference. (Empty black diamonds) The measured and expected amounts for the 75 spike-ins. (Black squares) The measured mean value and its standard deviation. The diagram displays one of four array experiments (complete data are shown in Supplemental Fig. 2). (B) Absolute expression level of the 25 highest expressed miRNAs detected in 1 μg of liver (n = 4). One microgram of liver total RNA was labeled with Cy5 and hybridized together with 2.5 fmol/miRNA of UR. The median miRNA amount calculated from the signal intensities after comparison with the UR was 633 copies per 10 pg of liver total RNA. (C) Dlog-plot showing the calculated amounts for the detected miRNAs in 500 ng and 1 μg of liver RNA. The regression coefficient is 0.997 and the slope 0.51 (expected slope: 0.5). (D) Comparison of microarray and qRT-PCR data for miR-16, miR-30b, and miR-122. One to ten nanograms of liver total RNA were used for the qRT-PCR. Copy numbers per 10 pg of total RNA were calculated using standard curves based on the UR (n = 3). Microarray data are the same as in B.
FIGURE 5.
MicroRNA copy numbers of CD34(+)/CD133(−) cells prepared from three different donors. (A) The 10 most abundant miRNAs in CD34(+)/CD133(−) cells are shown. The copy numbers per cell for the highest expressed miRNAs miR-223 and miR-451 were determined to be between 828 and 1972. (B, left) Net signal intensities and (right) miRNA copy numbers for miR-30b, miR-126-3p, and miR-106a are shown (donor 2).
Similar articles
- Detection and Quantification of MicroRNAs by Ligase-Assisted Sandwich Hybridization on a Microarray.
Iizuka R, Ueno T, Funatsu T. Iizuka R, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1368:53-65. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3136-1_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26614068 - Performing custom microRNA microarray experiments.
Zhang X, Zeng Y. Zhang X, et al. J Vis Exp. 2011 Oct 28;(56):e3250. doi: 10.3791/3250. J Vis Exp. 2011. PMID: 22064514 Free PMC article. - Rational probe optimization and enhanced detection strategy for microRNAs using microarrays.
Goff LA, Yang M, Bowers J, Getts RC, Padgett RW, Hart RP. Goff LA, et al. RNA Biol. 2005 Jul-Sep;2(3):93-100. doi: 10.4161/rna.2.3.2059. Epub 2005 Jul 20. RNA Biol. 2005. PMID: 17114923 - MicroRNA detection by microarray.
Li W, Ruan K. Li W, et al. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2009 Jun;394(4):1117-24. doi: 10.1007/s00216-008-2570-2. Epub 2009 Jan 9. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2009. PMID: 19132354 Review. - MicroRNA profiling of megakaryocytes.
Garzon R. Garzon R. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;496:293-8. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-553-4_19. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 18839118 Review.
Cited by
- The development and controversy of competitive endogenous RNA hypothesis in non-coding genes.
Lin W, Liu H, Tang Y, Wei Y, Wei W, Zhang L, Chen J. Lin W, et al. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 Jan;476(1):109-123. doi: 10.1007/s11010-020-03889-2. Epub 2020 Sep 25. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 32975695 Review. - Reviewing and updating the major molecular markers for stem cells.
Calloni R, Cordero EA, Henriques JA, Bonatto D. Calloni R, et al. Stem Cells Dev. 2013 May 1;22(9):1455-76. doi: 10.1089/scd.2012.0637. Epub 2013 Jan 22. Stem Cells Dev. 2013. PMID: 23336433 Free PMC article. Review. - Potential pitfalls in microRNA profiling.
Chugh P, Dittmer DP. Chugh P, et al. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2012 Sep-Oct;3(5):601-16. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1120. Epub 2012 May 7. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2012. PMID: 22566380 Free PMC article. Review. - Transcriptional and Post-Transcriptional Regulation of Thrombospondin-1 Expression: A Computational Model.
Zhao C, Isenberg JS, Popel AS. Zhao C, et al. PLoS Comput Biol. 2017 Jan 3;13(1):e1005272. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005272. eCollection 2017 Jan. PLoS Comput Biol. 2017. PMID: 28045898 Free PMC article. - CRISPR Editing Enables Consequential Tag-Activated MicroRNA-Mediated Endogene Deactivation.
Papasavva PL, Patsali P, Loucari CC, Kurita R, Nakamura Y, Kleanthous M, Lederer CW. Papasavva PL, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 19;23(3):1082. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031082. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163006 Free PMC article.
References
- Aravin A, Tuschl T. Identification and characterization of small RNAs involved in RNA silencing. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:5830–5840. - PubMed
- Canales RD, Luo Y, Willey JC, Austermiller B, Barbacioru CC, Boysen C, Hunkapiller K, Jensen RV, Knight CR, Lee KY, et al. Evaluation of DNA microarray results with quantitative gene expression platforms. Nat Biotechnol. 2006;24:1115–1122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials