Endoplasmic reticulum stress and intestinal inflammation - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Endoplasmic reticulum stress and intestinal inflammation
A Kaser et al. Mucosal Immunol. 2010 Jan.
Abstract
The intestinal epithelial cell (IEC) is increasingly recognized to play a prominent role as an important intermediary between the commensal microbiota and the intestinal immune system. Moreover, it is now recognized that intestinal inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) may arise primarily from IEC dysfunction due to unresolved endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress as a consequence of genetic disruption of X box binding protein-1 function. In addition to primary (genetic) abnormalities of the unfolded protein response, a variety of secondary (inflammation and environmental) factors are also likely to be important regulators of ER stress. ER stress pathways are also well known to regulate (and be regulated by) autophagy pathways. Therefore, the host's ability to manage ER stress is likely to be a major pathway in the pathogenesis of intestinal inflammation that arises primarily from the IEC. Herein we discuss ER stress in the IEC as both an originator and perpetuator of intestinal inflammation in IBD.
Figures
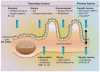
Figure 1
Multiple proximal effectors of ER stress response. Please see text for specific details. Adapted from reference. The transcriptional program of each factor are in the yellow areas.
Figure 2
Model: primary (genetic) and secondary (environmental) factors can drive ER stress in the intestinal epithelium and consequently inflammation.
References
- Blumberg RS, et al. Recent insights into the integration of the intestinal epithelium within the mucosal environment in health and disease. Mucosal. Immunol. 2008;1:330–334. - PubMed
- Artis D. Epithelial-cell recognition of commensal bacteria and maintenance of immune homeostasis in the gut. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008;8:411–420. - PubMed
- Xu W, et al. Epithelial cells trigger frontline immunoglobulin class switching through a pathway regulated by the inhibitor SLPI. Nat. Immunol. 2007;8:294–303. - PubMed
- Rimoldi M, et al. Intestinal immune homeostasis is regulated by the crosstalk between epithelial cells and dendritic cells. Nat. Immunol. 2005;6:507–514. - PubMed
- Zaph C, et al. Epithelial-cell-intrinsic IKK-beta expression regulates intestinal immune homeostasis. Nature. 2007;446:552–556. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials