Regulation of HIF-1alpha and VEGF by miR-20b tunes tumor cells to adapt to the alteration of oxygen concentration - PubMed (original) (raw)
Regulation of HIF-1alpha and VEGF by miR-20b tunes tumor cells to adapt to the alteration of oxygen concentration
Zhang Lei et al. PLoS One. 2009.
Abstract
The regulation of HIF-1alpha is considered to be realized by pVHL-mediated ubiquitin-26S proteasome pathway at a post-transcriptional level. The discovery of a class of small noncoding RNAs, called microRNAs, implies alternative mechanism of regulation of HIF-1alpha. Here, we show that miR-20b plays an important role in fine-tuning the adaptation of tumor cells to oxygen concentration. The inhibition of miR-20b increased the protein levels of HIF-1alpha and VEGF in normoxic tumor cells; the increase of miR-20b in hypoxic tumor cells, nevertheless, decreased the protein levels of HIF-1alpha and VEGF. By using luciferase reporter vector system, we confirmed that miR-20b directly targeted the 3'UTR of Hif1a and Vegfa. On the other hand, the forced overexpression of HIF-1alpha in normoxic tumor cells downregulated miR-20b expression. However, HIF-1alpha knockdown in hypoxic tumor cells caused the increase of miR-20b. The differential expression of miR-20b has important biological significance in tumor cells, either enhancing the growth or favoring the survival of tumor cells upon the oxygen supply. Thus, we identify a novel molecular regulation mechanism through which miR-20b regulates HIF-1alpha and VEGF and is regulated by HIF-1alpha so to keep tumor cells adapting to different oxygen concentrations.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
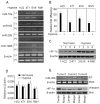
Figure 1. Expression of miR-20b is reversely correlated with HIF-1α level in tumor cells.
(A) The expressions of miR-18a, 155, 20b and 199b in tumor cell lines were detected by RT-PCR in normoxia (20% oxygen) or hypoxia (1% oxygen). (B) The detection of miR-20b in tumor cell lines by real time RT-PCR. The miR-20b level in the hypoxia groups was designated as 1. (C and D) The expression of HIF-1α in tumor cell lines was detected by Western blot (C) or real time RT-PCR (D). (E) Expressions of miR-20b and HIF-1α in different tumor regions. 1×105 H22 tumor cells were inoculated subcutaneously into mice. When tumor size was >9×9 mm, the central and marginal regions of tumor tissues were used for miR-20b and HIF-1α detection by RT-PCR and Western blot, respectively. Data from three tumor tissues were presented in this figure.
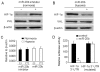
Figure 2. HIF-1α is targeted by miR-20b.
(A) miR-20b inhibitor increased HIF-1α protein in normoxic H22 cells. miR-20b inhibitor or control oligonucleotide was transfected into normoxic H22 cells. 48 hr later, the cells were used to detected HIF-1α and VHL proteins by Western blot. (B) miR-20b decreased HIF-1α protein in hypoxic H22 cells. miR-20b or control oligonucleotide was transfected into hypoxic H22 cells. 48 hr later, the cells were used to detect HIF-1α and VHL proteins by Western blot. (C) miR-20b inhibitor or miR-20b did not affect the mRNA levels of HIF-1α. The cells of above (A) and (B) were used for real time RT-PCR to detect HIF-1α mRNA expression. (D) miR-20b targeted 3′-UTR of HIF-1α mRNA. The specificity of miR-20b to 3′-UTR of HIF-1α mRNA was identified as described in Methods. *, P<0.01, compared with HIF-1α 3′-UTR group.
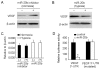
Figure 3. miR-20b is downregulated by HIF-1α.
(A and B) HIF-1α decreased miR-20b expression in normoxic H22 cells. HIF-1α vector or mock vector was transfected into normoxic H22 cells. 72 hr later, the cells were used for HIF-1α analysis by Western blot (A) and miR-20b analysis by RT-PCR and real time RT-PCR (B). (C and D) HIF-1α siRNA was transfected into hypoxic H22 cells. 72 hr later, the cells were used for HIF-1α analysis by Western blot (C) and miR-20b analysis by RT-PCR and real time RT-PCR (D). (E and F) VHL siRNA was transfected into normoxic H22 cells. 72 hr later, the cells were used for VHL and HIF-1α analysis by Western blot (E) and miR-20b analysis by RT-PCR and real time RT-PCR (F).
Figure 4. VEGF is targeted by miR-20b.
(A) miR-20b inhibitor increased VEGF protein in normoxic H22 cells. miR-20b inhibitor or control oligonucleotide was transfected into normoxic H22 cells. 48 hr later, the cells were used to detected VEGF expression by Western blot. (B) miR-20b decreased VEGF protein in hypoxic H22 cells. miR-20b or control oligonucleotide was transfected into hypoxic H22 cells. 48 hr later, the cells were used to detect VEGF expression by Western blot. (C) miR-20b inhibitor or miR-20b did not affect the mRNA levels of VEGF. The cells of above (A) and (B) were used for real time RT-PCR to detect VEGF mRNA expression. (D) miR-20b targeted 3′-UTR of VEGF mRNA. The specificity of miR-20b to 3′-UTR of VEGF mRNA was identified as described in Methods. *, P<0.01, compared with VEGF 3′-UTR group.
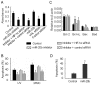
Figure 5. Differential expression of miR-20b affects different aspects of tumor cells.
(A) miR-20b was required for H22 cell growth. H22 cells were transfected with miR-20b inhibitor or miR-20b inhibitor + HIF-1α siRNA or miR-20b or VHL siRNA or control oligonucleotide for 24 hr. Then the cells were seeded in 96-well plate (5×103 per well) for 48 h in normoxia. The proliferation assay was performed with MTT Cell Proliferation Kit (Roche Diagnostics, IN) according to the manufacturer's instructions. *, P<0.05, compared with control. (B) Downregulation of miR-20b enhanced the resistance to apotosis. H22 cells were transfected with miR-20b inhibitor or miR-20b inhibitor + HIF-1α siRNA for 24 hr. Then the cells (1×106) were irradiated by UVB (200 J/m2) or treated with mitomycin C (MMC, 10 µg/ml)for 12 h. The cells were stained with PE-Annexin V and 7-AAD for apoptotic analysis by flow cytometry. *, P<0.05, compared with control. (C) Analysis of the mRNA expressions of Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, Bax and Bad genes. H22 cells were transfected with miR-20b inhibitor or miR-20b inhibitor + HIF-1α siRNA for 72 hr. The cells were used for the analysis of gene expression by real time RT-PCR. *, P<0.05, compared with control. (D) Normoxic H22 cells were transfected with miR-20b for 24 hr. Then the cells were cultured under hypoxic condition for 12 h, and stained with PE-Annexin V and 7-AAD for apoptotic analysis by flow cytometry. *, P<0.05, compared with control.
Similar articles
- MicroRNA-20b Downregulates HIF-1α and Inhibits the Proliferation and Invasion of Osteosarcoma Cells.
Liu M, Wang D, Li N. Liu M, et al. Oncol Res. 2016;23(5):257-66. doi: 10.3727/096504016X14562725373752. Oncol Res. 2016. PMID: 27098149 Free PMC article. - miR-20b modulates VEGF expression by targeting HIF-1 alpha and STAT3 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells.
Cascio S, D'Andrea A, Ferla R, Surmacz E, Gulotta E, Amodeo V, Bazan V, Gebbia N, Russo A. Cascio S, et al. J Cell Physiol. 2010 Jul;224(1):242-9. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22126. J Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20232316 - Long noncoding RNA H19 regulates HIF-1α/AXL signaling through inhibiting miR-20b-5p in endometrial cancer.
Zhu H, Jin YM, Lyu XM, Fan LM, Wu F. Zhu H, et al. Cell Cycle. 2019 Oct;18(19):2454-2464. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1648958. Epub 2019 Aug 14. Cell Cycle. 2019. PMID: 31411527 Free PMC article. Retracted. - HAF : the new player in oxygen-independent HIF-1alpha degradation.
Koh MY, Powis G. Koh MY, et al. Cell Cycle. 2009 May 1;8(9):1359-66. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.9.8303. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19377289 Free PMC article. Review. - Regulation of Cancer-Associated miRNAs Expression under Hypoxic Conditions.
Valencia-Cervantes J, Sierra-Vargas MP. Valencia-Cervantes J, et al. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2024 May 10;2024:5523283. doi: 10.1155/2024/5523283. eCollection 2024. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2024. PMID: 38766303 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Interplay between heme oxygenase-1 and miR-378 affects non-small cell lung carcinoma growth, vascularization, and metastasis.
Skrzypek K, Tertil M, Golda S, Ciesla M, Weglarczyk K, Collet G, Guichard A, Kozakowska M, Boczkowski J, Was H, Gil T, Kuzdzal J, Muchova L, Vitek L, Loboda A, Jozkowicz A, Kieda C, Dulak J. Skrzypek K, et al. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013 Sep 1;19(7):644-60. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5184. Epub 2013 Jun 27. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013. PMID: 23617628 Free PMC article. - Natalizumab restores aberrant miRNA expression profile in multiple sclerosis and reveals a critical role for miR-20b.
Ingwersen J, Menge T, Wingerath B, Kaya D, Graf J, Prozorovski T, Keller A, Backes C, Beier M, Scheffler M, Dehmel T, Kieseier BC, Hartung HP, Küry P, Aktas O. Ingwersen J, et al. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2015 Jan;2(1):43-55. doi: 10.1002/acn3.152. Epub 2014 Dec 5. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25642434 Free PMC article. - Investigating Expression Dynamics of miR-21 and miR-10b in Glioblastoma Cells In Vitro: Insights into Responses to Hypoxia and Secretion Mechanisms.
Charbit H, Lavon I. Charbit H, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 22;25(14):7984. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147984. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063226 Free PMC article. - MicroRNA-20b Downregulates HIF-1α and Inhibits the Proliferation and Invasion of Osteosarcoma Cells.
Liu M, Wang D, Li N. Liu M, et al. Oncol Res. 2016;23(5):257-66. doi: 10.3727/096504016X14562725373752. Oncol Res. 2016. PMID: 27098149 Free PMC article. - Adaptive and maladaptive cardiorespiratory responses to continuous and intermittent hypoxia mediated by hypoxia-inducible factors 1 and 2.
Prabhakar NR, Semenza GL. Prabhakar NR, et al. Physiol Rev. 2012 Jul;92(3):967-1003. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00030.2011. Physiol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22811423 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Choi KS, Bae MK, Jeong JW, Moon HE, Kim KW. Hypoxia-induced angiogenesis during carcinogenesis. J Biochem Mol Biol. 2003;36:120–127. - PubMed
- Pouysségur J, Dayan F, Mazure NM. Hypoxia signalling in cancer and approaches to enforce tumour regression. Nature. 2006;441:437–443. - PubMed
- Liao D, Johnson RS. Hypoxia: a key regulator of angiogenesis in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007;26:281–290. - PubMed
- Semenza GL. Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:721–732. - PubMed
- Weidemann A, Johnson RS. Biology of HIF-1alpha. Cell Death Differ. 2008;15:621–627. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources