CD8(+) T lymphocyte mobilization to virus-infected tissue requires CD4(+) T-cell help - PubMed (original) (raw)
CD8(+) T lymphocyte mobilization to virus-infected tissue requires CD4(+) T-cell help
Yusuke Nakanishi et al. Nature. 2009.
Abstract
CD4(+) T helper cells are well known for their role in providing critical signals during priming of cytotoxic CD8(+) T lymphocyte (CTL) responses in vivo. T-cell help is required for the generation of primary CTL responses as well as in promoting protective CD8(+) memory T-cell development. However, the role of CD4 help in the control of CTL responses at the effector stage is unknown. Here we show that fully helped effector CTLs are themselves not self-sufficient for entry into the infected tissue, but rely on the CD4(+) T cells to provide the necessary cue. CD4(+) T helper cells control the migration of CTL indirectly through the secretion of IFN-gamma and induction of local chemokine secretion in the infected tissue. Our results reveal a previously unappreciated role of CD4 help in mobilizing effector CTL to the peripheral sites of infection where they help to eliminate infected cells.
Figures
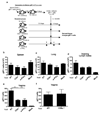
Figure 1. CD4 help is required for CTL migration into the vaginal mucosa after HSV-2 infection
(a) Naïve congenic 2 × 105 gBT-I cells were transferred into WT mice. Six days after TK− HSV-2 vaginal infection, 2 × 106 effector gBT-I cells isolated from these mice were transferred into secondary hosts (some treated with anti-IFN-γ Ab) infected with TK− HSV-2 3.5 days earlier. Numbers of gBT-I cells in the indicated tissues (b–f) were assessed 5 days post infection. The data are pooled from two independent experiments and presented as mean ± SEM (n = 5 – 6 mice per group). **, p < 0.01.
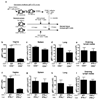
Figure 2. CD4 T cell-secreted IFN-γ mediates CTL entry into infected vaginal tissue
(a) HSV-primed WT or IFN-γ−/− CD4+ T cells (107) were adoptively transferred into CD4−/− (b–e) or IFNγ−/− mice (f–i) at 2.5 days post HSV-2 ivag infection. One day later, fully helped congenic effector gBT-I (2 × 106) cells were transferred into these mice. Five days after infection, the number of gBT-I cells in the indicated tissues was analyzed (b–i). Results are mean ± SEM (n = 4) and are representative of four independent experiments. Statistics were determined by unpaired two-tailed t-test. *, p < 0.05. **, p < 0.01.
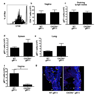
Figure 3. CTL recruitment to the infected tissue depends on CXCR3
Recipient mice were reconstituted with 105 WT or CXCR3−/− gBT-I cells. (a) At 3.5 days post infection, division of WT (blank), CXCR3−/− (filled), and uninfected (gray) gBT-I cells in the draining lymph nodes was analyzed. Numbers of total CD4+ T cells within the vagina (b) and gBT-I cells in the indicated tissues (c–f) were analyzed on day 6 post infection. (g) Vaginal tissues 7 days after infection were stained for gBT-I cells (red) and nuclei (blue). Arrows; basement membrane, yellow; vaginal lumen, white. Results are mean ± SEM (n = 4). Data are representative of three separate experiments. *, p < 0.05.
Figure 4. Secretion of CTL-recruiting chemokines in the infected tissue depends on CD4 T help
Four days after HSV-2 infection, vaginal wash was collected from WT, CD4−/− mice or mice that were treated with anti-IFN-γ Ab on day 3 p.i. (as in Fig. 1a). Cytokine and chemokine concentrations were determined by Luminex bead assay. Data were pooled from two independent experiments (n = 6) and represented as mean ± SEM. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-hoc multiple comparison).
Comment in
- Immunology: A helpers' guide to infection.
Gebhardt T, Carbone FR. Gebhardt T, et al. Nature. 2009 Nov 26;462(7272):418-9. doi: 10.1038/462418a. Nature. 2009. PMID: 19940905 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Immunology: A helpers' guide to infection.
Gebhardt T, Carbone FR. Gebhardt T, et al. Nature. 2009 Nov 26;462(7272):418-9. doi: 10.1038/462418a. Nature. 2009. PMID: 19940905 No abstract available. - A role for the CCR5-CCL5 interaction in the preferential migration of HSV-2-specific effector cells to the vaginal mucosa upon nasal immunization.
Joo S, Suwanto A, Sato A, Nakahashi-Ouchida R, Mori H, Uchida Y, Sato S, Kurashima Y, Yuki Y, Fujihashi K, Kawaguchi Y, Kiyono H. Joo S, et al. Mucosal Immunol. 2019 Nov;12(6):1391-1403. doi: 10.1038/s41385-019-0203-z. Epub 2019 Sep 24. Mucosal Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31551493 - Novel Role for Interleukin-17 in Enhancing Type 1 Helper T Cell Immunity in the Female Genital Tract following Mucosal Herpes Simplex Virus 2 Vaccination.
Bagri P, Anipindi VC, Nguyen PV, Vitali D, Stämpfli MR, Kaushic C. Bagri P, et al. J Virol. 2017 Nov 14;91(23):e01234-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01234-17. Print 2017 Dec 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28956763 Free PMC article. - The role of CD4(+) T helper cells in the cytotoxic T lymphocyte response to HIV-1.
Altfeld M, Rosenberg ES. Altfeld M, et al. Curr Opin Immunol. 2000 Aug;12(4):375-80. doi: 10.1016/s0952-7915(00)00103-5. Curr Opin Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10899028 Review. - Helper T cells, dendritic cells and CTL Immunity.
Behrens G, Li M, Smith CM, Belz GT, Mintern J, Carbone FR, Heath WR. Behrens G, et al. Immunol Cell Biol. 2004 Feb;82(1):84-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1711.2004.01211.x. Immunol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 14984599 Review.
Cited by
- A review of HSV pathogenesis, vaccine development, and advanced applications.
Bai L, Xu J, Zeng L, Zhang L, Zhou F. Bai L, et al. Mol Biomed. 2024 Aug 29;5(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s43556-024-00199-7. Mol Biomed. 2024. PMID: 39207577 Free PMC article. Review. - Advances in vaccine development for Chlamydia trachomatis.
Poston TB. Poston TB. Pathog Dis. 2024 Feb 7;82:ftae017. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftae017. Pathog Dis. 2024. PMID: 39043447 Free PMC article. Review. - Intratumoral immune triads are required for immunotherapy-mediated elimination of solid tumors.
Espinosa-Carrasco G, Chiu E, Scrivo A, Zumbo P, Dave A, Betel D, Kang SW, Jang HJ, Hellmann MD, Burt BM, Lee HS, Schietinger A. Espinosa-Carrasco G, et al. Cancer Cell. 2024 Jul 8;42(7):1202-1216.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2024.05.025. Epub 2024 Jun 20. Cancer Cell. 2024. PMID: 38906155 - Increased Natural Killer (NK)-cell cytotoxicity and Trypanosoma cruzi-specific memory B cells in subjects with discordant serology for Chagas disease.
Elias MJ, Cesar G, Caputo MB, De Rissio AM, Alvarez MG, Lococo B, Natale MA, Albizu CL, Podhorzer A, Parodi C, Albareda MC, Laucella SA. Elias MJ, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2024 Aug;1870(6):167237. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2024.167237. Epub 2024 May 13. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2024. PMID: 38750768 - Identification of Breast Cancer Subtypes Based on Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Related Genes and Analysis of Prognosis and Immune Microenvironment in Breast Cancer Patients.
Yi C, Yang J, Zhang T, Qin L, Chen D. Yi C, et al. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241241484. doi: 10.1177/15330338241241484. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 38725284 Free PMC article.
References
- Williams MA, Bevan MJ. Effector and memory CTL differentiation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:171–192. - PubMed
- Bennett SR, et al. Help for cytotoxic-T-cell responses is mediated by CD40 signalling. Nature. 1998;393:478–480. - PubMed
- Ridge JP, Di Rosa F, Matzinger P. A conditioned dendritic cell can be a temporal bridge between a CD4+ T-helper and a T-killer cell. Nature. 1998;393:474–478. - PubMed
- Schoenberger SP, Toes RE, van der Voort EI, Offringa R, Melief CJ. T-cell help for cytotoxic T lymphocytes is mediated by CD40-CD40L interactions. Nature. 1998;393:480–483. - PubMed
- Jennings SR, Bonneau RH, Smith PM, Wolcott RM, Chervenak R. CD4-positive T lymphocytes are required for the generation of the primary but not the secondary CD8-positive cytolytic T lymphocyte response to herpes simplex virus in C57BL/6 mice. Cell Immunol. 1991;133:234–252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI054359/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL51366/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI062428-05/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI054359/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI39759/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI062428/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI062428/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI062428/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI054359-06A2/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials