Therapeutic potential for novel drugs targeting the type 1 cholecystokinin receptor - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Therapeutic potential for novel drugs targeting the type 1 cholecystokinin receptor
Erin E Cawston et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Mar.
Abstract
Cholecystokinin (CCK) is a physiologically important gastrointestinal and neuronal peptide hormone, with roles in stimulating gallbladder contraction, pancreatic secretion, gastrointestinal motility and satiety. CCK exerts its effects via interactions with two structurally related class I guanine nucleotide-binding protein (G protein)-coupled receptors (GPCRs), the CCK(1) receptor and the CCK(2) receptor. Here, we focus on the CCK(1) receptor, with particular relevance to the broad spectrum of signalling initiated by activation with the natural full agonist peptide ligand, CCK. Distinct ligand-binding pockets have been defined for the natural peptide ligand and for some non-peptidyl small molecule ligands. While many CCK(1) receptor ligands have been developed and have had their pharmacology well described, their clinical potential has not yet been fully explored. The case is built for the potential importance of developing more selective partial agonists and allosteric modulators of this receptor that could have important roles in the treatment of common clinical syndromes.
Figures
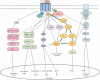
Figure 1
Schematic depiction of the signalling pathways stimulated by cholecystokinin (CCK) activation of the CCK1 receptor. CCK1 receptor activation by CCK is known to result in activation of Gq-initiated pathways with stimulation of classical second messengers (bold line) such as phospholipase C (PLC)/phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2)/diacylglycerol (DAG) and protein kinase C (PKC)/inositol 3, 4, 5-triphosphate (IP3) resulting in the release of intracellular calcium. Additionally, nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP) and cyclic ADP-ribose (cADPr) pathways have also been implicated in the release of calcium after ligand stimulation of the receptor. A number of other signalling pathways have been shown to be activated by ligand stimulation of the CCK1 receptor. These include the class I phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway involving Akt and stimulation of mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) that results in downstream activation of transcriptions factors, the NF-κB pathway as well as the Gs-initiated adenylate cyclase (AC) pathway. Three mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways have been shown to be stimulated by CCK1 receptor activation, p38-MAPK, extracellular-regulated kinase (ERK) and c-Jun amino-terminal kinase (JNK). The activation of the CCK1 receptor has also been shown to stimulate the phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), resulting in activation of Ras that in turn has been shown to be important in the activation of the JNK and ERK pathways. While no direct evidence has shown CCK activation of arrestin family proteins, these are known to have various signalling roles in many GPCRs and bind and potentially regulate several subsets of proteins from various signalling pathways (dashed lines).
Similar articles
- A type 1 cholecystokinin receptor mutant that mimics the dysfunction observed for wild type receptor in a high cholesterol environment.
Desai AJ, Harikumar KG, Miller LJ. Desai AJ, et al. J Biol Chem. 2014 Jun 27;289(26):18314-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.570200. Epub 2014 May 13. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24825903 Free PMC article. - Ligand-induced internalization of the type 1 cholecystokinin receptor independent of recognized signaling activity.
Cawston EE, Harikumar KG, Miller LJ. Cawston EE, et al. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012 Feb 1;302(3):C615-27. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00193.2011. Epub 2011 Nov 2. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22049215 Free PMC article. - Metabolic Actions of the Type 1 Cholecystokinin Receptor: Its Potential as a Therapeutic Target.
Miller LJ, Desai AJ. Miller LJ, et al. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Sep;27(9):609-619. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2016.04.002. Epub 2016 May 4. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 27156041 Free PMC article. Review. - Activation of cholecystokinin (CCK 1) and serotonin (5-HT 3) receptors increases the discharge of pancreatic vagal afferents.
Mussa BM, Sartor DM, Verberne AJ. Mussa BM, et al. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 Dec 28;601(1-3):198-206. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.11.007. Epub 2008 Nov 9. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 19026634 - Therapeutic and chemical developments of cholecystokinin receptor ligands.
de Tullio P, Delarge J, Pirotte B. de Tullio P, et al. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2000 Jan;9(1):129-46. doi: 10.1517/13543784.9.1.129. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2000. PMID: 11060666 Review.
Cited by
- Molecular basis for binding and subtype selectivity of 1,4-benzodiazepine antagonist ligands of the cholecystokinin receptor.
Cawston EE, Lam PC, Harikumar KG, Dong M, Ball AM, Augustine ML, Akgün E, Portoghese PS, Orry A, Abagyan R, Sexton PM, Miller LJ. Cawston EE, et al. J Biol Chem. 2012 May 25;287(22):18618-35. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.335646. Epub 2012 Mar 30. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22467877 Free PMC article. - Comparative pharmacology of cholecystokinin induced activation of cultured vagal afferent neurons from rats and mice.
Kinch DC, Peters JH, Simasko SM. Kinch DC, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34755. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034755. Epub 2012 Apr 13. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22514663 Free PMC article. - Cholecystokinin 1 receptor activation restores normal mTORC1 signaling and is protective to Purkinje cells of SCA mice.
Wozniak EAL, Chen Z, Paul S, Yang P, Figueroa KP, Friedrich J, Tschumperlin T, Berken M, Ingram M, Henzler C, Pulst SM, Orr HT. Wozniak EAL, et al. Cell Rep. 2021 Oct 12;37(2):109831. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109831. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34644575 Free PMC article. - Up-regulation of cholesterol absorption is a mechanism for cholecystokinin-induced hypercholesterolemia.
Zhou L, Yang H, Okoro EU, Guo Z. Zhou L, et al. J Biol Chem. 2014 May 9;289(19):12989-99. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.534388. Epub 2014 Apr 1. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24692543 Free PMC article. - The gastrin and cholecystokinin receptors mediated signaling network: a scaffold for data analysis and new hypotheses on regulatory mechanisms.
Tripathi S, Flobak Å, Chawla K, Baudot A, Bruland T, Thommesen L, Kuiper M, Lægreid A. Tripathi S, et al. BMC Syst Biol. 2015 Jul 24;9:40. doi: 10.1186/s12918-015-0181-z. BMC Syst Biol. 2015. PMID: 26205660 Free PMC article.
References
- Anagnostides AA, Chadwick VS, Selden AC, Barr J, Maton PN. Human pancreatic and biliary responses to physiological concentrations of cholecystokinin octapeptide. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985;69:259–263. - PubMed
- Aquino CJ, Armour DR, Berman JM, Birkemo LS, Carr RA, Croom DK, et al. Discovery of 1,5-benzodiazepines with peripheral cholecystokinin (CCK-A) receptor agonist activity. 1. Optimization of the agonist ‘trigger’. J Med Chem. 1996;39:562–569. - PubMed
- Ariens EJ, De Groot WM. Affinity and intrinsic activity in the theory of competitive inhibition. III. Homologous decamethonium-derivatives and succinyl-choline-esters. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1954;99:193–205. - PubMed
- Barak LS, Oakley RH, Shetzline MA. G protein-coupled receptor desensitization as a measure of signaling: modeling of arrestin recruitment to activated CCK-B receptors. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2003;1:409–424. - PubMed
- Beglinger C, Degen L, Matzinger D, D'Amato M, Drewe J. Loxiglumide, a CCK-A receptor antagonist, stimulates calorie intake and hunger feelings in humans. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2001;280:R1149–R1154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases