Treatment with interleukin-2 in malignant pleural mesothelioma: immunological and angiogenetic assessment and prognostic impact - PubMed (original) (raw)
Treatment with interleukin-2 in malignant pleural mesothelioma: immunological and angiogenetic assessment and prognostic impact
G Alì et al. Br J Cancer. 2009.
Abstract
Background: Administration of interleukin-2 (IL-2) has shown some effects on malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) tumour regression. The purpose of this study was to investigate the ability of IL-2 to modify immunological effector cells and angiogenesis in MPM patients and their prognostic value.
Methods: Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes (CD4, CD8, Foxp3), mast cells (MCs) (tryptase and chymase), microvessel count (MVC) and VEGF were determined by immunohistochemistry in two series of MPM patients: 60 patients treated with intra-pleural preoperative IL-2 and 33 patients untreated.
Results: Tryptase MCs, and CD8 and Foxp3 lymphocytes were significantly increased in the IL-2-treated group, whereas MVC was significantly lower in the same group. Moreover, in the IL-2-treated group, greater tryptase+MCs and greater Foxp3 lymphocytes were associated with improved and poorer clinical outcomes, respectively. Notably, when these two immunological parameters were combined, they predicted outcomes more effectively.
Conclusions: This study showed that IL-2 treatment leads to a significant increase of immunological parameters, concomitantly with a reduction in vasculature, providing new insight into the cancer mechanisms mediated by IL-2. Moreover, these results suggest that tryptase-positive MCs and Foxp3+ lymphocytes predict clinical outcomes in IL-2-treated patients, highlighting the critical role of the inflammatory response in mesothelioma cancer progression.
Figures
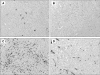
Figure 1
Immunohistochemical staining for tryptase-positive mast cells (A), Foxp3-positive lymphocytes (B), CD8-positive lymphocytes (C), and microvessel count (D) in mesotheliomas. Original magnification, × 100.
Figure 2
Kaplan–Meier overall survival (A) and time to progression (B) curves for tryptase MCs counts divided into two groups above and below the median value; Kaplan–Meier overall survival (C) and time to progression (D) curves for Foxp3 counts divided into two groups above and below the median value; (E) Kaplan–Meier overall survival curves for combination of tryptase MCs and Foxp3 counts.
Similar articles
- Multimodality treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma with or without immunotherapy: does it change anything?
Lucchi M, Picchi A, Alí G, Chella A, Guglielmi G, Cristaudo A, Fontanini G, Mussi A. Lucchi M, et al. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2010 Apr;10(4):572-6. doi: 10.1510/icvts.2009.223255. Epub 2010 Jan 6. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2010. PMID: 20053697 - Tryptase mast cells in malignant pleural mesothelioma as an independent favorable prognostic factor.
Alì G, Boldrini L, Lucchi M, Mussi A, Corsi V, Fontanini G. Alì G, et al. J Thorac Oncol. 2009 Mar;4(3):348-54. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181989ddb. J Thorac Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19155997 - Malignant pleural mesothelioma immune microenvironment and checkpoint expression: correlation with clinical-pathological features and intratumor heterogeneity over time.
Pasello G, Zago G, Lunardi F, Urso L, Kern I, Vlacic G, Grosso F, Mencoboni M, Ceresoli GL, Schiavon M, Pezzuto F, Pavan A, Vuljan SE, Del Bianco P, Conte P, Rea F, Calabrese F. Pasello G, et al. Ann Oncol. 2018 May 1;29(5):1258-1265. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy086. Ann Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29514216 - [Systemic Treatment of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma].
Nakano T. Nakano T. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2017 Dec;44(13):2041-2047. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2017. PMID: 29361614 Review. Japanese. - Anti-angiogenic therapies for malignant pleural mesothelioma.
Ceresoli GL, Zucali PA. Ceresoli GL, et al. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2012 Jun;21(6):833-44. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2012.681641. Epub 2012 Apr 23. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22519641 Review.
Cited by
- Terminal arteriolar network structure/function and plasma cytokine levels in db/db and ob/ob mouse skeletal muscle.
Georgi MK, Vigilance J, Dewar AM, Frame MD. Georgi MK, et al. Microcirculation. 2011 Apr;18(3):238-51. doi: 10.1111/j.1549-8719.2011.00084.x. Microcirculation. 2011. PMID: 21418374 Free PMC article. - Intratumoural immunotherapies for unresectable and metastatic melanoma: current status and future perspectives.
Middleton MR, Hoeller C, Michielin O, Robert C, Caramella C, Öhrling K, Hauschild A. Middleton MR, et al. Br J Cancer. 2020 Sep;123(6):885-897. doi: 10.1038/s41416-020-0994-4. Epub 2020 Jul 27. Br J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32713938 Free PMC article. Review. - Clinical Response of Live-Attenuated, Listeria monocytogenes Expressing Mesothelin (CRS-207) with Chemotherapy in Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma.
Hassan R, Alley E, Kindler H, Antonia S, Jahan T, Honarmand S, Nair N, Whiting CC, Enstrom A, Lemmens E, Tsujikawa T, Kumar S, Choe G, Thomas A, McDougall K, Murphy AL, Jaffee E, Coussens LM, Brockstedt DG. Hassan R, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Oct 1;25(19):5787-5798. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-0070. Epub 2019 Jul 1. Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31263030 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Antitumor activity of tumor-targeted RNA replicase-based plasmid that expresses interleukin-2 in a murine melanoma model.
Rodriguez BL, Blando JM, Lansakara-P DS, Kiguchi Y, DiGiovanni J, Cui Z. Rodriguez BL, et al. Mol Pharm. 2013 Jun 3;10(6):2404-15. doi: 10.1021/mp400033m. Epub 2013 May 17. Mol Pharm. 2013. PMID: 23641783 Free PMC article. - Immunotherapy and radiation therapy for malignant pleural mesothelioma.
Alley EW, Katz SI, Cengel KA, Simone CB 2nd. Alley EW, et al. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2017 Apr;6(2):212-219. doi: 10.21037/tlcr.2017.04.01. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28529903 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Akbar AN, Borthwick NJ, Wickremasinghe RG, Panayoitidis P, Pilling D, Bofill M, Krajewski S, Reed JC, Salmon M (1996) Interleukin-2 receptor common gamma-chain signaling cytokines regulate activated T cell apoptosis in response to growth factor withdrawal: selective induction of anti-apoptotic (bcl-2, bcl-xL) but not pro-apoptotic (bax, bcl-xS) gene expression. Eur J Immunol 26: 294–299 - PubMed
- Alì G, Boldrini L, Lucchi M, Mussi A, Corsi V, Fontanini G (2009) Tryptase mast cells in malignant pleural mesothelioma as an independent favorable prognostic factor. J Thorac Oncol 4: 348–354 - PubMed
- Anraku M, Cunningham KS, Yun Z, Tsao MS, Zhang L, Keshavjee S, Johnston MR, de Perrot M (2008) Impact of tumor-infiltrating T cells on survival in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 135: 823–829 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials