Multilayered control of gene expression by stress-activated protein kinases - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Multilayered control of gene expression by stress-activated protein kinases
Eulàlia de Nadal et al. EMBO J. 2010.
Abstract
Stress-activated protein kinases (SAPKs) are key elements for intracellular signalling networks that serve to respond and adapt to extracellular changes. Exposure of yeast to high osmolarity results in the activation of p38-related SAPK, Hog1, which is essential for reprogramming the gene expression capacity of the cell by regulation of several steps of the transcription process. At initiation, active Hog1 not only directly phosphorylates several transcription factors to alter their activities, but also associates at stress-responsive promoters through such transcription factors. Once at the promoters, Hog1 serves as a platform to recruit general transcription factors, chromatin-modifying activities and RNA Pol II. In addition, the SAPK pathway has a role in elongation. At the stress-responsive ORFs, Hog1 recruits the RSC chromatin-remodelling complex to modify nucleosome organization. Several SAPKs from yeast to mammals have maintained some of the regulatory abilities of Hog1. Thus, elucidating the control of gene expression by the Hog1 SAPK should help to understand how eukaryotic cells implement a massive and rapid change on their transcriptional capacity in response to adverse conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
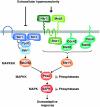
Figure 1
Hog1 stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK) signalling. Two independent upstream osmosensing mechanisms lead to the activation of specific MAPKKKs. A ‘two-component' osmosensor (Sln1–Ypd1 and Ssk1 proteins) regulates the Ssk2 and Ssk22 MAPKKKs, whereas the second branch of the pathway activates the Ste11 MAPKKK through the transmembrane protein Sho1 and the mucin-like proteins Msb2 and Hkr1. In response to osmostress, Pbs2 integrates both signals and activates the Hog1 SAPK, which induces a set of osmoadaptive responses.
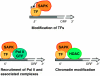
Figure 2
Stress-activated protein kinases (SAPKs) regulate transcription initiation of stress genes through several mechanisms. SAPKs may modulate initiation of transcription in response to stress by (1) direct phosphorylation of promoter-specific transcription factors; (2) stimulation of the recruitment of RNA Pol II and coactivators to the promoters; and (3) recruitment of the Rpd3 histone deacetylase complex and other chromatin modifying activities.
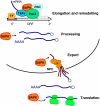
Figure 3
The Hog1 stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK) regulates different phases of the transcription cycle. In addition to transcription initiation, Hog1 acts as a stress specific transcription elongation factor. Moreover, Hog1 targeting of the RSC complex displaces nucleosomes contributing to the efficient activation of transcription. The roles of Hog1 in other gene expression related processes such as mRNA processing, transport and translation are now starting to be elucidated.
Similar articles
- The MAPK Hog1 recruits Rpd3 histone deacetylase to activate osmoresponsive genes.
De Nadal E, Zapater M, Alepuz PM, Sumoy L, Mas G, Posas F. De Nadal E, et al. Nature. 2004 Jan 22;427(6972):370-4. doi: 10.1038/nature02258. Nature. 2004. PMID: 14737171 - Osmostress-induced transcription by Hot1 depends on a Hog1-mediated recruitment of the RNA Pol II.
Alepuz PM, de Nadal E, Zapater M, Ammerer G, Posas F. Alepuz PM, et al. EMBO J. 2003 May 15;22(10):2433-42. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg243. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12743037 Free PMC article. - The stress-activated Hog1 kinase is a selective transcriptional elongation factor for genes responding to osmotic stress.
Proft M, Mas G, de Nadal E, Vendrell A, Noriega N, Struhl K, Posas F. Proft M, et al. Mol Cell. 2006 Jul 21;23(2):241-50. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.05.031. Mol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16857590 - Osmostress-induced gene expression--a model to understand how stress-activated protein kinases (SAPKs) regulate transcription.
de Nadal E, Posas F. de Nadal E, et al. FEBS J. 2015 Sep;282(17):3275-85. doi: 10.1111/febs.13323. Epub 2015 Jun 10. FEBS J. 2015. PMID: 25996081 Free PMC article. Review. - Stress-Activated Protein Kinases in Human Fungal Pathogens.
Day AM, Quinn J. Day AM, et al. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Jul 17;9:261. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00261. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31380304 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Control of Gene Expression via the Yeast CWI Pathway.
Sanz AB, García R, Pavón-Vergés M, Rodríguez-Peña JM, Arroyo J. Sanz AB, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 4;23(3):1791. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031791. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163713 Free PMC article. Review. - Dynamic remodeling of histone modifications in response to osmotic stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Magraner-Pardo L, Pelechano V, Coloma MD, Tordera V. Magraner-Pardo L, et al. BMC Genomics. 2014 Mar 30;15(1):247. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-247. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24678875 Free PMC article. - Rewiring yeast osmostress signalling through the MAPK network reveals essential and non-essential roles of Hog1 in osmoadaptation.
Babazadeh R, Furukawa T, Hohmann S, Furukawa K. Babazadeh R, et al. Sci Rep. 2014 Apr 15;4:4697. doi: 10.1038/srep04697. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 24732094 Free PMC article. - The conserved PBAF nucleosome-remodeling complex mediates the response to stress in Caenorhabditis elegans.
Kuzmanov A, Karina EI, Kirienko NV, Fay DS. Kuzmanov A, et al. Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Mar;34(6):1121-35. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01502-13. Epub 2014 Jan 13. Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24421384 Free PMC article. - Examining docking interactions on ERK2 with modular peptide substrates.
Lee S, Warthaka M, Yan C, Kaoud TS, Ren P, Dalby KN. Lee S, et al. Biochemistry. 2011 Nov 8;50(44):9500-10. doi: 10.1021/bi201103b. Epub 2011 Oct 18. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21955038 Free PMC article.
References
- Alepuz PM, Jovanovic A, Reiser V, Ammerer G (2001) Stress-induced map kinase Hog1 is part of transcription activation complexes. Mol Cell 7: 767–777 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases