Hyperbaric oxygen induces a cytoprotective and angiogenic response in human microvascular endothelial cells - PubMed (original) (raw)
Hyperbaric oxygen induces a cytoprotective and angiogenic response in human microvascular endothelial cells
Cassandra A Godman et al. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2010 Jul.
Abstract
A genome-wide microarray analysis of gene expression was carried out on human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC-1) exposed to hyperbaric oxygen treatment (HBOT) under conditions that approximated clinical settings. Highly up-regulated genes included immediate early transcription factors (FOS, FOSB, and JUNB) and metallothioneins. Six molecular chaperones were also up-regulated immediately following HBOT, and all of these have been implicated in protein damage control. Pathway analysis programs identified the Nrf-2-mediated oxidative stress response as one of the primary responders to HBOT. Several of the microarray changes in the Nrf2 pathway and a molecular chaperone were validated using quantitative PCR. For all of the genes tested (Nrf2, HMOX1, HSPA1A, M1A, ACTC1, and FOS), HBOT elicited large responses, whereas changes were minimal following treatment with 100% O(2) in the absence of elevated pressure. The increased expression of immediate early and cytoprotective genes corresponded with an HBOT-induced increase in cell proliferation and oxidative stress resistance. In addition, HBOT treatment enhanced endothelial tube formation on Matrigel plates, with particularly dramatic effects observed following two daily HBO treatments. Understanding how HBOT influences gene expression changes in endothelial cells may be beneficial for improving current HBOT-based wound-healing protocols. These data also point to other potential HBOT applications where stimulating protection and repair of the endothelium would be beneficial, such as patient preconditioning prior to major surgery.
Figures
Fig. 1
Scatterplots of normalized microarray data. These plots show the pairwise comparison of all 12 samples. Graphs represent the comparison of the normalized intensity data for every probe represented on the array between any two samples. The biological triplicates exhibit very tight correlations serving as a quality control mechanism. Comparisons between HBOT-treated and HBOT-untreated samples show increased and decreased gene expression
Fig. 2
Microarray data analysis. a Differentially regulated genes were selected based on a significant difference in at least one treatment level compared to control. Following statistical analysis, a total of 8,101 (21%) significantly regulated genes were identified. Of that list, about 695 increased and 901 decreased immediately following HBOT, whereas 3,280 increased and 3,968 decreased following the 24-h recovery. b Genes regulated ±5-fold were selected as top-responding genes. White bars indicate up-regulated genes; gray bars indicate down-regulation
Fig. 3
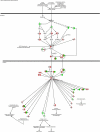
HBOT affects gene expression in the Nrf2 Pathway. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis predicted the Nrf2-mediated oxidative stress response pathway as having significantly changed gene expression for both time points. Molecules are divided into right (HBOT-0 h) and left (HBOT-24 h) halves. Red color indicates up-regulation, green indicates down-regulation, and white indicates no change in comparison to control
Fig. 4
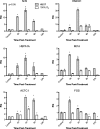
Validation of microarray data. HMEC-1 cells were treated with either HBOT or 100% O2 and RNA extracted at indicated times following treatment. RNA was converted to cDNA and subjected to qPCR for the indicated genes. Genes were selected from pathways of interest including the Nrf2 signaling pathway, cytoprotective genes, and the top-responding genes. HMOX1 heme-oxygenase 1, HSPA1A human heat shock protein 70, Mt1A metallothionein 1 A, ACTC1 actin, alpha cardiac muscle 1, FOS FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog
Fig. 5
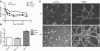
Functional effects of HBOT and 100% O2 on HMEC-1 cells. Cells were plated and incubated for 48 h before being subjected to one round of HBOT or 100% O2. Following recovery for 16 h, cell proliferation was assessed with the MTT assay. a HBOT protected against oxidative stress. Following recovery from HBOT or 100% O2, cells were treated with _t_-butylhydroperoxide (_t_-butyl OOH) for 4 h and then analyzed for cell viability using the MTT assay. b HBOT increased cell viability. c HBOT increased vascular tube formation. HMEC-1 cells received either one (1X) or two (2X) treatments separated by a 24-h recovery period of HBOT and were immediately plated on Matrigel coated plates. Representative images are shown for control samples (c1X and C 2X) as well as HBOT cells treated once or twice (HBOT 1X and HBOT 2X)
Similar articles
- Hyperbaric oxygen potentiates diabetic wound healing by promoting fibroblast cell proliferation and endothelial cell angiogenesis.
Huang X, Liang P, Jiang B, Zhang P, Yu W, Duan M, Guo L, Cui X, Huang M, Huang X. Huang X, et al. Life Sci. 2020 Oct 15;259:118246. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118246. Epub 2020 Aug 10. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32791151 - Poorly designed research does not help clarify the role of hyperbaric oxygen in the treatment of chronic diabetic foot ulcers.
Mutluoglu M, Uzun G, Bennett M, Germonpré P, Smart D, Mathieu D. Mutluoglu M, et al. Diving Hyperb Med. 2016 Sep;46(3):133-134. Diving Hyperb Med. 2016. PMID: 27723012 - Tissue-specific role of Nrf2 in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers during hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
Dhamodharan U, Karan A, Sireesh D, Vaishnavi A, Somasundar A, Rajesh K, Ramkumar KM. Dhamodharan U, et al. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 Jul;138:53-62. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.04.031. Epub 2019 Apr 26. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 31035003 - The Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygenation on Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Angiogenesis.
De Wolde SD, Hulskes RH, Weenink RP, Hollmann MW, Van Hulst RA. De Wolde SD, et al. Biomolecules. 2021 Aug 14;11(8):1210. doi: 10.3390/biom11081210. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34439876 Free PMC article. Review. - Proliferative retinopathy during hyperbaric oxygen treatment.
Tran V, Smart D. Tran V, et al. Diving Hyperb Med. 2017 Sep;47(3):203. doi: 10.28920/dhm47.3.203. Diving Hyperb Med. 2017. PMID: 28868603 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Case report: Dementia sensitivity to altitude changes and effective treatment with hyperbaric air and glutathione precursors.
Fogarty EF, Harch PG. Fogarty EF, et al. Front Neurol. 2024 Jun 19;15:1356662. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1356662. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38978816 Free PMC article. - Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in acute stroke: is it time for Justitia to open her eyes?
Mijajlovic MD, Aleksic V, Milosevic N, Bornstein NM. Mijajlovic MD, et al. Neurol Sci. 2020 Jun;41(6):1381-1390. doi: 10.1007/s10072-020-04241-8. Epub 2020 Jan 11. Neurol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31925614 Review. - Vascular biomechanical properties in mice with smooth muscle specific deletion of Ndst1.
Adhikari N, Billaud M, Carlson M, Lake SP, Montaniel KR, Staggs R, Guan W, Walek D, Desir S, Isakson BE, Barocas VH, Hall JL. Adhikari N, et al. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014 Jan;385(1-2):225-38. doi: 10.1007/s11010-013-1831-3. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24101444 Free PMC article. - Effect of hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning on peri-hemorrhagic focal edema and aquaporin-4 expression.
Fang J, Li H, Li G, Wang L. Fang J, et al. Exp Ther Med. 2015 Aug;10(2):699-704. doi: 10.3892/etm.2015.2539. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Exp Ther Med. 2015. PMID: 26622378 Free PMC article. - Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for healthy aging: From mechanisms to therapeutics.
Fu Q, Duan R, Sun Y, Li Q. Fu Q, et al. Redox Biol. 2022 Jul;53:102352. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102352. Epub 2022 May 27. Redox Biol. 2022. PMID: 35649312 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Alex J, Laden G, Cale AR, et al. Pretreatment with hyperbaric oxygen and its effect on neuropsychometric dysfunction and systemic inflammatory response after cardiopulmonary bypass: a prospective randomized double-blind trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005;130:1623–1630. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2005.08.018. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous