Transactive response DNA-binding protein 43 burden in familial Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Transactive response DNA-binding protein 43 burden in familial Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome
Carol F Lippa et al. Arch Neurol. 2009 Dec.
Abstract
Objective: To assess the transactive response DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) burden in familial forms of Alzheimer disease (FAD) and Down syndrome (DS) to determine whether TDP-43 inclusions are also present.
Design: Using standard immunohistochemical techniques, we examined brain tissue samples from 42 subjects with FAD and 14 with DS.
Results: We found pathological TDP-43 aggregates in 14.0% of participants (6 of 42 and 2 of 14 participants with FAD and DS, respectively). In both FAD and DS, TDP-43 immunoreactivity did not colocalize with neurofibrillary tangles. Occasionally participants with FAD or DS had TDP-43-positive neuropil threads or dots. Overall, the amygdala was most commonly affected, followed by the hippocampus, with no TDP-43 pathology in neocortical regions. A similar distribution of TDP-43 inclusions is seen in sporadic Alzheimer disease, but it differs from that seen in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia.
Conclusions: Transactive response DNA-binding protein 43 pathology occurs in FAD and DS, similar to that observed in sporadic Alzheimer disease. Thus, pathological TDP-43 may contribute the cognitive impairments in familial and sporadic forms of Alzheimer disease.
Figures
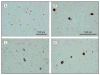
Figure 1
Photomicrographs of transactive response DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) pathology in the brains of patients with familial Alzheimer disease (FAD) and Down syndrome (DS). A, The TDP-43 inclusions in the amygdala at medium power magnification (original magnification ×20) are shown in a participant with Down syndrome (patient 11). Multiple neurons in the amygdala show immunoreactivity for the phosphorylation-specific TDP-43 monoclonal antibody. B–D, Higher-power magnification (original magnification ×60) of neuronal cytoplasmic staining in amygdala neurons was performed for patients withDS (B, patient 11), _PS-1_–positive FAD (C, patient 44), and_PS-2_–positive FAD (patient 45). In all participants, there is intense TDP-43 immunoreactivity in aggregates that extended throughout the cytoplasm. The appearance is similar in _PS-1_–positive FAD, _PS-2_–positive FAD, and DS.
Figure 2
Photomicrograph of transactive response DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) immunostaining of neuropathological features in patients with familial Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome using monoclonal antibody 1D3. A, In patient 11, TDP-43–positive threadlike structures are demonstrated in the neuropil. B, Granules in granulovacuolar degeneration (GVD) are immunoreactive to TDP-43 (patient 4). C, Diffuse and granular cytoplasmic staining for TDP-43 is shown in dentate granule cells (patient 11). However, none of the other TDP antibodies produced similar GVD or granular staining, so we infer that the granular and GVD staining seen here with the 1D3 monoclonal antibody does not reflect the presence of TDP-43 itself in these structures. Original magnification is ×60 for all images.
Similar articles
- TDP-43 pathological changes in early onset familial and sporadic Alzheimer's disease, late onset Alzheimer's disease and Down's syndrome: association with age, hippocampal sclerosis and clinical phenotype.
Davidson YS, Raby S, Foulds PG, Robinson A, Thompson JC, Sikkink S, Yusuf I, Amin H, DuPlessis D, Troakes C, Al-Sarraj S, Sloan C, Esiri MM, Prasher VP, Allsop D, Neary D, Pickering-Brown SM, Snowden JS, Mann DM. Davidson YS, et al. Acta Neuropathol. 2011 Dec;122(6):703-13. doi: 10.1007/s00401-011-0879-y. Epub 2011 Oct 4. Acta Neuropathol. 2011. PMID: 21968532 - Regional distribution of TDP-43 inclusions in Alzheimer disease (AD) brains: their relation to AD common pathology.
Kadokura A, Yamazaki T, Lemere CA, Takatama M, Okamoto K. Kadokura A, et al. Neuropathology. 2009 Oct;29(5):566-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1789.2009.01017.x. Epub 2009 Apr 21. Neuropathology. 2009. PMID: 19422539 - TDP-43 in aging and Alzheimer's disease - a review.
Wilson AC, Dugger BN, Dickson DW, Wang DS. Wilson AC, et al. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2011 Jan 30;4(2):147-55. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21326809 Free PMC article. Review. - The role of transactive response DNA-binding protein-43 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia.
Mackenzie IR, Rademakers R. Mackenzie IR, et al. Curr Opin Neurol. 2008 Dec;21(6):693-700. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0b013e3283168d1d. Curr Opin Neurol. 2008. PMID: 18989115 Free PMC article. Review. - Concurrence of TDP-43, tau and alpha-synuclein pathology in brains of Alzheimer's disease and dementia with Lewy bodies.
Higashi S, Iseki E, Yamamoto R, Minegishi M, Hino H, Fujisawa K, Togo T, Katsuse O, Uchikado H, Furukawa Y, Kosaka K, Arai H. Higashi S, et al. Brain Res. 2007 Dec 12;1184:284-94. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.09.048. Epub 2007 Oct 25. Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17963732
Cited by
- Clinicopathological Heterogeneity of Lewy Body Diseases: The Profound Influence of Comorbid Alzheimer's Disease.
Beach TG, Serrano GE, Zhang N, Driver-Dunckley ED, Sue LI, Shill HA, Mehta SH, Belden C, Tremblay C, Choudhury P, Atri A, Adler CH. Beach TG, et al. medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 4:2024.08.30.24312864. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.30.24312864. medRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39281742 Free PMC article. Preprint. - A genetic cause of Alzheimer disease: mechanistic insights from Down syndrome.
Wiseman FK, Al-Janabi T, Hardy J, Karmiloff-Smith A, Nizetic D, Tybulewicz VL, Fisher EM, Strydom A. Wiseman FK, et al. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2015 Sep;16(9):564-74. doi: 10.1038/nrn3983. Epub 2015 Aug 5. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26243569 Free PMC article. Review. - Associations of amygdala volume and shape with transactive response DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) pathology in a community cohort of older adults.
Makkinejad N, Schneider JA, Yu J, Leurgans SE, Kotrotsou A, Evia AM, Bennett DA, Arfanakis K. Makkinejad N, et al. Neurobiol Aging. 2019 May;77:104-111. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2019.01.022. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Neurobiol Aging. 2019. PMID: 30784812 Free PMC article. - The unfolded protein response is activated in disease-affected brain regions in progressive supranuclear palsy and Alzheimer's disease.
Stutzbach LD, Xie SX, Naj AC, Albin R, Gilman S; PSP Genetics Study Group; Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Devlin B, Schellenberg GD. Stutzbach LD, et al. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2013 Jul 6;1:31. doi: 10.1186/2051-5960-1-31. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2013. PMID: 24252572 Free PMC article. - UNC13A polymorphism contributes to frontotemporal disease in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Placek K, Baer GM, Elman L, McCluskey L, Hennessy L, Ferraro PM, Lee EB, Lee VMY, Trojanowski JQ, Van Deerlin VM, Grossman M, Irwin DJ, McMillan CT. Placek K, et al. Neurobiol Aging. 2019 Jan;73:190-199. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2018.09.031. Epub 2018 Sep 27. Neurobiol Aging. 2019. PMID: 30368160 Free PMC article.
References
- Wang HY, Wang IF, Bose J, Shen CK. Structural diversity and functional implications of the eukaryotic TDP gene family. Genomics. 2004;83(1):130–139. - PubMed
- Neumann M, Sampathu DM, Kwong LK, et al. Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in fronto-temporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science. 2006;314(5796):130–133. - PubMed
- Arai T, Hasegawa M, Akiyama H, et al. TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;351(3):602–611. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical