Minireview: posttranscriptional regulation of the insulin and insulin-like growth factor systems - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Minireview: posttranscriptional regulation of the insulin and insulin-like growth factor systems
Eun Kyung Lee et al. Endocrinology. 2010 Apr.
Abstract
Insulin and IGFs share structural similarities and regulate metabolic processes including glucose homeostasis. Acute alterations in glucose levels trigger rapid changes in insulin concentration and insulin signaling. These processes are tightly regulated by posttranscriptional mechanisms that alter the stability and translation of mRNAs encoding insulin and the insulin receptor. Long-term glucose homeostasis is also modulated by IGFs and IGF receptors, whose expression is likewise subject to changes in the stability and translation of the encoding mRNAs. The control of mRNA half-life and translation is governed by RNA-binding proteins and microRNAs that interact with target transcripts at the 3' and 5' untranslated regions. In this review, we describe the RNA-binding proteins and microRNAs that target the mRNAs encoding insulin, IGFs, and their receptors. We discuss how these mRNA-binding factors help to elicit timely, versatile, and tissue-specific changes in insulin and IGF function, thereby effecting critical control of energy metabolism.
Figures
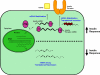
Figure 1
PTB coordinately up-regulates expression of insulin and insulin receptor. Under conditions requiring insulin signaling (top of the schematic), PTB both promotes the stabilization of mRNAs encoding insulin and insulin receptor and enhances the translation of the insulin receptor mRNA. Under conditions that do not require insulin signaling (bottom of the schematic), the mRNAs encoding insulin and insulin receptor are unstable (represented as discontinuous mRNAs) and therefore cannot be used for translation.
Similar articles
- CRNDE, a long non-coding RNA responsive to insulin/IGF signaling, regulates genes involved in central metabolism.
Ellis BC, Graham LD, Molloy PL. Ellis BC, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Feb;1843(2):372-86. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.10.016. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24184209 - Hormonal regulation of astroglial insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein gene expression by IGFs and insulin.
Bradshaw SL, Han VK. Bradshaw SL, et al. Endocrinology. 1993 Oct;133(4):1767-77. doi: 10.1210/endo.133.4.7691580. Endocrinology. 1993. PMID: 7691580 - Posttranscriptional regulation of insulin family ligands and receptors.
Panda AC, Grammatikakis I, Yoon JH, Abdelmohsen K. Panda AC, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Sep 18;14(9):19202-29. doi: 10.3390/ijms140919202. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24051403 Free PMC article. Review. - Translating the Untranslated Region.
Schwerk J, Savan R. Schwerk J, et al. J Immunol. 2015 Oct 1;195(7):2963-71. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500756. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26386038 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Alterations in polyadenylation and its implications for endocrine disease.
Rehfeld A, Plass M, Krogh A, Friis-Hansen L. Rehfeld A, et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2013 May 8;4:53. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2013.00053. eCollection 2013. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2013. PMID: 23658553 Free PMC article. - mTOR regulates the expression of DNA damage response enzymes in long-lived Snell dwarf, GHRKO, and PAPPA-KO mice.
Dominick G, Bowman J, Li X, Miller RA, Garcia GG. Dominick G, et al. Aging Cell. 2017 Feb;16(1):52-60. doi: 10.1111/acel.12525. Epub 2016 Sep 13. Aging Cell. 2017. PMID: 27618784 Free PMC article. - Molecular Mechanisms of Parathyroid Disorders in Chronic Kidney Disease.
Hassan A, Khalaily N, Kilav-Levin R, Nechama M, Volovelsky O, Silver J, Naveh-Many T. Hassan A, et al. Metabolites. 2022 Jan 25;12(2):111. doi: 10.3390/metabo12020111. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 35208186 Free PMC article. Review. - MicroRNA-100 Reduced Fetal Bovine Muscle Satellite Cell Myogenesis and Augmented Intramuscular Lipid Deposition by Modulating IGF1R.
Mir BA, Albrecht E, Ali A, Hansson O, Maak S. Mir BA, et al. Cells. 2022 Jan 28;11(3):451. doi: 10.3390/cells11030451. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35159261 Free PMC article. - Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor is suppressed through transcriptional repression and mRNA destabilization by a novel energy restriction-mimetic agent.
Chu PC, Kulp SK, Chen CS. Chu PC, et al. Carcinogenesis. 2013 Dec;34(12):2694-705. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgt251. Epub 2013 Jul 16. Carcinogenesis. 2013. PMID: 23864387 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
- Rhodes CJ 2000 Diabetes Mellitus. In: LeRoith D, Taylor SI, Olefsky JM, eds. Diabetes mellitus: a fundamental and clinical text. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 20–37
- Clemmons DR 2006 Involvement of insulin-like growth factor-I in the control of glucose homeostasis. Curr Opin Pharmacol 6:620–625 - PubMed
- Mitchell P, Tollervey D 2000 mRNA stability in eukaryotes. Curr Opin Genet Dev 10:193–198 - PubMed
- Orphanides G, Reinberg D 2002 A unified theory of gene expression. Cell 108:439–451 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical