The rate and molecular spectrum of spontaneous mutations in Arabidopsis thaliana - PubMed (original) (raw)
The rate and molecular spectrum of spontaneous mutations in Arabidopsis thaliana
Stephan Ossowski et al. Science. 2010.
Abstract
To take complete advantage of information on within-species polymorphism and divergence from close relatives, one needs to know the rate and the molecular spectrum of spontaneous mutations. To this end, we have searched for de novo spontaneous mutations in the complete nuclear genomes of five Arabidopsis thaliana mutation accumulation lines that had been maintained by single-seed descent for 30 generations. We identified and validated 99 base substitutions and 17 small and large insertions and deletions. Our results imply a spontaneous mutation rate of 7 x 10(-9) base substitutions per site per generation, the majority of which are G:C-->A:T transitions. We explain this very biased spectrum of base substitution mutations as a result of two main processes: deamination of methylated cytosines and ultraviolet light-induced mutagenesis.
Figures
Fig. 1
Distribution of spontaneous mutations across chromosomes. Labels indicate the type of mutation and colors their functional context or predicted effect. Short insertions and deletions are shown by the letters representing the affected bases preceded by a plus or aminus sign, respectively. Long deletions are depicted by aminus sign and the number of deleted base pairs in parentheses. An asterisk next to a C or a G means that the cytosine of the mutant base pair is known to be methylated (20). The definitions for colors are as follows: red, intergenic region; yellow, intron; dark blue, nonsynonymous substitution, shift of reading frame for short indels, or gene deletion for large deletions; green, synonymous substitution; purple, UTR; and light blue, transposable element.
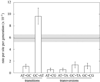
Fig. 2
Conditional mutation rates per A:T or G:C site per generation. Complementary mutations, such as A→C and T→G, are pooled. Error bars indicate standard errors of the mean. The overall mutation rate, which is the average of the total mutation rates at A:T and G:C sites, and its standard error in gray are shown in the background. Only estimates from the consensus method are shown.
References
- Lynch M, et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2008;105:9272.
- Arabidopsis Genome Initiative. Nature. 2000;408:796. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources