Synopsis and data synthesis of genetic association studies in hypertension for the adrenergic receptor family genes: the CUMAGAS-HYPERT database - PubMed (original) (raw)
Synopsis and data synthesis of genetic association studies in hypertension for the adrenergic receptor family genes: the CUMAGAS-HYPERT database
Georgios D Kitsios et al. Am J Hypertens. 2010 Mar.
Abstract
Background: The adrenergic receptor (adrenoceptor) family genes have been extensively studied as candidate genes in hypertension but the results of individual genetic association studies (GAS) are controversial and inconclusive. To clarify these data, a systematic assessment of GAS for adrenoceptor family genes in hypertension was conducted.
Methods: Data from 163 GAS involving 7 genes and 37 distinct genetic variants were analyzed and cataloged in CUMAGAS-HYPERT (Cumulative Meta-analysis of Genetic Association Studies-HYPERTension; a web-based information system, which allows the retrieval and synthesis of data from GAS in hypertension, available at http://biomath.med.uth.gr). Data from genome-wide association studies involving the adrenoceptor family genes were also systematically searched.
Results: Individual GAS reported inconsistent associations and had limited power to detect modest genetic effects, with only 1.2% having power >80%. Thirteen variants were investigated by three or more studies and their results were subject to meta-analysis. In the main meta-analyses, significant results were shown for five variants (ADRB1 p.Arg389Gly, ADRB1 p.Ser49Gly, ADRB2 g.9368308A>G, ADRB3 p.Trp64Arg, and ADRA1A p.Cys347Arg) under the allelic contrast and/or the dominant model. Subgroup analyses by ethnicity and gender detected significant associations for three variants (ADRB1 p.Arg389Gly in east Asians, ADRB2 p.Gln27Glu in whites, and ADRB3 p.Trp64Arg in whites and in males). Heterogeneity ranged from none to high. No significant associations were recorded from genome-wide studies.
Conclusions: There is evidence to implicate adrenoceptor genes in hypertension, although future studies designed to investigate epistatic and gene-environment interactions would allow more solid conclusions to be drawn about the role of these genes in hypertension.
Figures
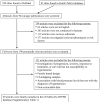
Figure 1
Flow chart of studies retrieved and studies excluded, with specification of reasons.
Comment in
- Sympathetic meta-analysis of adrenoceptor gene variants in hypertension.
Morris BJ. Morris BJ. Am J Hypertens. 2010 Mar;23(3):225. doi: 10.1038/ajh.2009.267. Am J Hypertens. 2010. PMID: 20154653 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Synopsis and meta-analysis of genetic association studies in osteoporosis for the focal adhesion family genes: the CUMAGAS-OSTEOporosis information system.
Zintzaras E, Doxani C, Koufakis T, Kastanis A, Rodopoulou P, Karachalios T. Zintzaras E, et al. BMC Med. 2011 Jan 26;9:9. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-9-9. BMC Med. 2011. PMID: 21269451 Free PMC article. - Field synopsis and synthesis of genetic association studies in osteoarthritis: the CUMAGAS-OSTEO information system.
Zintzaras E, Kitsios GD, Ziogas DC, Rodopoulou P, Karachalios T. Zintzaras E, et al. Am J Epidemiol. 2010 Apr 15;171(8):851-8. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwq016. Epub 2010 Mar 17. Am J Epidemiol. 2010. PMID: 20237151 Review. - Synopsis and synthesis of candidate-gene association studies in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: the CUMAGAS-CLL information system.
Zintzaras E, Kitsios GD. Zintzaras E, et al. Am J Epidemiol. 2009 Sep 15;170(6):671-8. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwp201. Epub 2009 Aug 21. Am J Epidemiol. 2009. PMID: 19700502 - ADRB3 polymorphism rs4994 (Trp64Arg) associates significantly with bodyweight elevation and dyslipidaemias in Saudis but not rs1801253 (Arg389Gly) polymorphism in ARDB1.
Daghestani M, Daghestani M, Daghistani M, Eldali A, Hassan ZK, Elamin MH, Warsy A. Daghestani M, et al. Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Mar 27;17(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0679-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 29587766 Free PMC article. - Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.
Crider K, Williams J, Qi YP, Gutman J, Yeung L, Mai C, Finkelstain J, Mehta S, Pons-Duran C, Menéndez C, Moraleda C, Rogers L, Daniels K, Green P. Crider K, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- EINVis: a visualization tool for analyzing and exploring genetic interactions in large-scale association studies.
Wu Y, Zhu X, Chen J, Zhang X. Wu Y, et al. Genet Epidemiol. 2013 Nov;37(7):675-85. doi: 10.1002/gepi.21754. Epub 2013 Aug 11. Genet Epidemiol. 2013. PMID: 23934759 Free PMC article. - Alpha-adrenergic receptor gene polymorphisms and cardiovascular reactivity to stress in Black adolescents and young adults.
Kelsey RM, Alpert BS, Dahmer MK, Krushkal J, Quasney MW. Kelsey RM, et al. Psychophysiology. 2012 Mar;49(3):401-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2011.01319.x. Epub 2011 Nov 14. Psychophysiology. 2012. PMID: 22091949 Free PMC article. - Computational resources associating diseases with genotypes, phenotypes and exposures.
Zhang W, Zhang H, Yang H, Li M, Xie Z, Li W. Zhang W, et al. Brief Bioinform. 2019 Nov 27;20(6):2098-2115. doi: 10.1093/bib/bby071. Brief Bioinform. 2019. PMID: 30102366 Free PMC article. - Synopsis and meta-analysis of genetic association studies in osteoporosis for the focal adhesion family genes: the CUMAGAS-OSTEOporosis information system.
Zintzaras E, Doxani C, Koufakis T, Kastanis A, Rodopoulou P, Karachalios T. Zintzaras E, et al. BMC Med. 2011 Jan 26;9:9. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-9-9. BMC Med. 2011. PMID: 21269451 Free PMC article. - β1-adrenoceptor gene Arg389Gly polymorphism and essential hypertension risk in general population: a meta-analysis.
Wang H, Liu J, Liu K, Liu Y, Wang Z, Lou Y, Niu Q, Gu W, Wang L, Li M, Zhu X, Wen S. Wang H, et al. Mol Biol Rep. 2013 Jun;40(6):4055-63. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-2483-1. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Mol Biol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23588958
References
- Cowley AW., Jr The genetic dissection of essential hypertension. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7:829–840. - PubMed
- Binder A. A review of the genetics of essential hypertension. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2007;22:176–184. - PubMed
- Hamet P, Seda O. Current status of genome-wide scanning for hypertension. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2007;22:292–297. - PubMed
- Zintzaras E, Kitsios G, Kent D, Camp NJ, Atwood L, Hopkins PN, Hunt SC. Genome-wide scans meta-analysis for pulse pressure. Hypertension. 2007;50:557–564. - PubMed
- DeQuattro V, Feng M. The sympathetic nervous system: the muse of primary hypertension. J Hum Hypertens. 2002;16(Suppl 1):S64–S69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical