Prevalence and prognostic significance of KIT mutations in pediatric patients with core binding factor AML enrolled on serial pediatric cooperative trials for de novo AML - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2010 Mar 25;115(12):2372-9.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-09-241075. Epub 2010 Jan 7.
Todd A Alonzo, Robert B Gerbing, Phoenix A Ho, Rong Zeng, Yaddanapudi Ravindranath, Gary Dahl, Norman J Lacayo, David Becton, Myron Chang, Howard J Weinstein, Betsy Hirsch, Susana C Raimondi, Nyla A Heerema, William G Woods, Beverly J Lange, Craig Hurwitz, Robert J Arceci, Jerald P Radich, Irwin D Bernstein, Michael C Heinrich, Soheil Meshinchi
Affiliations
- PMID: 20056794
- PMCID: PMC2845895
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-09-241075
Prevalence and prognostic significance of KIT mutations in pediatric patients with core binding factor AML enrolled on serial pediatric cooperative trials for de novo AML
Jessica A Pollard et al. Blood. 2010.
Abstract
KIT receptor tyrosine kinase mutations are implicated as a prognostic factor in adults with core binding factor (CBF) acute myeloid leukemia (AML). However, their prevalence and prognostic significance in pediatric CBF AML is not well established. We performed KIT mutational analysis (exon 8 and exon 17) on diagnostic specimens from 203 pediatric patients with CBF AML enrolled on 4 pediatric AML protocols. KIT mutations were detected in 38 (19%) of 203 (95% CI, 14%-25%) patient samples of which 20 (52.5%) of 38 (95% CI, 36%-69%) involved exon 8, 17 (45%) of 38 (95% CI, 29%-62%) involved exon 17, and 1 (2.5%; 95% CI, 0%-14%) involved both locations. Patients with KIT mutations had a 5-year event-free survival of 55% (+/- 17%) compared with 59% (+/- 9%) for patients with wild-type KIT (P = .86). Rates of complete remission, overall survival, disease-free survival, or relapse were not significantly different for patients with or without KIT mutations. Location of the KIT mutation and analysis by cytogenetic subtype [t(8;21) vs inv(16)] also lacked prognostic significance. Our study shows that KIT mutations lack prognostic significance in a large series of pediatric patients with CBF AML. This finding, which differs from adult series and a previously published pediatric study, may reflect variations in therapeutic approaches and/or biologic heterogeneity within CBF AML. Two of 4 studies included in this analysis are registered at http://clinicaltrials.gov as NCT00002798 (CCG-2961) and NCT00070174 (COG AAML03P1).
Figures
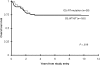
Figure 1
OS for patients with CBF AML with KIT mutations or WT KIT.
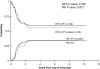
Figure 2
DFS and RR rates for patients with CBF AML with KIT mutations or WT KIT.
Similar articles
- Core binding factor acute myeloid leukaemia and c-KIT mutations.
Riera L, Marmont F, Toppino D, Frairia C, Sismondi F, Audisio E, Di Bello C, D'Ardia S, Di Celle PF, Messa E, Inghirami G, Vitolo U, Pich A. Riera L, et al. Oncol Rep. 2013 May;29(5):1867-72. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2328. Epub 2013 Mar 5. Oncol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23467883 - KIT mutations correlate with adverse survival in children with core-binding factor acute myeloid leukemia.
Chen X, Dou H, Wang X, Huang Y, Lu L, Bin J, Su Y, Zou L, Yu J, Bao L. Chen X, et al. Leuk Lymphoma. 2018 Apr;59(4):829-836. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2017.1361025. Epub 2017 Aug 9. Leuk Lymphoma. 2018. PMID: 28792268 - KIT D816 mutation associates with adverse outcomes in core binding factor acute myeloid leukemia, especially in the subgroup with RUNX1/RUNX1T1 rearrangement.
Kim HJ, Ahn HK, Jung CW, Moon JH, Park CH, Lee KO, Kim SH, Kim YK, Kim HJ, Sohn SK, Kim SH, Lee WS, Kim KH, Mun YC, Kim H, Park J, Min WS, Kim HJ, Kim DH; L/MDS working party, Korean Society of Hematology. Kim HJ, et al. Ann Hematol. 2013 Jan;92(2):163-71. doi: 10.1007/s00277-012-1580-5. Epub 2012 Sep 28. Ann Hematol. 2013. PMID: 23053179 - Prognostic Significance of KIT Mutations in Core-Binding Factor Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
Chen W, Xie H, Wang H, Chen L, Sun Y, Chen Z, Li Q. Chen W, et al. PLoS One. 2016 Jan 15;11(1):e0146614. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146614. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26771376 Free PMC article. Review. - Prognostic Importance of C-KIT Mutations in Core Binding Factor Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Systematic Review.
Ayatollahi H, Shajiei A, Sadeghian MH, Sheikhi M, Yazdandoust E, Ghazanfarpour M, Shams SF, Shakeri S. Ayatollahi H, et al. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2017 Mar;10(1):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.hemonc.2016.08.005. Epub 2016 Sep 3. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2017. PMID: 27613372 Review.
Cited by
- Adverse prognostic impact of KIT mutations in childhood CBF-AML: the results of the Japanese Pediatric Leukemia/Lymphoma Study Group AML-05 trial.
Tokumasu M, Murata C, Shimada A, Ohki K, Hayashi Y, Saito AM, Fujimoto J, Horibe K, Nagao M, Itoh H, Kamikubo Y, Nakayama H, Kinoshita A, Tomizawa D, Taga T, Tawa A, Tanaka S, Heike T, Adachi S. Tokumasu M, et al. Leukemia. 2015 Dec;29(12):2438-41. doi: 10.1038/leu.2015.121. Epub 2015 May 15. Leukemia. 2015. PMID: 25975190 No abstract available. - Clinical Impact of Additional Cytogenetic Aberrations, cKIT and RAS Mutations, and Treatment Elements in Pediatric t(8;21)-AML: Results From an International Retrospective Study by the International Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster Study Group.
Klein K, Kaspers G, Harrison CJ, Beverloo HB, Reedijk A, Bongers M, Cloos J, Pession A, Reinhardt D, Zimmerman M, Creutzig U, Dworzak M, Alonzo T, Johnston D, Hirsch B, Zapotocky M, De Moerloose B, Fynn A, Lee V, Taga T, Tawa A, Auvrignon A, Zeller B, Forestier E, Salgado C, Balwierz W, Popa A, Rubnitz J, Raimondi S, Gibson B. Klein K, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2015 Dec 20;33(36):4247-58. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.61.1947. Epub 2015 Nov 16. J Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26573082 Free PMC article. - Pediatric PK/PD Phase I Trial of Pexidartinib in Relapsed and Refractory Leukemias and Solid Tumors Including Neurofibromatosis Type I-Related Plexiform Neurofibromas.
Boal LH, Glod J, Spencer M, Kasai M, Derdak J, Dombi E, Ahlman M, Beury DW, Merchant MS, Persenaire C, Liewehr DJ, Steinberg SM, Widemann BC, Kaplan RN. Boal LH, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Dec 1;26(23):6112-6121. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-1696. Epub 2020 Sep 17. Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32943455 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Children's Oncology Group's 2013 blueprint for research: acute myeloid leukemia.
Gamis AS, Alonzo TA, Perentesis JP, Meshinchi S; COG Acute Myeloid Leukemia Committee. Gamis AS, et al. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2013 Jun;60(6):964-71. doi: 10.1002/pbc.24432. Epub 2012 Dec 19. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23255301 Free PMC article. Review. - Prevalence and prognostic implications of WT1 mutations in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia (AML): a report from the Children's Oncology Group.
Ho PA, Zeng R, Alonzo TA, Gerbing RB, Miller KL, Pollard JA, Stirewalt DL, Heerema NA, Raimondi SC, Hirsch B, Franklin JL, Lange B, Meshinchi S. Ho PA, et al. Blood. 2010 Aug 5;116(5):702-10. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-02-268953. Epub 2010 Apr 22. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20413658 Free PMC article.
References
- Grimwade D, Walker H, Oliver F, et al. The importance of diagnostic cytogenetics on outcome in AML: analysis of 1, 612 patients entered into the MRC AML 10 trial. The Medical Research Council Adult and Children's Leukaemia Working Parties. Blood. 1998;92(7):2322–2333. - PubMed
- Paschka P, Marcucci G, Ruppert AS, et al. Adverse prognostic significance of KIT mutations in adult acute myeloid leukemia with inv(16) and t(8;21): a Cancer and Leukemia Group B Study. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(24):3904–3911. - PubMed
- Hann IM, Webb DK, Gibson BE, Harrison CJ. MRC trials in childhood acute myeloid leukaemia. Ann Hematol. 2004;83(Suppl 1):S108–S112. - PubMed
- d'Auriol L, Mattei MG, Andre C, Galibert F. Localization of the human c-kit protooncogene on the q11-q12 region of chromosome 4. Hum Genet. 1988;78(4):374–376. - PubMed
- Renneville A, Roumier C, Biggio V, et al. Cooperating gene mutations in acute myeloid leukemia: a review of the literature. Leukemia. 2008;22(5):915–931. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K12 CA076930/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA10262-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA114563-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA114563/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA098543/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5K12CA076930-08/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA98543/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical