XIAP is not required for human tumor cell survival in the absence of an exogenous death signal - PubMed (original) (raw)
XIAP is not required for human tumor cell survival in the absence of an exogenous death signal
John Sensintaffar et al. BMC Cancer. 2010.
Abstract
Background: The X-linked Inhibitor of Apoptosis (XIAP) has attracted much attention as a cancer drug target. It is the only member of the IAP family that can directly inhibit caspase activity in vitro, and it can regulate apoptosis and other biological processes through its C-terminal E3 ubiquitin ligase RING domain. However, there is controversy regarding XIAP's role in regulating tumor cell proliferation and survival under normal growth conditions in vitro.
Methods: We utilized siRNA to systematically knock down XIAP in ten human tumor cell lines and then monitored both XIAP protein levels and cell viability over time. To examine the role of XIAP in the intrinsic versus extrinsic cell death pathways, we compared the viability of XIAP depleted cells treated either with a variety of mechanistically distinct, intrinsic pathway inducing agents, or the canonical inducer of the extrinsic pathway, TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL).
Results: XIAP knockdown had no effect on the viability of six cell lines, whereas the effect in the other four was modest and transient. XIAP knockdown only sensitized tumor cells to TRAIL and not the mitochondrial pathway inducing agents.
Conclusions: These data indicate that XIAP has a more central role in regulating death receptor mediated apoptosis than it does the intrinsic pathway mediated cell death.
Figures
Figure 1
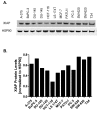
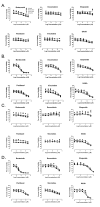
XIAP protein levels in a panel of human tumor cell lines. A. XIAP levels were monitored by Western blot from lysates of tumor cells. B. Quantification by LICOR Odyssey imaging. XIAP levels were normalized to the loading control HSP90 (Materials and Methods).
Figure 2
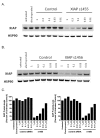
Dose dependent increase in XIAP knockdown with XIAP siRNA s1455 and s1456. SW620 cells were electroporated with the concentrations of siRNA indicated. After 48 hr, cells were lysed and XIAP levels were monitored by Western blot. A. s1455 B. s1456 C. Quantification by LICOR Odyssey imaging. Percent XIAP levels are expressed relative to the mean of untreated cells.
Figure 3
Kinetics of siRNA mediated XIAP knockdown. SW620 cells were electroporated with 1 μM s1455 or 1 μM control siRNA. Samples were collected every 24 hours and XIAP levels were detected by Western Blot (A) and (B) quantified by LICOR Odyssey imaging. XIAP values were normalized to the loading control, HSP90. Percent XIAP protein levels are expressed relative to the mean of control siRNA at 24 hr. 1 μM control siRNA (unfilled square) and 1 μM XIAP siRNA (black square).
Figure 4
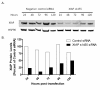
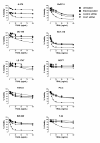
XIAP depletion in a panel of tumor cell lines. A. XIAP levels were monitored by Western blot from lysates of untreated cells (unfilled square), electroporated cells, (grey square), cells electroporated with 1 μM control siRNA (dark grey square), or 1 μM s1455 XIAP siRNA (black square) 48 hr following electroporation. XIAP levels were quantified by LICOR Odyssey imaging. Percent XIAP levels are expressed relative to the untreated control for each cell line. B. Viablity of XIAP depleted cells was measured at 24, 48, 72 and 96 hr post electroporation; untreated cells (unfilled square), electroporated cells (light grey square), cells electroporated with 1 μM control siRNA (dark grey square), or 1 μM s1455 XIAP siRNA (black square).
Figure 5
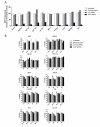
Effect of XIAP depletion on tumor cell viability and TRAIL sensitivity. XIAP depleted cells were exposed to TRAIL 40 hr following electroporation, and viability was measured 24 hr following TRAIL exposure Untreated cells (black circle); Electroporated cells (black square); 1 μM control siRNA (black triangle) 1 μM XIAP siRNA (inverted black triangle). Percent viability is expressed relative to untreated controls for each cell line. A similar result was obtained with the s1456 siRNA in SW620 cells (Additional File 2).
Figure 6
Effect of XIAP depletion on chemosensitivity of HCT-116 and SW620 cells. Cells were electroporated with 1 μM control siRNA (con siRNA) or 1 μM s1455 XIAP siRNA. HCT-116 and SW-620 were treated with an array of chemotherapeutic agents for 24 hr (A and C, respectively) or 48 hr (B and D). For the 24 hr exposure, the agents were added 32 hr following electroporation. For the 48 hr exposure, the agents were added 24 hr following electroporation. Untreated cells (black circle); Electroporated cells (black square); 1 μM control siRNA (black triangle) XIAP siRNA (inverted black triangle).
Similar articles
- X-linked inhibitor regulating TRAIL-induced apoptosis in chemoresistant human primary glioblastoma cells.
Roa WH, Chen H, Fulton D, Gulavita S, Shaw A, Th'ng J, Farr-Jones M, Moore R, Petruk K. Roa WH, et al. Clin Invest Med. 2003 Oct;26(5):231-42. Clin Invest Med. 2003. PMID: 14596484 - Specific down-regulation of XIAP with RNA interference enhances the sensitivity of canine tumor cell-lines to TRAIL and doxorubicin.
Spee B, Jonkers MD, Arends B, Rutteman GR, Rothuizen J, Penning LC. Spee B, et al. Mol Cancer. 2006 Sep 5;5:34. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-5-34. Mol Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16953886 Free PMC article. - XIAP-targeting drugs re-sensitize PIK3CA-mutated colorectal cancer cells for death receptor-induced apoptosis.
Ehrenschwender M, Bittner S, Seibold K, Wajant H. Ehrenschwender M, et al. Cell Death Dis. 2014 Dec 11;5(12):e1570. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.534. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 25501831 Free PMC article. - The role of XIAP in resistance to TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) in Leukemia.
Saraei R, Soleimani M, Movassaghpour Akbari AA, Farshdousti Hagh M, Hassanzadeh A, Solali S. Saraei R, et al. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Nov;107:1010-1019. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.08.065. Epub 2018 Aug 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 30257312 Review. - XIAP as a ubiquitin ligase in cellular signaling.
Galbán S, Duckett CS. Galbán S, et al. Cell Death Differ. 2010 Jan;17(1):54-60. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2009.81. Cell Death Differ. 2010. PMID: 19590513 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- CRNDE affects the malignant biological characteristics of human glioma stem cells by negatively regulating miR-186.
Zheng J, Li XD, Wang P, Liu XB, Xue YX, Hu Y, Li Z, Li ZQ, Wang ZH, Liu YH. Zheng J, et al. Oncotarget. 2015 Sep 22;6(28):25339-55. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4509. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26231038 Free PMC article. - Smac mimetics: implications for enhancement of targeted therapies in leukemia.
Weisberg E, Ray A, Barrett R, Nelson E, Christie AL, Porter D, Straub C, Zawel L, Daley JF, Lazo-Kallanian S, Stone R, Galinsky I, Frank D, Kung AL, Griffin JD. Weisberg E, et al. Leukemia. 2010 Dec;24(12):2100-9. doi: 10.1038/leu.2010.212. Epub 2010 Sep 16. Leukemia. 2010. PMID: 20844561 Free PMC article. - XIAP as a Target of New Small Organic Natural Molecules Inducing Human Cancer Cell Death.
Muñoz D, Brucoli M, Zecchini S, Sandoval-Hernandez A, Arboleda G, Lopez-Vallejo F, Delgado W, Giovarelli M, Coazzoli M, Catalani E, De Palma C, Perrotta C, Cuca L, Clementi E, Cervia D. Muñoz D, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2019 Sep 9;11(9):1336. doi: 10.3390/cancers11091336. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31505859 Free PMC article. - A Novel Role of IGF1 in Apo2L/TRAIL-Mediated Apoptosis of Ewing Tumor Cells.
van Valen F, Harrer H, Hotfilder M, Dirksen U, Pap T, Gosheger G, Humpf HU, Jürgens H. van Valen F, et al. Sarcoma. 2012;2012:782970. doi: 10.1155/2012/782970. Epub 2012 Oct 3. Sarcoma. 2012. PMID: 23091403 Free PMC article. - Effect of different culture systems and 3, 5, 3'-triiodothyronine/follicle-stimulating hormone on preantral follicle development in mice.
Zhang C, Wang X, Wang Z, Niu W, Zhu B, Xia G. Zhang C, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Apr 15;8(4):e61947. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061947. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23596531 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials