Trans-Proteomic Pipeline supports and improves analysis of electron transfer dissociation data sets - PubMed (original) (raw)
Trans-Proteomic Pipeline supports and improves analysis of electron transfer dissociation data sets
Eric W Deutsch et al. Proteomics. 2010 Mar.
Abstract
Electron transfer dissociation (ETD) is an alternative fragmentation technique to CID that has recently become commercially available. ETD has several advantages over CID. It is less prone to fragmenting amino acid side chains, especially those that are modified, thus yielding fragment ion spectra with more uniform peak intensities. Further, precursor ions of longer peptides and higher charge states can be fragmented and identified. However, analysis of ETD spectra has a few important differences that require the optimization of the software packages used for the analysis of CID data or the development of specialized tools. We have adapted the Trans-Proteomic Pipeline to process ETD data. Specifically, we have added support for fragment ion spectra from high-charge precursors, compatibility with charge-state estimation algorithms, provisions for the use of the Lys-C protease, capabilities for ETD spectrum library building, and updates to the data formats to differentiate CID and ETD spectra. We show the results of processing data sets from several different types of ETD instruments and demonstrate that application of the ETD-enhanced Trans-Proteomic Pipeline can increase the number of spectrum identifications at a fixed false discovery rate by as much as 100% over native output from a single sequence search engine.
Figures
Figure 1
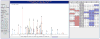
Example screenshot of a spectrum from Dataset 1 in the TPP interface for 4+ ALPIRRDDEVLVVRGSK. Each identified peak is labeled with its ion series, series number, and charge identification. Charge reduced precursor peaks are labeled with the prefix M++++. On the left are some user-settable parameters for the spectrum display. On the right, the m/z values for expected c, z•, and y series ions are listed, and shaded if detected in the spectrum.
Figure 2
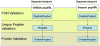
Schematic overview of the workflow of the post-processing and validation of the results of the SEQUEST and OMSSA sequence database searches using the TPP tools. PeptideProphet was used to model and validate the peptide spectrum matches (PSMs). The iProphet tool was used to coalesce the results to the distinct peptide sequence level. ProteinProphet was used to infer the identified proteins and assign probabilities to each protein based on the upstream analysis.
Figure 3
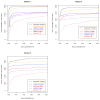
Number of PSMs as a function of FDR for the SEQUEST search before (red dotted) and after TPP processing (red solid), OMSSA search before (blue dotted) and after TPP processing (blue solid), combined (orange), and SpectraST spectral library search (black) for the three datasets. All three datasets are from different yeast whole-cell lysate samples; Dataset 1 was obtained with an LTQ Orbitrap ETD, while Datasets 2 and 3 were obtained with LTQ ETD instruments in different labs. In all three cases, applying two search engines and the TPP tools nearly doubled the number of identified spectra at a 1% FDR over using SEQUEST raw scores.
Similar articles
- Enhanced peptide identification by electron transfer dissociation using an improved Mascot Percolator.
Wright JC, Collins MO, Yu L, Käll L, Brosch M, Choudhary JS. Wright JC, et al. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 Aug;11(8):478-91. doi: 10.1074/mcp.O111.014522. Epub 2012 Apr 6. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22493177 Free PMC article. - Improved peptide identification for proteomic analysis based on comprehensive characterization of electron transfer dissociation spectra.
Sun RX, Dong MQ, Song CQ, Chi H, Yang B, Xiu LY, Tao L, Jing ZY, Liu C, Wang LH, Fu Y, He SM. Sun RX, et al. J Proteome Res. 2010 Dec 3;9(12):6354-67. doi: 10.1021/pr100648r. Epub 2010 Nov 12. J Proteome Res. 2010. PMID: 20883037 - A new probabilistic database search algorithm for ETD spectra.
Sadygov RG, Good DM, Swaney DL, Coon JJ. Sadygov RG, et al. J Proteome Res. 2009 Jun;8(6):3198-205. doi: 10.1021/pr900153b. J Proteome Res. 2009. PMID: 19354237 Free PMC article. - The utility of ETD mass spectrometry in proteomic analysis.
Mikesh LM, Ueberheide B, Chi A, Coon JJ, Syka JE, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF. Mikesh LM, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Dec;1764(12):1811-22. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2006.10.003. Epub 2006 Oct 30. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 17118725 Free PMC article. Review. - Open source libraries and frameworks for mass spectrometry based proteomics: a developer's perspective.
Perez-Riverol Y, Wang R, Hermjakob H, Müller M, Vesada V, Vizcaíno JA. Perez-Riverol Y, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jan;1844(1 Pt A):63-76. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2013.02.032. Epub 2013 Mar 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 23467006 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Precursor charge state prediction for electron transfer dissociation tandem mass spectra.
Sharma V, Eng JK, Feldman S, von Haller PD, MacCoss MJ, Noble WS. Sharma V, et al. J Proteome Res. 2010 Oct 1;9(10):5438-44. doi: 10.1021/pr1006685. J Proteome Res. 2010. PMID: 20731383 Free PMC article. - Membrane trafficking and exocytosis are upregulated in port wine stain blood vessels.
Yin R, Rice SJ, Wang J, Gao L, Tsai J, Anvari RT, Zhou F, Liu X, Wang G, Tang Y, Mihm MC Jr, Belani CP, Chen DB, Nelson JS, Tan W. Yin R, et al. Histol Histopathol. 2019 May;34(5):479-490. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-051. Epub 2018 Oct 10. Histol Histopathol. 2019. PMID: 30302745 Free PMC article. - Visualize: a free and open source multifunction tool for proteomics data analysis.
Halligan BD, Greene AS. Halligan BD, et al. Proteomics. 2011 Mar;11(6):1058-63. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201000556. Epub 2011 Feb 7. Proteomics. 2011. PMID: 21365761 Free PMC article. - Potential molecular mechanisms of overgrazing-induced dwarfism in sheepgrass (Leymus chinensis) analyzed using proteomic data.
Ren W, Xie J, Hou X, Li X, Guo H, Hu N, Kong L, Zhang J, Chang C, Wu Z. Ren W, et al. BMC Plant Biol. 2018 May 8;18(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1304-7. BMC Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 29739327 Free PMC article. - Enhanced peptide identification by electron transfer dissociation using an improved Mascot Percolator.
Wright JC, Collins MO, Yu L, Käll L, Brosch M, Choudhary JS. Wright JC, et al. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 Aug;11(8):478-91. doi: 10.1074/mcp.O111.014522. Epub 2012 Apr 6. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22493177 Free PMC article.
References
- Nesvizhskii AI, Vitek O, Aebersold R. Analysis and validation of proteomic data generated by tandem mass spectrometry. Nat Methods. 2007;4(10):787–97. - PubMed
- Kall L, et al. Semi-supervised learning for peptide identification from shotgun proteomics datasets. Nat Methods. 2007;4(11):923–5. - PubMed
- Coon JJ, et al. Electron transfer dissociation of peptide anions. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2005;16(6):880–2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01-HV-28179/HV/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HV28179/HV/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- PM50 GMO76547/PHS HHS/United States
- N01 HV028179/HV/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM076547-01/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM076547/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources