FYCO1 is a Rab7 effector that binds to LC3 and PI3P to mediate microtubule plus end-directed vesicle transport - PubMed (original) (raw)
FYCO1 is a Rab7 effector that binds to LC3 and PI3P to mediate microtubule plus end-directed vesicle transport
Serhiy Pankiv et al. J Cell Biol. 2010.
Abstract
Autophagy is the main eukaryotic degradation pathway for long-lived proteins, protein aggregates, and cytosolic organelles. Although the protein machinery involved in the biogenesis of autophagic vesicles is well described, very little is known about the mechanism of cytosolic transport of autophagosomes. In this study, we have identified an adaptor protein complex, formed by the two autophagic membrane-associated proteins LC3 and Rab7 and the novel FYVE and coiled-coil (CC) domain-containing protein FYCO1, that promotes microtubule (MT) plus end-directed transport of autophagic vesicles. We have characterized the LC3-, Rab7-, and phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate-binding domains in FYCO1 and mapped part of the CC region essential for MT plus end-directed transport. We also propose a mechanism for selective autophagosomal membrane recruitment of FYCO1.
Figures
Figure 1.
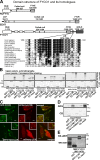
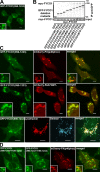
FYCO1 is a novel LC3B-interacting protein. (A and B) Endogenous FYCO1 binds to GST-LC3B. GST-LC3B bound to glutathione–Sepharose beads was incubated with HeLa cell lysate, and copurified proteins were identified by Coomassie blue staining and mass spectrometry (A) or immunoblotting with anti-FYCO1 antibody (B). (C) GST-LC3B but not GST-p62 or GST alone binds to FYCO1 in a GST pull-down assay. GST, GST-LC3B, or GST-p62 bound to glutathione–Sepharose beads was incubated with [35S]methionine-labeled myc-FYCO1. Formed protein complexes were isolated and visualized by autoradiography (top) or Coomassie blue staining (bottom). (D) GFP-LC3B immunoprecipitates endogenous FYCO1 from HeLa cell lysate. HeLa cells expressing GFP or GFP-LC3B were lysed and processed as in B. IP, immunoprecipitation; MM, molecular mass; WB, Western blot.
Figure 2.
The interaction between FYCO1 and LC3B is mediated by a short conserved acidic motif C-terminally from the FYVE domain in FYCO1 and both N- and C-terminal domains of LC3B. (A) Schematic structure of FYCO1 and its homologous proteins RUFY1b and EEA1. In the multialignment sequence, identity is indicated by black highlighting, and residues highlighted in gray indicate substitutions to chemically similar amino acids in more than 50% of the compared sequences. (B) The region of FYCO1 between aa 1,276 and 1,294 is essential and sufficient for the interaction with LC3B. GST or GST-LC3B were incubated with [S35]methionine-labeled deletion mutants of FYCO1 and processed as in Fig. 1 C. (C) LIR is essential for colocalization of FYCO1 with LC3B in HeLa cells. HeLa cells expressing the indicated constructs were imaged by confocal microscopy. Insets show an enlarged field of interest. (D) Both N- and C-terminal domains of LC3B are needed for efficient interaction with FYCO1. GST, GST-LC3B, or its deletion mutants were incubated with [S35]methionine-labeled myc-FYCO1 and processed as in Fig. 1 C. ARG, autoradiography; CB, Coomassie blue. (E) The interaction between FYCO1 and LC3B is direct. GST or GST-LC3B was incubated with recombinant MBP-FYCO1863–1,478. Protein complexes were isolated and visualized by immunoblotting with anti-GST or anti-MBP antibodies. WB, Western blot. Bars: (C) 10 µm; (C, insets) 1 µm.
Figure 3.
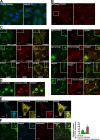
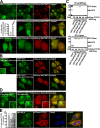
FYCO1 decorates cytosolic vesicles and cytosolic punctuated structures containing the protein markers of autophagosomes/LEs/lysosomes. (A) Endogenous FYCO1 localizes to the cytosolic punctuated structures. HeLa cells cultured in complete growth medium (left) or in HBSS for 3 h (right) were fixed and stained with anti-FYCO1 antibody (green) and Draq5 (blue). (B) Overexpressed mCherry-FYCO1 localizes to the cytosolic punctuated structures and cytosolic vesicles in stably transfected HeLa cells. (C) FYCO1 partially colocalizes with LC3B, LAMP1, ATG5, ATG16L, p62, and HuntingtinQ64 and does not colocalize with EEA1. HeLa cells or mouse embryonic fibroblasts (for ATG16L staining) were transfected with the indicated vectors or stained with the indicated antibodies and imaged 24 h after transfection. For p62 staining, HeLa cells were incubated with 0.2 µM BafA1 for 12 h before fixation. (D) FYCO1 colocalizes with LC3B on the rim but not inside of the vesical structures. HeLa cells cotransfected with GFP-FYCO1, mCherry-LC3B, and myc-p62 were imaged by confocal microscopy 48 h after transfection. (E and F) FYCO1-decorated structures are heterogenous in their luminal content. (E) HeLa cells transfected with CFP-FYCO1 and mChery-YFP-p62 were imaged 48 h after transfection. (F) HeLa cells transfected with GFP-FYCO1 were labeled with LysoTracker red for 60 min and Alexa Fluor 647–dextran (10,000 D) for 4 h in normal growth medium to stain late endocytic compartments (left). Relative number of FYCO1 structures ± SD colocalized with LysoTracker red or Alexa Fluor 647–dextran (10,000 D; right). (B, C, E, and F) Insets show an enlarged field of interest. Bars: (A, B [left], C, E, and F) 10 µm; (B [right] and D) 1 µm.
Figure 4.
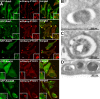
FYCO1 colocalizes with Rab7 and decorates the limiting membranes of autophagosomes, LEs, and lysosomes. (A) HeLa cells transfected with the indicated constructs were imaged by confocal microscopy 24 h after transfection. Insets show an enlarged field of interest. (B–D) Immunoelectron micrographs of HeLa cells transfected with GFP-FYCO1 and stained with anti-GFP polyclonal antibody (10-nm gold particle). Bars: (A) 10 µm; (A, insets) 1 µm.
Figure 5.
FYCO1 can dimerize and is recruited to intracellular membranes in an FYVE domain–dependent manner. (A) FYCO1 shows only weak or no colocalization with a PI3P probe 2xFYVEHrs. HeLa cells were imaged 24 h after transfection with the indicated constructs. (B) The FYVE domain of FYCO1 is essential but not sufficient for its recruitment to the cytosolic vesicles. HeLa cells were imaged 24 h after transfection with the indicated constructs. (C) FYCO1 can self-interact in a CC-dependent manner. Full-length GFP-FYCO1 was cotranscribed and cotranslated with the indicated deletion mutants of myc-tagged FYCO1 in rabbit reticulocyte lysate. S35-labeled FYCO1 complexes were immunoprecipitated with anti-myc antibody, separated by SDS-PAGE, and visualized by autoradiography. IP, immunoprecipitation. (D) Dimers but not a monomer of the FYVE domain from FYCO1 can bind PI3P in protein–lipid overlay assay. PIP Strips were incubated with 1-µg/ml solutions of MBP-FYVEFYCO1, MBP-2xFYVEFYCO1, or MBP-FYCO1863–1,233 for 1 h, and bound proteins were detected by immunostaining with anti-MBP antibody. LPA, lysophosphatic acid; LPC, lysophosphocholine; PI, phosphatidylinositol; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PC, phosphatidylcholine; S1P, sphingosine-1-phosphate; PA, phosphatidic acid; PS, phosphatidylserine. (E) The construct containing a tandem fusion of two FYVE domains from FYCO1 (2xFYVEFYCO1) localizes to the nuclear envelope and ER in HeLa cells. HeLa cells were imaged 24 h after transfection with the indicated constructs. (A and E) Insets show an enlarged field of interest. (F) 2xFYVEFYCO1 does not colocalize with 2xFYVEHrs (left) and PXp40phox (right). HeLa cells were imaged 24 h after transfection with the indicated constructs. Bars, 10 µm.
Figure 6.
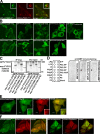
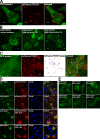
The FYVE domain from FYCO1 containing the dimerizing CC is recruited to late endosomal/lysosomal structures. (A) FYCO1990–1,233 is the smallest FYVE domain–containing deletion mutant of FYCO1 consistently recruited to cytosolic vesicles. HeLa cells transiently transfected with FYCO1990–1,233 were imaged 24 h after transfection. (B) FYCO1990–1,233 is the smallest FYVE domain–containing deletion mutant of FYCO1 that can efficiently interact with the full-length FYCO1. Full-length myc-FYCO1 was cotranscribed and cotranslated with the indicated deletion mutants of GFP-tagged FYCO1 in rabbit reticulocyte lysate. S35-labeled FYCO1 complexes were immunoprecipitated with anti-myc antibody, separated by SDS-PAGE, and visualized by autoradiography. IP, immunoprecipitation. (C) FYCO1990–1,233 strongly colocalizes with Rab7, LysoTracker red, and Alexa Fluor 647–dextran (10,000 D) but only weakly with PXp40phox. HeLa cells transfected with the indicated constructs or labeled with LysoTracker red for 60 min and Alexa Fluor 647–dextran (10,000 D) for 4 h were imaged 24 h after transfection. (D) FYCO1 construct containing a CC region followed by a tandem repeat of two FYVE domains from FYCO1 (FYCO1990–1,233+1,156–1,233) localizes to the ER and perinuclear vesicles and only weakly colocalizes with PXp40phox. HeLa cells were imaged 24 h after transfection with the indicated constructs. (A, C, and D) Insets show an enlarged field of interest. Bars, 10 µm.
Figure 7.
Rab7 forms a complex with FYCO1 and induces the recruitment of FYCO1 to intracellular membranes. (A) Rab7Q67L recruits FYCO11,038–1,233 and FYCO11,091–1,233 but not FYCO11,156–1,233 to the cytosolic vesicles. HeLa cells transfected with GFP-FYCO11,038–1,233 (top), GFP-FYCO11,091–1,233 (bottom), or GFP-FYCO11,156–1,233 (middle right) with or without mCherry-Rab7Q67L were imaged 24 h after transfection. The graph shows the relative number of cells ± SD with GFP-FYCO11,038–1,233 recruited to intracellular membranes without and with cotransfected mCherry-Rab7Q67L. (B) Rab7Q67L recruits the 2xFYVEFYCO1 construct containing a short CC region in front of the first FYVE domain (FYCO11,091–1,233+1,156–1,233) but not a 2xFYVE alone to the perinuclear vesicles. HeLa cells transfected with GFP-FYCO11,091–1,233+1,156–1,233 or GFP-FYCO11,156–1,233+1,156–1,233 with or without mCherry-Rab7Q67L were imaged 24 h after transfection. (C) Rab7 coimmunoprecipitates with FYCO1 from HEK293 cell lysate. HEK293 cells stably transfected with 3xFlag-FYCO1 were cotransfected with GTP-locked mutants of Rab5, -7, -11, and -24 and lysed 24 h after transfection, and protein complexes were immunoprecipitated with anti–Flag M2 agarose affinity gel. Bound proteins were eluted with Flag peptide, resolved by SDS-PAGE, and visualized by immunoblotting with anti-GFP and anti-Flag antibody. IP, immunoprecipitation; WB, Western blot. (D) Leucine-1151 and tryptophan-1152 are important for the recruitment of FYCO1 to Rab7-containing vesicles. HeLa cells transfected with GFP-FYCO1990–1,233L1151A/W1152A with or without mCherry-Rab7Q67L were imaged 24 h after transfection. (B and D) Insets show an enlarged field of interest. (E) RILP but not Rab7 or ORP1L competes with FYCO1 for recruitment to intracellular vesicles. (right) HeLa cells cotransfected with GFP-RILP together with mCherry-FYCO1 and stained with Draq5 were imaged 24 h after transfection. (left) Relative number of HeLa cells cotransfected with mCherry-FYCO1 and the indicated constructs, in which FYCO1 is recruited to the intracellular vesicles. Error bars represent SD. Bars, 10 µm.
Figure 8.
FYCO1 redistributes Rab7- and ORP1L-decorated vesicles to the MT plus end. (A) Overexpressed FYCO1 is enriched in the cell periphery, close to the MT plus end. HeLa cells were imaged 48 h after transfection with mCherry-FYCO1 and GFP-tubulin. (B) Peripheral enrichment of FYCO1 is dependent on intact MTs. HeLa cells were transfected with GFP-FYCO1 and cultured in normal medium (left) or treated with 5 µM colcemid (middle) or 5 µM latrunculin A (right) for 2 h. (C) FYCO1-decorated vesicles move along the MT tracks. HeLa cells transfected with mCherry-FYCO1 and GFP-tubulin were live imaged by confocal microscopy 48 h after transfection. Movements of FYCO1-decorated structures were tracked with ImageJ MTrackJ plug-in (National Institutes of Health) and presented as 8-min-long tracks in the overlay image. (D) Full-length FYCO1 but not the FYCO1 lacking aa 555–1,136 can redistribute Rab7 and ORP1L to the cell periphery. HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated constructs and stained with DRAQ5. (E) The region of FYCO1 between aa 675 and 771 is essential for the MT plus end translocation of FYCO1-decorated structures. HeLa cells were imaged 24 h after transfection with the indicated constructs. Bars: (A, B, D, and E) 10 µm; (C) 5 µm.
Figure 9.
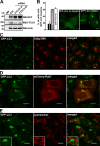
Depletion of FYCO1 leads to the accumulation of perinuclear clusters of autophagosomes. (A) Western blot (WB) of cell lysates from HeLa cells stably expressing GFP-LC3 48 h after transient transfection with siRNA against FYCO1 (siRNAs: A, Applied Biosystems; D, Thermo Fisher Scientific). MM, molecular mass. (B) Representative images of HeLa cells with or without the perinuclear clusters of GFP-LC3–positive vesicles (right) and quantification of the number of cells with this phenotype 48 h after transient transfection with siRNAs against FYCO1 (left). Error bars represent SDs based on three independent experiments. (C, D, and E) The perinuclear clusters of GFP-LC3–positive vesicles colocalize with mCherry-Rab7 but not with Golgi protein marker 58K or LysoTracker red. GFP-LC3 HeLa cells were transiently transfected with siRNA against FYCO1 (Thermo Fisher Scientific) 48 h before imaging or cotransfected with mCherry-Rab7. Cells were either fixed and stained with anti-Golgi 58K antibody or incubated with 50 nM LysoTracker red for 1 h. Insets show an enlarged field of interest. Bars, 10 µm.
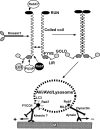
Figure 10.
Proposed model of FYCO1 function in the MT-dependent transport of autophagic vesicles.
Similar articles
- FYCO1: linking autophagosomes to microtubule plus end-directing molecular motors.
Pankiv S, Johansen T. Pankiv S, et al. Autophagy. 2010 May;6(4):550-2. doi: 10.4161/auto.6.4.11670. Epub 2010 May 16. Autophagy. 2010. PMID: 20364109 - FYCO1 Contains a C-terminally Extended, LC3A/B-preferring LC3-interacting Region (LIR) Motif Required for Efficient Maturation of Autophagosomes during Basal Autophagy.
Olsvik HL, Lamark T, Takagi K, Larsen KB, Evjen G, Øvervatn A, Mizushima T, Johansen T. Olsvik HL, et al. J Biol Chem. 2015 Dec 4;290(49):29361-74. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.686915. Epub 2015 Oct 14. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26468287 Free PMC article. - Structural basis of FYCO1 and MAP1LC3A interaction reveals a novel binding mode for Atg8-family proteins.
Cheng X, Wang Y, Gong Y, Li F, Guo Y, Hu S, Liu J, Pan L. Cheng X, et al. Autophagy. 2016 Aug 2;12(8):1330-9. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2016.1185590. Epub 2016 May 31. Autophagy. 2016. PMID: 27246247 Free PMC article. - Rab GTPases and microtubule motors.
Horgan CP, McCaffrey MW. Horgan CP, et al. Biochem Soc Trans. 2011 Oct;39(5):1202-6. doi: 10.1042/BST0391202. Biochem Soc Trans. 2011. PMID: 21936789 Review. - Molecular basis of canonical and bactericidal autophagy.
Noda T, Yoshimori T. Noda T, et al. Int Immunol. 2009 Nov;21(11):1199-204. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxp088. Epub 2009 Sep 7. Int Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19737785 Review.
Cited by
- Autophagosomes take the Klp98-A train.
Mauvezin C, Neufeld TP. Mauvezin C, et al. Small GTPases. 2017 Jan 2;8(1):16-19. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2016.1184776. Epub 2016 May 4. Small GTPases. 2017. PMID: 27142690 Free PMC article. - Transcriptome Profiling of Developing Murine Lens Through RNA Sequencing.
Khan SY, Hackett SF, Lee MC, Pourmand N, Talbot CC Jr, Riazuddin SA. Khan SY, et al. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015 Jul;56(8):4919-26. doi: 10.1167/iovs.14-16253. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015. PMID: 26225632 Free PMC article. - WDR91 specifies the endosomal retrieval subdomain for retromer-dependent recycling.
Liu N, Liu K, Yang C. Liu N, et al. J Cell Biol. 2022 Dec 5;221(12):e202203013. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202203013. Epub 2022 Oct 3. J Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 36190447 Free PMC article. - Mitochondria at the Crossroads of Cholestatic Liver Injury: Targeting Novel Therapeutic Avenues.
Li X, Ruan T, Wang S, Sun X, Liu C, Peng Y, Tao Y. Li X, et al. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2024 Sep 28;12(9):792-801. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2024.00087. Epub 2024 Jul 15. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 39280065 Free PMC article. Review. - Phosphoinositides differentially regulate protrudin localization through the FYVE domain.
Gil JE, Kim E, Kim IS, Ku B, Park WS, Oh BH, Ryu SH, Cho W, Heo WD. Gil JE, et al. J Biol Chem. 2012 Nov 30;287(49):41268-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.419127. Epub 2012 Oct 5. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23043110 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases