Genetic control over the resting brain - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2010 Jan 19;107(3):1223-8.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0909969107.
A M Winkler, P Kochunov, L Almasy, R Duggirala, M A Carless, J C Curran, R L Olvera, A R Laird, S M Smith, C F Beckmann, P T Fox, J Blangero
Affiliations
- PMID: 20133824
- PMCID: PMC2824276
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0909969107
Genetic control over the resting brain
D C Glahn et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010.
Abstract
The default-mode network, a coherent resting-state brain network, is thought to characterize basal neural activity. Aberrant default-mode connectivity has been reported in a host of neurological and psychiatric illnesses and in persons at genetic risk for such illnesses. Whereas the neurophysiologic mechanisms that regulate default-mode connectivity are unclear, there is growing evidence that genetic factors play a role. In this report, we estimate the importance of genetic effects on the default-mode network by examining covariation patterns in functional connectivity among 333 individuals from 29 randomly selected extended pedigrees. Heritability for default-mode functional connectivity was 0.424 +/- 0.17 (P = 0.0046). Although neuroanatomic variation in this network was also heritable, the genetic factors that influence default-mode functional connectivity and gray-matter density seem to be distinct, suggesting that unique genes influence the structure and function of the network. In contrast, significant genetic correlations between regions within the network provide evidence that the same genetic factors contribute to variation in functional connectivity throughout the default mode. Specifically, the left parahippocampal region was genetically correlated with all other network regions. In addition, the posterior cingulate/precuneus region, medial prefrontal cortex, and right cerebellum seem to form a subnetwork. Default-mode functional connectivity is influenced by genetic factors that cannot be attributed to anatomic variation or a single region within the network. By establishing the heritability of default-mode functional connectivity, this experiment provides the obligatory evidence required before these measures can be considered as endophenotypes for psychiatric or neurological illnesses or to identify genes influencing intrinsic brain function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
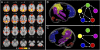
Fig. 1.
(A) Group-ICA map of the default-mode network derived from resting state scans of 333 individuals from large extended pedigrees. (B) Significant genetic correlations for functional connectivity between heritable regions in the default-mode network. The left parahippocampal gyrus (green) was genetically correlated with the posterior cingulate/precuneus (yellow), medial prefrontal (blue), right cerebellar (red), and right temporal-parietal (pink) regions. In addition, the posterior cingulate/precuneus, medial prefrontal, and right cerebellar regions form a circuit influenced by the same genetic factors. (C) Significant environmental correlations between these same regions.
Similar articles
- Establishing the resting state default mode network derived from functional magnetic resonance imaging tasks as an endophenotype: A twins study.
Korgaonkar MS, Ram K, Williams LM, Gatt JM, Grieve SM. Korgaonkar MS, et al. Hum Brain Mapp. 2014 Aug;35(8):3893-902. doi: 10.1002/hbm.22446. Epub 2014 Jan 22. Hum Brain Mapp. 2014. PMID: 24453120 Free PMC article. - The precuneus/posterior cingulate cortex plays a pivotal role in the default mode network: Evidence from a partial correlation network analysis.
Fransson P, Marrelec G. Fransson P, et al. Neuroimage. 2008 Sep 1;42(3):1178-84. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.05.059. Epub 2008 Jun 12. Neuroimage. 2008. PMID: 18598773 - Heritability of the Effective Connectivity in the Resting-State Default Mode Network.
Xu J, Yin X, Ge H, Han Y, Pang Z, Liu B, Liu S, Friston K. Xu J, et al. Cereb Cortex. 2017 Dec 1;27(12):5626-5634. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhw332. Cereb Cortex. 2017. PMID: 27913429 - Neuroimaging endophenotypes: strategies for finding genes influencing brain structure and function.
Glahn DC, Thompson PM, Blangero J. Glahn DC, et al. Hum Brain Mapp. 2007 Jun;28(6):488-501. doi: 10.1002/hbm.20401. Hum Brain Mapp. 2007. PMID: 17440953 Free PMC article. Review. - Chronic Fatigue in Cancer, Brain Connectivity and Reluctance to Engage in Physical Activity: A Mini-Review.
André N, Gastinger S, Rébillard A. André N, et al. Front Oncol. 2021 Dec 20;11:774347. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.774347. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34988017 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Molecular mechanisms underlying the neural correlates of working memory.
Xu X, Zhao H, Song Y, Cai H, Zhao W, Tang J, Zhu J, Yu Y. Xu X, et al. BMC Biol. 2024 Oct 21;22(1):238. doi: 10.1186/s12915-024-02039-0. BMC Biol. 2024. PMID: 39428484 Free PMC article. - Neurogenetics of Brain Connectivity: Current Approaches to the Study (Review).
Proshina EA, Deynekina TS, Martynova OV. Proshina EA, et al. Sovrem Tekhnologii Med. 2024;16(1):66-76. doi: 10.17691/stm2024.16.1.07. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Sovrem Tekhnologii Med. 2024. PMID: 39421629 Free PMC article. Review. - Heritability of movie-evoked brain activity and connectivity.
Gruskin DC, Vieira DJ, Lee JK, Patel GH. Gruskin DC, et al. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 16:2024.09.16.612469. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.16.612469. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39345386 Free PMC article. Preprint. - Heritability of functional gradients in the human subcortico-cortical connectivity.
Wu X, Zhang Y, Xue M, Li J, Li X, Cui Z, Gao JH, Yang G. Wu X, et al. Commun Biol. 2024 Jul 12;7(1):854. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06551-5. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 38997510 Free PMC article. - Shared genetics linking sociability with the brain's default mode network.
Fanelli G, Robinson J, Fabbri C, Bralten J, Roth Mota N, Arenella M, Sprooten E, Franke B, Kas M, Andlauer TF, Serretti A. Fanelli G, et al. medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 25:2024.05.24.24307883. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.24.24307883. medRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38826220 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
- Biswal B, Yetkin FZ, Haughton VM, Hyde JS. Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magn Reson Med. 1995;34:537–541. - PubMed
- Fox MD, Raichle ME. Spontaneous fluctuations in brain activity observed with functional magnetic resonance imaging. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8:700–711. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- MC_U120097117/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MH59490/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059490/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH059490/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH083824/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- EB006395/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- MH078111/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH0708143/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K01 EB006395/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- MH083824/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH078111/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH074457/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources