Childhood obesity, other cardiovascular risk factors, and premature death - PubMed (original) (raw)
Childhood obesity, other cardiovascular risk factors, and premature death
Paul W Franks et al. N Engl J Med. 2010.
Abstract
Background: The effect of childhood risk factors for cardiovascular disease on adult mortality is poorly understood.
Methods: In a cohort of 4857 American Indian children without diabetes (mean age, 11.3 years; 12,659 examinations) who were born between 1945 and 1984, we assessed whether body-mass index (BMI), glucose tolerance, and blood pressure and cholesterol levels predicted premature death. Risk factors were standardized according to sex and age. Proportional-hazards models were used to assess whether each risk factor was associated with time to death occurring before 55 years of age. Models were adjusted for baseline age, sex, birth cohort, and Pima or Tohono O'odham Indian heritage.
Results: There were 166 deaths from endogenous causes (3.4% of the cohort) during a median follow-up period of 23.9 years. Rates of death from endogenous causes among children in the highest quartile of BMI were more than double those among children in the lowest BMI quartile (incidence-rate ratio, 2.30; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.46 to 3.62). Rates of death from endogenous causes among children in the highest quartile of glucose intolerance were 73% higher than those among children in the lowest quartile (incidence-rate ratio, 1.73; 95% CI, 1.09 to 2.74). No significant associations were seen between rates of death from endogenous or external causes and childhood cholesterol levels or systolic or diastolic blood-pressure levels on a continuous scale, although childhood hypertension was significantly associated with premature death from endogenous causes (incidence-rate ratio, 1.57; 95% CI, 1.10 to 2.24).
Conclusions: Obesity, glucose intolerance, and hypertension in childhood were strongly associated with increased rates of premature death from endogenous causes in this population. In contrast, childhood hypercholesterolemia was not a major predictor of premature death from endogenous causes.
2010 Massachusetts Medical Society
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
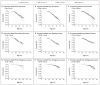
Figure 1. Kaplan–Meier Curves for Premature Death
The graphs show the rates of premature death from all causes, external causes, and endogenous causes according to quartiles of age-standardized and sex-standardized body-mass index at different baseline ages during childhood and adolescence. Plots were computed with the use of baseline data. Age at baseline for each age group was taken as the midpoint of the age range.
Comment in
- Are children the future of type 2 diabetes prevention?
Gregg EW. Gregg EW. N Engl J Med. 2010 Feb 11;362(6):548-50. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe0912192. N Engl J Med. 2010. PMID: 20147721 No abstract available. - Childhood obesity, other cardiovascular risk factors, and premature death.
Russell M, Trevisan M, Stranges S. Russell M, et al. N Engl J Med. 2010 May 13;362(19):1840; author reply 1841-2. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1002801. N Engl J Med. 2010. PMID: 20463345 No abstract available. - Childhood obesity, other cardiovascular risk factors, and premature death.
Plagemann A, Harder T, Dudenhausen JW. Plagemann A, et al. N Engl J Med. 2010 May 13;362(19):1840-1; author reply 1841-2. N Engl J Med. 2010. PMID: 20468084 No abstract available. - Childhood obesity, other cardiovascular risk factors, and premature death.
De Filippo G, Rendina D, Strazzullo P. De Filippo G, et al. N Engl J Med. 2010 May 13;362(19):1841; author reply 1841-2. N Engl J Med. 2010. PMID: 20468085 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Childhood obesity, other cardiovascular risk factors, and premature death.
De Filippo G, Rendina D, Strazzullo P. De Filippo G, et al. N Engl J Med. 2010 May 13;362(19):1841; author reply 1841-2. N Engl J Med. 2010. PMID: 20468085 No abstract available. - Effect of hypertension on mortality in Pima Indians.
Sievers ML, Bennett PH, Roumain J, Nelson RG. Sievers ML, et al. Circulation. 1999 Jul 6;100(1):33-40. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.100.1.33. Circulation. 1999. PMID: 10393678 - Metabolic Risk Factors and Type 2 Diabetes Incidence in American Indian Children.
Wheelock KM, Sinha M, Knowler WC, Nelson RG, Fufaa GD, Hanson RL. Wheelock KM, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Apr;101(4):1437-44. doi: 10.1210/jc.2015-4309. Epub 2016 Feb 25. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 26913636 Free PMC article. - Reverse Epidemiology of Traditional Cardiovascular Risk Factors in the Geriatric Population.
Ahmadi SF, Streja E, Zahmatkesh G, Streja D, Kashyap M, Moradi H, Molnar MZ, Reddy U, Amin AN, Kovesdy CP, Kalantar-Zadeh K. Ahmadi SF, et al. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2015 Nov 1;16(11):933-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2015.07.014. Epub 2015 Sep 9. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2015. PMID: 26363864 Free PMC article. Review. - Essential hypertension in children, a growing worldwide problem.
Sabri M, Gheissari A, Mansourian M, Mohammadifard N, Sarrafzadegan N. Sabri M, et al. J Res Med Sci. 2019 Dec 23;24:109. doi: 10.4103/jrms.JRMS_641_19. eCollection 2019. J Res Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31949460 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Individuation of a cut-off value of triglyceride-glucose index for incident diabetes mellitus in patients with essential hypertension.
Perticone M, Shehaj E, Suraci E, Andreozzi F, Perticone F. Perticone M, et al. Intern Emerg Med. 2024 Nov 1. doi: 10.1007/s11739-024-03803-4. Online ahead of print. Intern Emerg Med. 2024. PMID: 39485603 - Impact of Weight Status on Hemodynamic Parameters and Aerobic Fitness in School-Aged Children: A Study in a Rural School Community.
Lukhele NP, Millard L, Breukelman GJ. Lukhele NP, et al. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024 Oct 10;21(10):1340. doi: 10.3390/ijerph21101340. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39457313 Free PMC article. - Obesity and Left Ventricular Function in American Indian Adolescents: Strong Heart Family Study.
Burns J, Lopez KN, Stephens SB, Deen JF. Burns J, et al. J Racial Ethn Health Disparities. 2024 Oct 18. doi: 10.1007/s40615-024-02216-5. Online ahead of print. J Racial Ethn Health Disparities. 2024. PMID: 39422831 - The association of plasma asprosin with anthropometric and metabolic parameters in Korean children and adolescents.
Kim SH, Kim SE, Chun YH. Kim SH, et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Oct 3;15:1452277. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1452277. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39421535 Free PMC article. - Cardiometabolic risk in children and adolescents with obesity: a position paper of the Italian Society for Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetology.
Valerio G, Di Bonito P, Calcaterra V, Cherubini V, Corica D, De Sanctis L, Di Sessa A, Faienza MF, Fornari E, Iughetti L, Licenziati MR, Manco M, Del Giudice EM, Morandi A, Salerno M, Street ME, Umano GR, Wasniewska M, Maffeis C. Valerio G, et al. Ital J Pediatr. 2024 Oct 8;50(1):205. doi: 10.1186/s13052-024-01767-x. Ital J Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39380079 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Olshansky SJ, Passaro DJ, Hershow RC, et al. A potential decline in life expectancy in the United States in the 21st century. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1138–45. - PubMed
- Pavkov ME, Bennett PH, Knowler WC, Krakoff J, Sievers ML, Nelson RG. Effect of youth-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus on incidence of end-stage renal disease and mortality in young and middle-aged Pima Indians. JAMA. 2006;296:421–6. - PubMed
- Fagot-Campagna A, Saaddine JB, Flegal KM, Beckles GL. Diabetes, impaired fasting glucose, and elevated HbA1c in U.S. adolescents: the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diabetes Care. 2001;24:834–7. - PubMed
- Andersen LB, Harro M, Sardinha LB, et al. Physical activity and clustered cardiovascular risk in children: a cross-sectional study (The European Youth Heart Study) Lancet. 2006;368:299–304. - PubMed
- Lakka HM, Laaksonen DE, Lakka TA, et al. The metabolic syndrome and total and cardiovascular disease mortality in middle-aged men. JAMA. 2002;288:2709–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical