A phase II trial of erlotinib in patients with recurrent malignant gliomas and nonprogressive glioblastoma multiforme postradiation therapy - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical Trial
doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nop015. Epub 2009 Dec 14.
Lauren E Abrey, Andrew B Lassman, Susan M Chang, Kathleen R Lamborn, John G Kuhn, W K Alfred Yung, Mark R Gilbert, Kenneth A Aldape, Patrick Y Wen, Howard A Fine, Minesh Mehta, Lisa M Deangelis, Frank Lieberman, Timothy F Cloughesy, H Ian Robins, Janet Dancey, Michael D Prados; North American Brain Tumor Consortium
Affiliations
- PMID: 20150372
- PMCID: PMC2940554
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nop015
Clinical Trial
A phase II trial of erlotinib in patients with recurrent malignant gliomas and nonprogressive glioblastoma multiforme postradiation therapy
Jeffrey J Raizer et al. Neuro Oncol. 2010 Jan.
Abstract
Patients with (a) recurrent malignant glioma (MG): glioblastoma (GBM) or recurrent anaplastic glioma (AG), and (b) nonprogressive (NP) GBM following radiation therapy (RT) were eligible. Primary objective for recurrent MG was progression-free survival at 6 months (PFS-6) and overall survival at 12 months for NP GBM post-RT. Secondary objectives for recurrent MGs were response, survival, assessment of toxicity, and pharmacokinetics (PKs). Treatment with enzyme-inducing antiepileptic drugs was not allowed. Patients received 150 mg/day erlotinib. Patients requiring surgery were treated 7 days prior to tumor removal for PK analysis and effects of erlotinib on epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and intracellular signaling pathways. Ninety-six patients were evaluable (53 recurrent MG and 43 NP GBM); 5 patients were not evaluable for response. PFS-6 in recurrent GBM was 3% with a median PFS of 2 months; PFS-6 in recurrent AG was 27% with a median PFS of 2 months. Twelve-month survival was 57% in NP GBMs post-RT. Primary toxicity was dermatologic. The tissue-to-plasma ratio normalized to nanograms per gram dry weight for erlotinib and OSI-420 ranged from 25% to 44% and 30% to 59%, respectively, for pretreated surgical patients. No effect on EGFR or intratumoral signaling was seen. Patients with NP GBM post-RT who developed rash in cycle 1 had improved survival (P < .001). Single-agent activity of erlotinib is minimal for recurrent MGs and marginally beneficial following RT for NP GBM patients. Development of rash in cycle 1 correlates with survival in patients with NP GBM after RT.
Figures
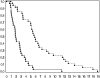
Fig. 1.
Kaplan–Meier curves for recurrent GBMs for OS (upper curve) and PFS (lower curve).
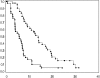
Fig. 2.
Kaplan–Meier curves for recurrent AGs for OS (upper curve) and PFS (lower curve).
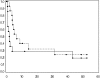
Fig. 3.
Kaplan–Meier curves NP GBMs post-RT for OS (upper curve) and PFS (lower curve).
Similar articles
- A phase I trial of erlotinib in patients with nonprogressive glioblastoma multiforme postradiation therapy, and recurrent malignant gliomas and meningiomas.
Raizer JJ, Abrey LE, Lassman AB, Chang SM, Lamborn KR, Kuhn JG, Yung WK, Gilbert MR, Aldape KD, Wen PY, Fine HA, Mehta M, Deangelis LM, Lieberman F, Cloughesy TF, Robins HI, Dancey J, Prados MD; North American Brain Tumor Consortium. Raizer JJ, et al. Neuro Oncol. 2010 Jan;12(1):87-94. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nop017. Epub 2009 Dec 14. Neuro Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20150371 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Phase II trial of bevacizumab and erlotinib in patients with recurrent malignant glioma.
Sathornsumetee S, Desjardins A, Vredenburgh JJ, McLendon RE, Marcello J, Herndon JE, Mathe A, Hamilton M, Rich JN, Norfleet JA, Gururangan S, Friedman HS, Reardon DA. Sathornsumetee S, et al. Neuro Oncol. 2010 Dec;12(12):1300-10. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noq099. Epub 2010 Aug 17. Neuro Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20716591 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - A phase I/II trial of vandetanib for patients with recurrent malignant glioma.
Kreisl TN, McNeill KA, Sul J, Iwamoto FM, Shih J, Fine HA. Kreisl TN, et al. Neuro Oncol. 2012 Dec;14(12):1519-26. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nos265. Epub 2012 Oct 25. Neuro Oncol. 2012. PMID: 23099652 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Randomized phase II trial of erlotinib versus temozolomide or carmustine in recurrent glioblastoma: EORTC brain tumor group study 26034.
van den Bent MJ, Brandes AA, Rampling R, Kouwenhoven MC, Kros JM, Carpentier AF, Clement PM, Frenay M, Campone M, Baurain JF, Armand JP, Taphoorn MJ, Tosoni A, Kletzl H, Klughammer B, Lacombe D, Gorlia T. van den Bent MJ, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2009 Mar 10;27(8):1268-74. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.17.5984. Epub 2009 Feb 9. J Clin Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19204207 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - HER1/EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme.
Raizer JJ. Raizer JJ. J Neurooncol. 2005 Aug;74(1):77-86. doi: 10.1007/s11060-005-0603-7. J Neurooncol. 2005. PMID: 16078112 Review.
Cited by
- Clinical outcomes with erlotinib in patients with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation.
Mok TS, D'arcangelo M, Califano R. Mok TS, et al. Drugs. 2012 Jun 19;72 Suppl 1:3-10. doi: 10.2165/1163014-S0-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22712792 Review. - A Systematic Review of Glioblastoma-Targeted Therapies in Phases II, III, IV Clinical Trials.
Cruz Da Silva E, Mercier MC, Etienne-Selloum N, Dontenwill M, Choulier L. Cruz Da Silva E, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 9;13(8):1795. doi: 10.3390/cancers13081795. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33918704 Free PMC article. Review. - Salvage Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy with or without Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy for Recurrent Glioblastoma Multiforme: A Single Institution Experience.
Hasan S, Chen E, Lanciano R, Yang J, Hanlon A, Lamond J, Arrigo S, Ding W, Mikhail M, Ghaneie A, Brady L. Hasan S, et al. Front Oncol. 2015 May 15;5:106. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2015.00106. eCollection 2015. Front Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26029663 Free PMC article. - A New Systemic Disease Mouse Model for Glioblastoma Capable of Single-Tumour-Cell Detection.
Ware TMB, Luwor RB, Zhu HJ. Ware TMB, et al. Cells. 2024 Jan 19;13(2):192. doi: 10.3390/cells13020192. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38275817 Free PMC article. - Radiotherapy plus nimotuzumab or placebo in the treatment of high grade glioma patients: results from a randomized, double blind trial.
Solomón MT, Selva JC, Figueredo J, Vaquer J, Toledo C, Quintanal N, Salva S, Domíngez R, Alert J, Marinello JJ, Catalá M, Griego MG, Martell JA, Luaces PL, Ballesteros J, de-Castro N, Bach F, Crombet T. Solomón MT, et al. BMC Cancer. 2013 Jun 19;13:299. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-299. BMC Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23782513 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
- DeAngelis LM. Chemotherapy for brain tumors—a new beginning. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1036–1038. - PubMed
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:987–996. - PubMed
- Nagane M, Coufal F, Lin H, et al. A common mutant epidermal growth factor receptor confers enhanced tumorigenicity on human glioblastoma cells by increasing proliferation and reducing apoptosis. Cancer Res. 1996;56:5079–5086. - PubMed
- Rasheed BK, Wiltshire RN, Bigner SH, et al. Molecular pathogenesis of malignant gliomas. Curr Opin Oncol. 1999;11:162–167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000005/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR0865/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00079/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA62407-08/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA16672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5-U01CA62399-09/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00056/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR003186-190379/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- CA62422/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA62405/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA62399/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA62412/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA62399/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR003186/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA62421-08/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA62426/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous