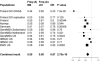Genome-wide association study in a high-risk isolate for multiple sclerosis reveals associated variants in STAT3 gene - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2010 Feb 12;86(2):285-91.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.01.017.
Virpi Leppä, Anna-Maija Sulonen, Teppo Varilo, Suvi Kallio, Anu Kemppinen, Shaun Purcell, Keijo Koivisto, Pentti Tienari, Marja-Liisa Sumelahti, Irina Elovaara, Tuula Pirttilä, Mauri Reunanen, Arpo Aromaa, Annette Bang Oturai, Helle Bach Søndergaard, Hanne F Harbo, Inger-Lise Mero, Stacey B Gabriel, Daniel B Mirel, Stephen L Hauser, Ludwig Kappos, Chris Polman, Philip L De Jager, David A Hafler, Mark J Daly, Aarno Palotie, Janna Saarela, Leena Peltonen
Affiliations
- PMID: 20159113
- PMCID: PMC2820168
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.01.017
Genome-wide association study in a high-risk isolate for multiple sclerosis reveals associated variants in STAT3 gene
Eveliina Jakkula et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2010.
Abstract
Genetic risk for multiple sclerosis (MS) is thought to involve both common and rare risk alleles. Recent GWAS and subsequent meta-analysis have established the critical role of the HLA locus and identified new common variants associated to MS. These variants have small odds ratios (ORs) and explain only a fraction of the genetic risk. To expose potentially rare, high-impact alleles, we conducted a GWAS of 68 distantly related cases and 136 controls from a high-risk internal isolate of Finland with increased prevalence and familial occurrence of MS. The top 27 loci with p < 10(-4) were tested in 711 cases and 1029 controls from Finland, and the top two findings were validated in 3859 cases and 9110 controls from more heterogeneous populations. SNP (rs744166) within the STAT3 gene was associated to MS (p = 2.75 x 10(-10), OR 0.87, confidence interval 0.83-0.91). The protective haplotype for MS in STAT3 is a risk allele for Crohn disease, implying that STAT3 represents a shared risk locus for at least two autoimmune diseases. This study also demonstrates the potential of special isolated populations in search for variants contributing to complex traits.
Copyright (c) 2010 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Figure 1
Population-Specific Association for the STAT3 rs744166 A Allele The rs744166 A allele that tags a putative MS protective haplotype associated to MS and shows consistent reduced risk in all studied populations with available genotypes. The results are presented here by study set. Each line represents one study set showing the name of the set, A allele frequencies for cases and controls, ORs, p value for association, and graphic illustration of the odds ratio (square, size relative to study set size) with the 95% confidence intervals for the odds ratio (thin lines).
Figure 2
Description of the Associated LD Region in STAT3 The associated SNP and haplotypes are in a 54 kb LD block covering the beginning and immediate 5′ region of the STAT3 gene. The associated rs744166 SNP is marked with a red arrow, and the other two SNPs, rs6503695 and rs957970, used in the haplotype analysis are marked with yellow arrows. The SNP marked with the blue arrow (rs2293152) was listed among the 100 top SNPs suggestively associated to MS in a previous meta-analysis.
Similar articles
- STAT3 locus in inflammatory bowel disease and multiple sclerosis susceptibility.
Cénit MC, Alcina A, Márquez A, Mendoza JL, Díaz-Rubio M, de las Heras V, Izquierdo G, Arroyo R, Fernández O, de la Concha EG, Matesanz F, Urcelay E. Cénit MC, et al. Genes Immun. 2010 Apr;11(3):264-8. doi: 10.1038/gene.2010.10. Epub 2010 Mar 4. Genes Immun. 2010. PMID: 20200543 - Use of a genetic isolate to identify rare disease variants: C7 on 5p associated with MS.
Kallio SP, Jakkula E, Purcell S, Suvela M, Koivisto K, Tienari PJ, Elovaara I, Pirttilä T, Reunanen M, Bronnikov D, Viander M, Meri S, Hillert J, Lundmark F, Harbo HF, Lorentzen AR, De Jager PL, Daly MJ, Hafler DA, Palotie A, Peltonen L, Saarela J. Kallio SP, et al. Hum Mol Genet. 2009 May 1;18(9):1670-83. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddp073. Epub 2009 Feb 16. Hum Mol Genet. 2009. PMID: 19221116 Free PMC article. - Independent replication of STAT3 association with multiple sclerosis risk in a large German case-control sample.
Lill CM, Schjeide BM, Akkad DA, Blaschke P, Winkelmann A, Gerdes LA, Hoffjan S, Luessi F, Dörner T, Li SC, Steinhagen-Thiessen E, Lindenberger U, Chan A, Hartung HP, Aktas O, Lohse P, Kümpfel T, Kubisch C, Epplen JT, Zettl UK, Bertram L, Zipp F. Lill CM, et al. Neurogenetics. 2012 Feb;13(1):83-6. doi: 10.1007/s10048-011-0305-6. Epub 2011 Nov 18. Neurogenetics. 2012. PMID: 22095036 - [The genetic profile of multiple sclerosis: risk genes and the "dark matter"].
Lill CM, Zipp F. Lill CM, et al. Nervenarzt. 2012 Jun;83(6):705-13. doi: 10.1007/s00115-011-3438-9. Nervenarzt. 2012. PMID: 22430841 Review. German. - Multiple sclerosis genetics.
Cree BA. Cree BA. Handb Clin Neurol. 2014;122:193-209. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-52001-2.00009-1. Handb Clin Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24507519 Review.
Cited by
- Multiple sclerosis.
Nylander A, Hafler DA. Nylander A, et al. J Clin Invest. 2012 Apr;122(4):1180-8. doi: 10.1172/JCI58649. Epub 2012 Apr 2. J Clin Invest. 2012. PMID: 22466660 Free PMC article. Review. - The Role of Genetic Factors in the Development of Acute Respiratory Viral Infection COVID-19: Predicting Severe Course and Outcomes.
Minashkin MM, Grigortsevich NY, Kamaeva AS, Barzanova VV, Traspov AA, Godkov MA, Ageev FA, Petrikov SS, Pozdnyakova NV. Minashkin MM, et al. Biomedicines. 2022 Feb 25;10(3):549. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10030549. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35327350 Free PMC article. - Roles of Fatty Acids in Microglial Polarization: Evidence from In Vitro and In Vivo Studies on Neurodegenerative Diseases.
Sanjay, Park M, Lee HJ. Sanjay, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 30;23(13):7300. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137300. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806302 Free PMC article. Review. - Genome-wide association study implicates NDST3 in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
Lencz T, Guha S, Liu C, Rosenfeld J, Mukherjee S, DeRosse P, John M, Cheng L, Zhang C, Badner JA, Ikeda M, Iwata N, Cichon S, Rietschel M, Nöthen MM, Cheng AT, Hodgkinson C, Yuan Q, Kane JM, Lee AT, Pisanté A, Gregersen PK, Pe'er I, Malhotra AK, Goldman D, Darvasi A. Lencz T, et al. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2739. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3739. Nat Commun. 2013. PMID: 24253340 Free PMC article. - Environmental Influencers, MicroRNA, and Multiple Sclerosis.
Mohammed EM. Mohammed EM. J Cent Nerv Syst Dis. 2020 Jan 20;12:1179573519894955. doi: 10.1177/1179573519894955. eCollection 2020. J Cent Nerv Syst Dis. 2020. PMID: 32009827 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Ebers G.C., Sadovnick A.D., Risch N.J., Canadian Collaborative Study Group A genetic basis for familial aggregation in multiple sclerosis. Nature. 1995;377:150–151. - PubMed
- Mumford C.J., Wood N.W., Kellar-Wood H., Thorpe J.W., Miller D.H., Compston D.A. The British Isles survey of multiple sclerosis in twins. Neurology. 1994;44:11–15. - PubMed
- Jersild C., Fog T. Histocompatibility (HL-A) antigens associated with multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol. Scand. Suppl. 1972;51:377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 MH071425/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 089061/Z/09/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 NS043559/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS 43559/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 RR020278/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous