5-Cyanotryptophan as an Infrared Probe of Local Hydration Status of Proteins - PubMed (original) (raw)
5-Cyanotryptophan as an Infrared Probe of Local Hydration Status of Proteins
Matthias M Waegele et al. Chem Phys Lett. 2009.
Abstract
The nitrile (C≡N) stretching vibration is sensitive to environment, making nitrile-derivatized amino acids an increasingly utilized tool to study various biological processes. Herein, we show that the bandwidth of the C≡N stretching vibration of 5-cyanotryptophan is particularly sensitive to water, rendering it an attractive infrared probe of local hydration status. We confirm the utility of this probe in biological applications by using it to examine how the hydration status of individual tryptophan sidechains of an antimicrobial peptide, indolicidin, changes upon peptide binding to model membranes. Furthermore, we show that p-cyanophenylalanine and 5-cyanotryptophan constitute a useful fluorescence energy transfer pair.
Figures
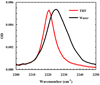
Figure 1
C≡N stretching bands of 5-cyanoindole in THF and a water/methanol mixture (95/5, v/v), as indicated.
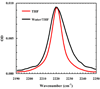
Figure 2
C≡N stretching bands of Fmoc-L-TrpCN in THF and a water/THF mixture (60/40, v/v), as indicated. The concentration of Fmoc-L-TrpCN was estimated to be ~3.3 mM based on weight, and the optical pathlength was about 130 µm. For easy comparison, the spectrum measured in water/THF mixture has been scaled by a factor of 1.3.
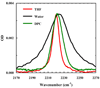
Figure 3
C≡N stretching bands of Trp9/TrpCN in THF, water, and DPC micelles, as indicated. The peptide concentration was ~2 mM in all solvents, except water where the concentration was not determined. For easy comparison, the spectra obtained in water and DPC micelles have been scaled, by a factor of 2.2 and 0.62, respectively.
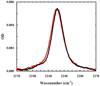
Figure 4
Comparison of the C≡N stretching bands of Trp11/TrpCN (red) and Trp9/TrpCN (blue) in DPC micelles. The Trp9/TrpCN data are identical to those used in Figure 3 and the Trp11/TrpCN spectrum was scaled by a factor of 1.3.
Figure 5
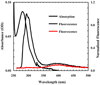
Absorption spectrum of Ac-TrpCN-NH2 in water (black), fluorescence spectrum of an equimolar (~20 µM) aqueous solution of PheCN and Ac-TrpCN-NH2 (blue), and fluorescence spectrum of PheCN-Ala-TrpCN-NH2 (red) in water (~16 µM). For fluorescence measurements, the excitation wavelength was 232 nm.
Similar articles
- Computational Modeling of the Nitrile Stretching Vibration of 5-Cyanoindole in Water.
Waegele MM, Gai F. Waegele MM, et al. J Phys Chem Lett. 2010 Feb 1;1(4):781-786. doi: 10.1021/jz900429z. J Phys Chem Lett. 2010. PMID: 20436926 Free PMC article. - C≡N stretching vibration of 5-cyanotryptophan as an infrared probe of protein local environment: what determines its frequency?
Zhang W, Markiewicz BN, Doerksen RS, Smith AB III, Gai F. Zhang W, et al. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2016 Mar 14;18(10):7027-34. doi: 10.1039/c5cp04413h. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2016. PMID: 26343769 Free PMC article. - Photoenhancement of the C≡N Stretching Vibration Intensity of Aromatic Nitriles.
Liu J, Feng RR, Zhou L, Gai F, Zhang W. Liu J, et al. J Phys Chem Lett. 2022 Oct 20;13(41):9745-9751. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.2c02418. Epub 2022 Oct 12. J Phys Chem Lett. 2022. PMID: 36222647 - Utility of 5-Cyanotryptophan Fluorescence as a Sensitive Probe of Protein Hydration.
Markiewicz BN, Mukherjee D, Troxler T, Gai F. Markiewicz BN, et al. J Phys Chem B. 2016 Feb 11;120(5):936-44. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.5b12233. Epub 2016 Jan 28. J Phys Chem B. 2016. PMID: 26783936 Free PMC article. - Using nitrile-derivatized amino acids as infrared probes of local environment.
Getahun Z, Huang CY, Wang T, De León B, DeGrado WF, Gai F. Getahun Z, et al. J Am Chem Soc. 2003 Jan 15;125(2):405-11. doi: 10.1021/ja0285262. J Am Chem Soc. 2003. PMID: 12517152
Cited by
- AMOEBA Force Field Predicts Accurate Hydrogen Bond Counts of Nitriles in SNase by Revealing Water-Protein Interaction in Vibrational Absorption Frequencies.
Lin YC, Ren P, Webb LJ. Lin YC, et al. J Phys Chem B. 2023 Jun 29;127(25):5609-5619. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.3c02060. Epub 2023 Jun 20. J Phys Chem B. 2023. PMID: 37339399 Free PMC article. - Quenching of _p_-Cyanophenylalanine Fluorescence by Various Anions.
Pazos IM, Roesch RM, Gai F. Pazos IM, et al. Chem Phys Lett. 2013 Mar 20;563:93-96. doi: 10.1016/j.cplett.2013.02.015. Chem Phys Lett. 2013. PMID: 23645934 Free PMC article. - Synthesis and Evaluation of the Sensitivity and Vibrational Lifetimes of Thiocyanate and Selenocyanate Infrared Reporters.
Levin DE, Schmitz AJ, Hines SM, Hines KJ, Tucker MJ, Brewer SH, Fenlon EE. Levin DE, et al. RSC Adv. 2016;43(6):36231-36237. doi: 10.1039/C5RA27363C. Epub 2016 Apr 12. RSC Adv. 2016. PMID: 27114820 Free PMC article. - Nitrile Substituents at the Conjugated Dipyridophenazine Moiety as Infrared Redox Markers in Electrochemically Reduced Heteroleptic Ru(II) Polypyridyl Complexes.
Sumner E, Pižl M, McQuaid KT, Hartl F. Sumner E, et al. Inorg Chem. 2024 Feb 5;63(5):2460-2469. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.3c03484. Epub 2024 Jan 23. Inorg Chem. 2024. PMID: 38262043 Free PMC article. - Fermi resonance as a means to determine the hydrogen-bonding status of two infrared probes.
Rodgers JM, Abaskharon RM, Ding B, Chen J, Zhang W, Gai F. Rodgers JM, et al. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2017 Jun 21;19(24):16144-16150. doi: 10.1039/c7cp02442h. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2017. PMID: 28604875 Free PMC article.
References
- Reimers JR, Hall LE. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999;121:3730.
- Andrews SS, Boxer SG. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2000;104:11853.
- Getahun Z, Huang C-Y, Wang T, De Leon B, DeGrado WF, Gai F. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003;125:405. - PubMed
- Dalosto SD, Vanderkooi JM, Sharp KA. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2004;108:6450. - PubMed
- Kurochkin DV, Naraharisetty SRG, Rubtsov IV. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2005;109:10799. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources