Amine Terminated SAMs: Investigating Why Oxygen is Present in these Films - PubMed (original) (raw)
Amine Terminated SAMs: Investigating Why Oxygen is Present in these Films
J E Baio et al. J Electron Spectros Relat Phenomena. 2009.
Abstract
Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) on gold prepared from amine-terminated alkanethiols have long been employed as model positively charged surfaces. Yet in previous studies significant amounts of unexpected oxygen containing species are always detected in amine terminated SAMs. Thus, the goal of this investigation was to determine the source of these oxygen species and minimize their presence in the SAM. The surface composition, structure, and order of amine-terminated SAMs on Au were characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectroscopy (ToF-SIMS), sum frequency generation (SFG) and near edge X-ray absorption fine structure (NEXAFS) spectroscopy. XPS determined compositions of amine-terminated SAMs in the current study exhibited oxygen concentrations of 2.4 ± 0.4 atomic %, a substantially lower amount of oxygen than reported in previously published studies. High-resolution XPS results from the S(2p), C(1s) and N(1s) regions did not detect any oxidized species. Angle-resolved XPS indicated that the small amount of oxygen detected was located at or near the amine head group. Small amounts of oxidized nitrogen, carbon and sulfur secondary ions, as well as ions attributed to water, were detected in the ToF-SIMS data due to the higher sensitivity of ToF-SIMS. The lack of N-O, S-O, and C-O stretches in the SFG spectra are consistent with the XPS and ToF-SIMS results and together show that oxidation of the amine-terminated thiols alone can only account for, at most, a small fraction of the oxygen detected by XPS. Both the SFG and angle-dependent NEXAFS indicated the presence of gauche defects in the amine SAMs. However, the SFG spectral features near 2865 cm(-1), assigned to the stretch of the methylene group next to the terminal amine unit, demonstrate the SAM is reasonably ordered. The SFG results also show another broad feature near 3200 cm(-1) related to hydrogen-bonded water. From this multi-technique investigation it is clear that the majority of the oxygen detected within these amine-terminated SAMs arises from the presence of oxygen containing adsorbates such as tightly bound water.
Figures
Figure 1
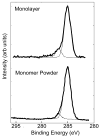
High-resolution XPS C1s spectra of the Cl−NH3+(CH2)11SH powder (bottom) and the NH2-SAM on Au (top). In both cases the spectra have peaks at 285eV (CHx) and 286.6eV (C-N/C-O).
Figure 2
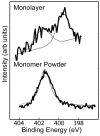
High-resolution XPS N1s spectra of the Cl−NH3+(CH2)11SH powder (bottom) and the NH2-SAM on Au (top). The powder spectrum has a single peak at 401.4eV (protonated amine). The NH2-SAM on Au spectrum has peaks at 399.5eV (C-N) and 401.4 eV (protonated amine).
Figure 3
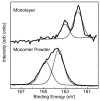
High-resolution XPS S2p spectra of the Cl−NH3+(CH2)11SH powder (bottom) and the NH2-SAM on Au (top). Each spectrum was fit using one S2p doublet with a splitting of 1.2eV.
Figure 4
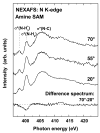
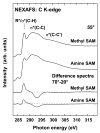
NEXAFS spectra of the nitrogen _K_-edge for amine SAMs acquired at angles of 70°, 55° and 20° along with the 70 and the 20° difference spectrum.
Figure 5
NEXAFS spectra of the carbon _K_-edge for the NH2- and CH3-terminated SAMs acquired at 55° along with their respective difference spectra (70°-20°).
Figure 6
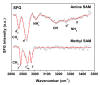
SFG spectrum of NH2- (upper trace) and CH3-terminated (lower trace) SAMs on gold. Solid lines are best fits based on equation 1.
Similar articles
- Multi-technique Characterization of Self-assembled Carboxylic Acid Terminated Alkanethiol Monolayers on Nanoparticle and Flat Gold Surfaces.
Techane SD, Gamble LJ, Castner DG. Techane SD, et al. J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2011 Apr 21;115(19):9432-9441. doi: 10.1021/jp201213g. J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2011. PMID: 21603069 Free PMC article. - Ambient-ageing processes in amine self-assembled monolayers on microarray slides as studied by ToF-SIMS with principal component analysis, XPS, and NEXAFS spectroscopy.
Min H, Girard-Lauriault PL, Gross T, Lippitz A, Dietrich P, Unger WE. Min H, et al. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012 Apr;403(2):613-23. doi: 10.1007/s00216-012-5862-5. Epub 2012 Mar 4. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012. PMID: 22392374 - Probing the orientation of electrostatically immobilized Protein G B1 by time-of-flight secondary ion spectrometry, sum frequency generation, and near-edge X-ray adsorption fine structure spectroscopy.
Baio JE, Weidner T, Baugh L, Gamble LJ, Stayton PS, Castner DG. Baio JE, et al. Langmuir. 2012 Jan 31;28(4):2107-12. doi: 10.1021/la203907t. Epub 2011 Dec 22. Langmuir. 2012. PMID: 22148958 Free PMC article. - XPS, TOF-SIMS, NEXAFS, and SPR characterization of nitrilotriacetic acid-terminated self-assembled monolayers for controllable immobilization of proteins.
Cheng F, Gamble LJ, Castner DG. Cheng F, et al. Anal Chem. 2008 Apr 1;80(7):2564-73. doi: 10.1021/ac702380w. Epub 2008 Feb 27. Anal Chem. 2008. PMID: 18302347 Free PMC article. - XPS and ToF-SIMS investigation of alpha-helical and beta-strand peptide adsorption onto SAMs.
Apte JS, Collier G, Latour RA, Gamble LJ, Castner DG. Apte JS, et al. Langmuir. 2010 Mar 2;26(5):3423-32. doi: 10.1021/la902888y. Langmuir. 2010. PMID: 19891457 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Probing the orientation of electrostatically immobilized cytochrome C by time of flight secondary ion mass spectrometry and sum frequency generation spectroscopy.
Baio JE, Weidner T, Ramey D, Pruzinsky L, Castner DG. Baio JE, et al. Biointerphases. 2013 Dec;8(1):18. doi: 10.1186/1559-4106-8-18. Epub 2013 Jul 26. Biointerphases. 2013. PMID: 24706131 Free PMC article. - Assembly and structure of alpha-helical peptide films on hydrophobic fluorocarbon surfaces.
Weidner T, Samuel NT, McCrea K, Gamble LJ, Ward RS, Castner DG. Weidner T, et al. Biointerphases. 2010 Mar;5(1):9-16. doi: 10.1116/1.3317116. Biointerphases. 2010. PMID: 20408730 Free PMC article. - Polyvinylpyrrolidone-Coordinated Single-Site Platinum Catalyst Exhibits High Activity for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction.
Li C, Chen Z, Yi H, Cao Y, Du L, Hu Y, Kong F, Kramer Campen R, Gao Y, Du C, Yin G, Zhang IY, Tong Y. Li C, et al. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020 Sep 7;59(37):15902-15907. doi: 10.1002/anie.202005282. Epub 2020 Jun 29. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020. PMID: 32436325 Free PMC article. - Multi-technique Characterization of Self-assembled Carboxylic Acid Terminated Alkanethiol Monolayers on Nanoparticle and Flat Gold Surfaces.
Techane SD, Gamble LJ, Castner DG. Techane SD, et al. J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2011 Apr 21;115(19):9432-9441. doi: 10.1021/jp201213g. J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2011. PMID: 21603069 Free PMC article. - Influence of polymerisation on the reversibility of low-energy proton exchange reactions by Para-Aminothiolphenol.
Balakrishnan D, Lamblin G, Thomann JS, Guillot J, Duday D, van den Berg A, Olthuis W, Pascual-García C. Balakrishnan D, et al. Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 13;7(1):15401. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13589-5. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29133808 Free PMC article.
References
- Bain CD, Evall J, Whitesides GM. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 1989;111:7155–7164.
- Ostuni E, Yan L, Whitesides GM. Colloids and Surfaces B-Biointerfaces. 1999;15:3–30.
- Wink T, vanZuilen SJ, Bult A, vanBennekom WP. Analyst. 1997;122:R43–R50. - PubMed
- Wang H, Castner DG, Ratner BD, Jiang SY. Langmuir. 2004;20:1877–1887. - PubMed
- Chuang WH, Lin JC. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A. 2007;82A:820–830. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- R01 EB006163/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P41 EB002027-24/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM074511-04/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB006163-03/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM074511/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P41 EB002027/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous