Genomic gems: SINE RNAs regulate mRNA production - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Genomic gems: SINE RNAs regulate mRNA production
Steven L Ponicsan et al. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2010 Apr.
Abstract
Mammalian short interspersed elements (SINEs) are abundant retrotransposons that have long been considered junk DNA; however, RNAs transcribed from mouse B2 and human Alu SINEs have recently been found to control mRNA production at multiple levels. Upon cell stress B2 and Alu RNAs bind RNA polymerase II (Pol II) and repress transcription of some protein-encoding genes. Bi-directional transcription of a B2 SINE establishes a boundary that places the growth hormone locus in a permissive chromatin state during mouse development. Alu RNAs embedded in Pol II transcripts can promote evolution and proteome diversity through exonization via alternative splicing. Given the diverse means by which SINE encoded RNAs impact production of mRNAs, this genomic junk is proving to contain hidden gems.
2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
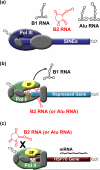
Figure 1
SINE RNAs control the heat shock response in mouse and human cells. A) Pol III transcribed SINE RNAs increase upon heat shock. B) During heat shock, mouse B2 RNA or human Alu RNA enters complexes at the promoters of repressed genes. TFIIF facilitates dissociation of B1 RNA from Pol II. C) Heat shock activated genes are resistant to repression by B2 RNA and Alu RNA.
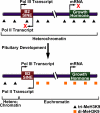
Figure 2
A B2 SINE serves as a boundary element to regulate transcription during pituitary development in mouse cells. Bidirectional transcription of a B2 SINE upstream of the growth hormone locus facilitates a change in chromatin structure from a repressive heterochromatic state to a permissive euchromatic state.
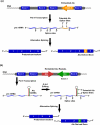
Figure 3
Alu RNA exonization promotes proteome diversity. A) Shown is an example in which embedded Alu RNA is exonized via alternative splicing into an mRNA. B) Alu RNA indirect repeats embedded in an mRNA can become double stranded and undergo A-to-I editing, resulting in Alu exonization.
Similar articles
- InvAluable junk: the cellular impact and function of Alu and B2 RNAs.
Walters RD, Kugel JF, Goodrich JA. Walters RD, et al. IUBMB Life. 2009 Aug;61(8):831-7. doi: 10.1002/iub.227. IUBMB Life. 2009. PMID: 19621349 Free PMC article. Review. - Transcriptome-wide effects of inverted SINEs on gene expression and their impact on RNA polymerase II activity.
Tajaddod M, Tanzer A, Licht K, Wolfinger MT, Badelt S, Huber F, Pusch O, Schopoff S, Janisiw M, Hofacker I, Jantsch MF. Tajaddod M, et al. Genome Biol. 2016 Oct 25;17(1):220. doi: 10.1186/s13059-016-1083-0. Genome Biol. 2016. PMID: 27782844 Free PMC article. - Human Alu RNA is a modular transacting repressor of mRNA transcription during heat shock.
Mariner PD, Walters RD, Espinoza CA, Drullinger LF, Wagner SD, Kugel JF, Goodrich JA. Mariner PD, et al. Mol Cell. 2008 Feb 29;29(4):499-509. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.12.013. Mol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18313387 - Alu mobile elements: from junk DNA to genomic gems.
Dridi S. Dridi S. Scientifica (Cairo). 2012;2012:545328. doi: 10.6064/2012/545328. Epub 2012 Dec 16. Scientifica (Cairo). 2012. PMID: 24278713 Free PMC article. Review. - Transposable B2 SINE elements can provide mobile RNA polymerase II promoters.
Ferrigno O, Virolle T, Djabari Z, Ortonne JP, White RJ, Aberdam D. Ferrigno O, et al. Nat Genet. 2001 May;28(1):77-81. doi: 10.1038/ng0501-77. Nat Genet. 2001. PMID: 11326281
Cited by
- General transcription factors and subunits of RNA polymerase III: Paralogs for promoter- and cell type-specific transcription in multicellular eukaryotes.
Teichmann M, Dieci G, Pascali C, Boldina G. Teichmann M, et al. Transcription. 2010 Nov;1(3):130-135. doi: 10.4161/trns.1.3.13192. Epub 2010 Jul 30. Transcription. 2010. PMID: 21326886 Free PMC article. - Evolutionary rate of human tissue-specific genes are related with transposable element insertions.
Jin P, Qin S, Chen X, Song Y, Li-Ling J, Xu X, Ma F. Jin P, et al. Genetica. 2012 Dec;140(10-12):513-23. doi: 10.1007/s10709-013-9700-2. Epub 2013 Jan 22. Genetica. 2012. PMID: 23337972 - Genomic relationship between SINE retrotransposons, Pol III-Pol II transcription, and chromatin organization: the journey from junk to jewel.
Lunyak VV, Atallah M. Lunyak VV, et al. Biochem Cell Biol. 2011 Oct;89(5):495-504. doi: 10.1139/o11-046. Epub 2011 Sep 14. Biochem Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21916613 Free PMC article. Review. - RUDI, a short interspersed element of the V-SINE superfamily widespread in molluscan genomes.
Luchetti A, Šatović E, Mantovani B, Plohl M. Luchetti A, et al. Mol Genet Genomics. 2016 Jun;291(3):1419-29. doi: 10.1007/s00438-016-1194-z. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Mol Genet Genomics. 2016. PMID: 26987730 - Mechanism of down-regulation of RNA polymerase III-transcribed non-coding RNA genes in macrophages by Leishmania.
Rana T, Misra S, Mittal MK, Farrow AL, Wilson KT, Linton MF, Fazio S, Willis IM, Chaudhuri G. Rana T, et al. J Biol Chem. 2011 Feb 25;286(8):6614-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.181735. Epub 2010 Dec 13. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21149457 Free PMC article.
References
- Thomas MC, Chiang CM. The general transcription machinery and general cofactors. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2006;41:105–178. - PubMed
- Kadonaga JT. Regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription by sequence-specific DNA binding factors. Cell. 2004;116:247–257. - PubMed
- Li B, Carey M, Workman JL. The role of chromatin during transcription. Cell. 2007;128:707–719. - PubMed
- Naar AM, Lemon BD, Tjian R. Transcriptional coactivator complexes. Annu Rev Biochem. 2001;70:475–501. - PubMed
- Moore MJ, Proudfoot NJ. Pre-mRNA processing reaches back to transcription and ahead to translation. Cell. 2009;136:688–700. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources