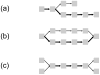Assembly algorithms for next-generation sequencing data - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Assembly algorithms for next-generation sequencing data
Jason R Miller et al. Genomics. 2010 Jun.
Abstract
The emergence of next-generation sequencing platforms led to resurgence of research in whole-genome shotgun assembly algorithms and software. DNA sequencing data from the Roche 454, Illumina/Solexa, and ABI SOLiD platforms typically present shorter read lengths, higher coverage, and different error profiles compared with Sanger sequencing data. Since 2005, several assembly software packages have been created or revised specifically for de novo assembly of next-generation sequencing data. This review summarizes and compares the published descriptions of packages named SSAKE, SHARCGS, VCAKE, Newbler, Celera Assembler, Euler, Velvet, ABySS, AllPaths, and SOAPdenovo. More generally, it compares the two standard methods known as the de Bruijn graph approach and the overlap/layout/consensus approach to assembly.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: None.
Figures
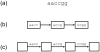
Figure 1
A read represented by K-mer graphs. (a) The read is represented by two types of K-mer graph with K=4. Larger values of K are used for real data. (b) The graph has a node for every K-mer in the read plus a directed edge for every pair of K-mers that overlap by K-1 bases in the read. (c) An equivalent graph has an edge for every K-mer in the read and the nodes implicitly represent overlaps of K-1 bases. In these examples, the paths are simple because the value K=4 is larger than the 2bp repeats in the read. The read sequence is easily reconstructed from the path in either graph.
Figure 2
A pair-wise overlap represented by a K-mer graph. (a) Two reads have an error-free overlap of 4 bases. (b) One K-mer graph, with K=4, represents both reads. The pair-wise alignment is a by-product of the graph construction. (c) The simple path through the graph implies a contig whose consensus sequence is easily reconstructed from the path.
Figure 3
Complexity in K-mer graphs can be diagnosed with read multiplicity information. In these graphs, edges represented in more reads are drawn with thicker arrows. (a) An errant base call toward the end of a read causes a “spur” or short dead-end branch. The same pattern could be induced by coincidence of zero coverage after polymorphism near a repeat. (b) An errant base call near a read middle causes a “bubble” or alternate path. Polymorphisms between donor chromosomes would be expected to induce a bubble with parity of read multiplicity on the divergent paths. (c) Repeat sequences lead to the “frayed rope” pattern of convergent and divergent paths.
Figure 4
Three methods to resolve graph complexity. (a) Read threading joins paths across collapsed repeats that are shorter than the read lengths. (b) Mate threading joins paths across collapsed repeats that are shorter than the paired-end distances. (c) Path following chooses one path if its length fits the paired-end constraint. Reads and mates are shown as patterned lines. Not all tangles can be resolved by reads and mates. The non-branching paths are illustrative; they could be simplified to single edges or nodes.
Similar articles
- Benchmarking of de novo assembly algorithms for Nanopore data reveals optimal performance of OLC approaches.
Cherukuri Y, Janga SC. Cherukuri Y, et al. BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 22;17 Suppl 7(Suppl 7):507. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2895-8. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27556636 Free PMC article. - Clover: a clustering-oriented de novo assembler for Illumina sequences.
Hsieh MF, Lu CL, Tang CY. Hsieh MF, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020 Nov 17;21(1):528. doi: 10.1186/s12859-020-03788-9. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 33203354 Free PMC article. - Comparative studies of de novo assembly tools for next-generation sequencing technologies.
Lin Y, Li J, Shen H, Zhang L, Papasian CJ, Deng HW. Lin Y, et al. Bioinformatics. 2011 Aug 1;27(15):2031-7. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr319. Epub 2011 Jun 2. Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 21636596 Free PMC article. - Comparison of the two major classes of assembly algorithms: overlap-layout-consensus and de-bruijn-graph.
Li Z, Chen Y, Mu D, Yuan J, Shi Y, Zhang H, Gan J, Li N, Hu X, Liu B, Yang B, Fan W. Li Z, et al. Brief Funct Genomics. 2012 Jan;11(1):25-37. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elr035. Epub 2011 Dec 19. Brief Funct Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22184334 Review. - Overview of Next-generation Sequencing Platforms Used in Published Draft Plant Genomes in Light of Genotypization of Immortelle Plant (Helichrysium Arenarium).
Hodzic J, Gurbeta L, Omanovic-Miklicanin E, Badnjevic A. Hodzic J, et al. Med Arch. 2017 Aug;71(4):288-292. doi: 10.5455/medarh.2017.71.288-292. Med Arch. 2017. PMID: 28974852 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Intraisolate mitochondrial genetic polymorphism and gene variants coexpression in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi.
Beaudet D, de la Providencia IE, Labridy M, Roy-Bolduc A, Daubois L, Hijri M. Beaudet D, et al. Genome Biol Evol. 2014 Dec 19;7(1):218-27. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evu275. Genome Biol Evol. 2014. PMID: 25527836 Free PMC article. - Genetic basis of a violation of Dollo's Law: re-evolution of rotating sex combs in Drosophila bipectinata.
Seher TD, Ng CS, Signor SA, Podlaha O, Barmina O, Kopp A. Seher TD, et al. Genetics. 2012 Dec;192(4):1465-75. doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.145524. Epub 2012 Oct 19. Genetics. 2012. PMID: 23086218 Free PMC article. - Assessment of metagenomic assembly using simulated next generation sequencing data.
Mende DR, Waller AS, Sunagawa S, Järvelin AI, Chan MM, Arumugam M, Raes J, Bork P. Mende DR, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31386. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031386. Epub 2012 Feb 23. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22384016 Free PMC article. - Complete genome and characteristics of cluster BC bacteriophage SoJo, isolated using Streptomyces mirabilis NRRL B-2400 in Columbia, MD.
Kumar SV, Schaffer N, Bharmal Z, Mood Q; 2022 UMBC Phage Hunters; Erill I, Caruso SM. Kumar SV, et al. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2024 Apr 11;13(4):e0006824. doi: 10.1128/mra.00068-24. Epub 2024 Feb 23. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2024. PMID: 38394246 Free PMC article. - DIME: a novel framework for de novo metagenomic sequence assembly.
Guo X, Yu N, Ding X, Wang J, Pan Y. Guo X, et al. J Comput Biol. 2015 Feb;22(2):159-77. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2014.0251. J Comput Biol. 2015. PMID: 25684202 Free PMC article.
References
- Sanger F, Coulson AR, Barrell BG, Smith AJ, Roe BA. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980;143:161–78. - PubMed
- Mardis ER. The impact of next-generation sequencing technology on genetics. Trends Genet. 2008;24:133–41. - PubMed
- Morozova O, Marra MA. Applications of next-generation sequencing technologies in functional genomics. Genomics. 2008;92:255–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources