What is flux balance analysis? - PubMed (original) (raw)
What is flux balance analysis?
Jeffrey D Orth et al. Nat Biotechnol. 2010 Mar.
Abstract
Flux balance analysis is a mathematical approach for analyzing the flow of metabolites through a metabolic network. This primer covers the theoretical basis of the approach, several practical examples and a software toolbox for performing the calculations.
Figures
Figure 1
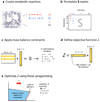
Formulation of an FBA problem.(a) First, a metabolic network reconstruction is built, consisting of a list of stoichiometrically balanced biochemical reactions. (b) Next, this reconstruction is converted into a mathematical model by forming a matrix (labeled S) in which each row represents a metabolite and each column represents a reaction. (c) At steady state, the flux through each reaction is given by the equation Sv = 0. Since there are more reactions than metabolites in large models, there is more than one possible solution to this equation. (d) An objective function is defined as Z = cTv, where c is a vector of weights (indicating how much each reaction contributes to the objective function). In practice, when only one reaction is desired for maximization or minimization, c is a vector of zeros with a one at the position of the reaction of interest. When simulating growth, the objective function will have a 1 at the position of the biomass reaction. (e) Finally, linear programming can be used to identify a particular flux distribution that maximizes or minimizes this objective function while observing the constraints imposed by the mass balance equations and reaction bounds.
Figure 2
The conceptual basis of constraint-based modeling and FBA. With no constraints, the flux distribution of a biological network may lie at any point in a solution space. When mass balance constraints imposed by the stoichiometric matrix S (1) and capacity constraints imposed by the lower and upper bounds (ai and bi) (2) are applied to a network, it defines an allowable solution space. The network may acquire any flux distribution within this space, but points outside this space are denied by the constraints. Through optimization of an objective function, FBA can identify a single optimal flux distribution that lies on the edge of the allowable solution space.
Similar articles
- Detecting the Significant Flux Backbone of Escherichia coli metabolism.
Güell O, Sagués F, Serrano MÁ. Güell O, et al. FEBS Lett. 2017 May;591(10):1437-1451. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12650. Epub 2017 May 2. FEBS Lett. 2017. PMID: 28391640 - Dynamic flux balance analysis for synthetic microbial communities.
Henson MA, Hanly TJ. Henson MA, et al. IET Syst Biol. 2014 Oct;8(5):214-29. doi: 10.1049/iet-syb.2013.0021. IET Syst Biol. 2014. PMID: 25257022 Free PMC article. Review. - Flux balance analysis accounting for metabolite dilution.
Benyamini T, Folger O, Ruppin E, Shlomi T. Benyamini T, et al. Genome Biol. 2010;11(4):R43. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-4-r43. Epub 2010 Apr 16. Genome Biol. 2010. PMID: 20398381 Free PMC article. - The biomass objective function.
Feist AM, Palsson BO. Feist AM, et al. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2010 Jun;13(3):344-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2010.03.003. Epub 2010 Apr 27. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20430689 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Genome-scale metabolic modelling when changes in environmental conditions affect biomass composition.
Schulz C, Kumelj T, Karlsen E, Almaas E. Schulz C, et al. PLoS Comput Biol. 2021 May 24;17(5):e1008528. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008528. eCollection 2021 May. PLoS Comput Biol. 2021. PMID: 34029317 Free PMC article. - Microalgal Metabolic Network Model Refinement through High-Throughput Functional Metabolic Profiling.
Chaiboonchoe A, Dohai BS, Cai H, Nelson DR, Jijakli K, Salehi-Ashtiani K. Chaiboonchoe A, et al. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2014 Dec 10;2:68. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2014.00068. eCollection 2014. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25540776 Free PMC article. - Kinetic Modeling of Hepatic Metabolism and Simulation of Treatment Effects.
Egners A, Cramer T, Wallach I, Berndt N. Egners A, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2769:211-225. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3694-7_16. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38315400 - MetaboTools: A Comprehensive Toolbox for Analysis of Genome-Scale Metabolic Models.
Aurich MK, Fleming RM, Thiele I. Aurich MK, et al. Front Physiol. 2016 Aug 3;7:327. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00327. eCollection 2016. Front Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27536246 Free PMC article. - Metabolic requirements for cancer cell proliferation.
Keibler MA, Wasylenko TM, Kelleher JK, Iliopoulos O, Vander Heiden MG, Stephanopoulos G. Keibler MA, et al. Cancer Metab. 2016 Aug 18;4:16. doi: 10.1186/s40170-016-0156-6. eCollection 2016. Cancer Metab. 2016. PMID: 27540483 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources