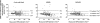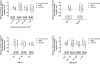Performance of the Cockcroft-Gault, MDRD, and new CKD-EPI formulas in relation to GFR, age, and body size - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Performance of the Cockcroft-Gault, MDRD, and new CKD-EPI formulas in relation to GFR, age, and body size
Wieneke Marleen Michels et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010 Jun.
Abstract
Background and objectives: We compared the estimations of Cockcroft-Gault, Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD), and Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equations to a gold standard GFR measurement using (125)I-iothalamate, within strata of GFR, gender, age, body weight, and body mass index (BMI).
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: For people who previously underwent a GFR measurement, bias, precision, and accuracies between measured and estimated kidney functions were calculated within strata of the variables. The relation between the absolute bias and the variables was tested with linear regression analysis.
Results: Overall (n = 271, 44% male, mean measured GFR 72.6 ml/min per 1.73 m(2) [SD 30.4 ml/min per 1.73 m(2)]), mean bias was smallest for MDRD (P < 0.01). CKD-EPI had highest accuracy (P < 0.01 compared with Cockcroft-Gault), which did not differ from MDRD (P = 0.14). The absolute bias of all formulas was related to age. For MDRD and CKD-EPI, absolute bias was also related to the GFR; for Cockcroft-Gault, it was related to body weight and BMI as well. In all extreme subgroups, MDRD and CKD-EPI provided highest accuracies.
Conclusions: The absolute bias of all formulas is influenced by age; CKD-EPI and MDRD are also influenced by GFR. Cockcroft-Gault is additionally influenced by body weight and BMI. In general, CKD-EPI gives the best estimation of GFR, although its accuracy is close to that of the MDRD.
Figures
Figure 1.
Bland-Altman figures of the estimated and measured kidney function. Bland-Altman plots—the difference between the estimated and measured renal function—is plotted against the measured GFR; therefore, a positive difference suggests an overestimation by the formula, whereas a negative difference suggests an underestimation. The dashed lines represent the mean difference between estimated and measured GFR; the solid lines represent the lines of agreement, calculated as mean difference plus or minus two times the SD of this difference.
Figure 2.
Comparison of the bias and precisions over subgroups. Mean bias and precision between estimated and measured GFR for to various strata of GFR, gender, age, and BMI. The mean bias was calculated as the mean of the differences between the estimated and measured GFR per subgroup, whereas the precision was the SD of this difference.
Comment in
- The CKD-EPI equation for estimating GFR from serum creatinine: real improvement or more of the same?
Rule AD. Rule AD. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010 Jun;5(6):951-3. doi: 10.2215/CJN.03110410. Epub 2010 May 6. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010. PMID: 20448068 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- CKD-EPI instead of MDRD for candidates to kidney donation.
Lujan PR, Chiurchiu C, Douthat W, de Arteaga J, de la Fuente J, Capra RH, Massari PU. Lujan PR, et al. Transplantation. 2012 Sep 27;94(6):637-41. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e3182603260. Transplantation. 2012. PMID: 22918217 - Predictive performance of the modification of diet in renal disease and Cockcroft-Gault equations for estimating renal function.
Froissart M, Rossert J, Jacquot C, Paillard M, Houillier P. Froissart M, et al. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005 Mar;16(3):763-73. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2004070549. Epub 2005 Jan 19. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005. PMID: 15659562 - [Assessment of the new CKD-EPI equation to estimate the glomerular filtration rate].
Montañés Bermúdez R, Bover Sanjuán J, Oliver Samper A, Ballarín Castán JA, Gràcia García S. Montañés Bermúdez R, et al. Nefrologia. 2010;30(2):185-94. doi: 10.3265/Nefrologia.pre2009.Dic.5838. Epub 2009 Dec 14. Nefrologia. 2010. PMID: 20038962 Spanish. - Use of estimated glomerular filtration rate for drug dosing in the chronic kidney disease patient.
Hudson JQ, Nyman HA. Hudson JQ, et al. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2011 Sep;20(5):482-91. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e328348c11f. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2011. PMID: 21709552 Review. - Evaluation of glomerular filtration rate and of albuminuria/proteinuria.
Cirillo M. Cirillo M. J Nephrol. 2010 Mar-Apr;23(2):125-32. J Nephrol. 2010. PMID: 20213606 Review.
Cited by
- Association between renal dysfunction and outcomes of lung cancer: A systematic review and meta‑analysis.
Qian H, Li S, Hu Z. Qian H, et al. Oncol Lett. 2024 Aug 28;28(5):514. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14648. eCollection 2024 Nov. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39247494 Free PMC article. - Advanced Oxidative Protein Products Had a Diagnostic Accuracy for Identifying Chronic Kidney Disease in Adult Population.
Villalpando-Sánchez DC, Barajas-Medina CA, Alvarez-Aguilar C, López-Ortiz G, Romero-Henríquez LF, Gómez-García A. Villalpando-Sánchez DC, et al. Metabolites. 2024 Jan 7;14(1):37. doi: 10.3390/metabo14010037. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 38248840 Free PMC article. - How to adjust drug doses in chronic kidney disease.
Stefani M, Singer RF, Roberts DM. Stefani M, et al. Aust Prescr. 2019 Oct;42(5):163-167. doi: 10.18773/austprescr.2019.054. Epub 2019 Oct 1. Aust Prescr. 2019. PMID: 31631931 Free PMC article. Review. - Should Cystatin C eGFR Become Routine Clinical Practice?
Spencer S, Desborough R, Bhandari S. Spencer S, et al. Biomolecules. 2023 Jul 5;13(7):1075. doi: 10.3390/biom13071075. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37509111 Free PMC article. Review. - Incidence and outcomes of acute kidney injury in octogenarians in Jordan.
Oweis AO, Alshelleh SA. Oweis AO, et al. BMC Res Notes. 2018 May 8;11(1):279. doi: 10.1186/s13104-018-3397-3. BMC Res Notes. 2018. PMID: 29739428 Free PMC article.
References
- Fawaz A, Badr KF: Measuring filtration function in clinical practice. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 15: 643–647, 2006 - PubMed
- Levey AS, Coresh J, Greene T, Stevens LA, Zhang YL, Hendriksen S, Kusek JW, Van Lente F: Using standardized serum creatinine values in the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease study equation for estimating glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med 145: 247–254, 2006 - PubMed
- Cockcroft DW, Gault MH: Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron 16: 31–41, 1976 - PubMed
- Boudville N, Salama M, Jeffrey GP, Ferrari P: The inaccuracy of cystatin C and creatinine-based equations in predicting GFR in orthotopic liver transplant recipients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24: 2926–2930, 2009 - PubMed
- Donadio C, Consani C, Ardini M, Caprio F, Grassi G, Lucchesi A: Prediction of glomerular filtration rate from body cell mass and plasma creatinine. Curr Drug Discov Technol 1: 221–228, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical