Damage to ventromedial prefrontal cortex impairs judgment of harmful intent - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Damage to ventromedial prefrontal cortex impairs judgment of harmful intent
Liane Young et al. Neuron. 2010.
Abstract
Moral judgments, whether delivered in ordinary experience or in the courtroom, depend on our ability to infer intentions. We forgive unintentional or accidental harms and condemn failed attempts to harm. Prior work demonstrates that patients with damage to the ventromedial prefrontal cortex (VMPC) deliver abnormal judgments in response to moral dilemmas and that these patients are especially impaired in triggering emotional responses to inferred or abstract events (e.g., intentions), as opposed to real or actual outcomes. We therefore predicted that VMPC patients would deliver abnormal moral judgments of harmful intentions in the absence of harmful outcomes, as in failed attempts to harm. This prediction was confirmed in the current study: VMPC patients judged attempted harms, including attempted murder, as more morally permissible relative to controls. These results highlight the critical role of the VMPC in processing harmful intent for moral judgment.
(c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
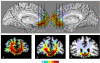
Figure 1
Lesion overlap of the 9 VMPC subjects using the MAP-3 technique. Top panel shows the left and right mesial views of the template brain. Panels 1,2,3 show three coronal sections through VMPC at the levels indicated in the top panel. The numbers of overlaps at each voxel is shown in the color bar.
Figure 2
Experimental design and stimuli. (top) The combination of intent (neutral vs. negative) and outcome (neutral vs. negative) factors yielded a 2×2 design with four conditions. (bottom) Full text of an example “failed attempt to harm” scenario. Bold sections indicate words that differed across conditions.
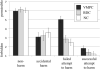
Figure 3
Moral judgments for all four conditions. Judgments are shown for each participant group, on 7-point scale. Error bars represent standard error of the mean. VMPC participants judged failed attempts to harm as significantly more permissible than the brain-damaged comparison (BDC) participants and the normal comparison (NC) participants (P values < 0.001).
Similar articles
- It is the outcome that counts! Damage to the ventromedial prefrontal cortex disrupts the integration of outcome and belief information for moral judgment.
Ciaramelli E, Braghittoni D, di Pellegrino G. Ciaramelli E, et al. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2012 Nov;18(6):962-71. doi: 10.1017/S1355617712000690. Epub 2012 Aug 29. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2012. PMID: 22929298 - When ignorance is no excuse: Different roles for intent across moral domains.
Young L, Saxe R. Young L, et al. Cognition. 2011 Aug;120(2):202-14. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2011.04.005. Epub 2011 May 23. Cognition. 2011. PMID: 21601839 Clinical Trial. - Harming kin to save strangers: further evidence for abnormally utilitarian moral judgments after ventromedial prefrontal damage.
Thomas BC, Croft KE, Tranel D. Thomas BC, et al. J Cogn Neurosci. 2011 Sep;23(9):2186-96. doi: 10.1162/jocn.2010.21591. Epub 2010 Oct 14. J Cogn Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 20946057 Free PMC article. - Investigating emotion in moral cognition: a review of evidence from functional neuroimaging and neuropsychology.
Young L, Koenigs M. Young L, et al. Br Med Bull. 2007;84:69-79. doi: 10.1093/bmb/ldm031. Epub 2007 Nov 20. Br Med Bull. 2007. PMID: 18029385 Review. - Social perception in moral judgments of interpersonal transgressions.
Adams GS, O'Connor KS, Belmi P. Adams GS, et al. Curr Opin Psychol. 2022 Apr;44:177-181. doi: 10.1016/j.copsyc.2021.09.006. Epub 2021 Sep 16. Curr Opin Psychol. 2022. PMID: 34688999 Review.
Cited by
- Damage to the ventromedial prefrontal cortex reduces interpersonal disgust.
Ciaramelli E, Sperotto RG, Mattioli F, di Pellegrino G. Ciaramelli E, et al. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2013 Feb;8(2):171-80. doi: 10.1093/scan/nss087. Epub 2012 Jul 25. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 22842816 Free PMC article. - Testosterone administration in females modulates moral judgment and patterns of brain activation and functional connectivity.
Chen C, Decety J, Huang PC, Chen CY, Cheng Y. Chen C, et al. Hum Brain Mapp. 2016 Oct;37(10):3417-30. doi: 10.1002/hbm.23249. Epub 2016 May 4. Hum Brain Mapp. 2016. PMID: 27145084 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Increased moral condemnation of accidental harm in institutionalized adolescents.
Baez S, Herrera E, García AM, Huepe D, Santamaría-García H, Ibáñez A. Baez S, et al. Sci Rep. 2018 Aug 2;8(1):11609. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29956-9. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30072749 Free PMC article. - Parsing the neural correlates of moral cognition: ALE meta-analysis on morality, theory of mind, and empathy.
Bzdok D, Schilbach L, Vogeley K, Schneider K, Laird AR, Langner R, Eickhoff SB. Bzdok D, et al. Brain Struct Funct. 2012 Oct;217(4):783-96. doi: 10.1007/s00429-012-0380-y. Epub 2012 Jan 24. Brain Struct Funct. 2012. PMID: 22270812 Free PMC article. - A Neurobehavioral Approach to Addiction: Implications for the Opioid Epidemic and the Psychology of Addiction.
Bechara A, Berridge KC, Bickel WK, Morón JA, Williams SB, Stein JS. Bechara A, et al. Psychol Sci Public Interest. 2019 Oct;20(2):96-127. doi: 10.1177/1529100619860513. Psychol Sci Public Interest. 2019. PMID: 31591935 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Anderson SW, Barrash J, Bechara A, Tranel D. Impairments of emotion and real-world complex behavior following childhood- or adult-onset damage to ventromedial prefrontal cortex. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2006;12:224–235. - PubMed
- Baird JA, Astington JW. The role of mental state understanding in the development of moral cognition and moral action. New Directions for Child and Adolescent Development. 2004;103:37–49. - PubMed
- Barrash J, Tranel D, Anderson S. Acquired personality disturbances associated with bilateral damage to the ventromedial prefrontal region. Developmental Neuropsychology. 2000;18:355–381. - PubMed
- Bechara A, Damasio AR. The somatic marker hypothesis: A neural theory of economic decision. Games and Economic Behavior. 2005;52:336–372.
- Bechara A, Damasio H, Damasio AR. Emotion, decision making and the orbitofrontal cortex. Cereb Cortex. 2000;10:295–307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources