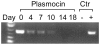Mycoplasma suppression of THP-1 Cell TLR responses is corrected with antibiotics - PubMed (original) (raw)
Mycoplasma suppression of THP-1 Cell TLR responses is corrected with antibiotics
Ekaterina Zakharova et al. PLoS One. 2010.
Abstract
Mycoplasma contamination of cultured cell lines is a serious problem in research, altering cellular response to different stimuli thus compromising experimental results. We found that chronic mycoplasma contamination of THP-1 cells suppresses responses of THP-1 cells to TLR stimuli. For example, E. coli LPS induced IL-1 beta was suppressed by 6 fold and IL-8 by 10 fold in mycoplasma positive THP-1 cells. Responses to live F. novicida challenge were suppressed by 50-fold and 40-fold respectively for IL-1beta and IL-8. Basal TLR4 expression level in THP-1 cells was decreased by mycoplasma by 2.4-fold (p = 0.0003). Importantly, cell responses to pathogen associated molecular patterns are completely restored by mycoplasma clearance with Plasmocin. Thus, routine screening of cell lines for mycoplasma is important for the maintenance of reliable experimental data and contaminated cell lines can be restored to their baseline function with antibiotic clearance of mycoplasma.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Figure 1. Plasmocin-dependent removal of mycoplasmal contamination of THP-1 cells.
THP-1 cells, chronically infected with mycoplasma, were treated with Plasmocin (25 µg/ml every 3 days) and aliquots were taken every three to four days for detection of mycoplasma by PCR. DNA from mycoplasma negative (−) and positive (+) cells was served as control (Ctr).
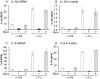
Figure 2. Chronic mycoplasma infection inhibits THP-1 cells response to PAMPs.
THP-1 cells, mycoplasma negative (−), positive (+) or treated with Plasmocin and confirmed to be a mycoplasma negative (P) were stimulated either with E. coli LPS or F. novicida (F.n.) for 15 hours in antibiotic-free media. Gene expression was measured in relative copy numbers (RCN) and cytokine concentration in ng/ml. Mycoplasma positive cells show decrease in expression of IL-1β message (A) and mature cytokine release (B), as well as IL-8 mRNA expression (C) and protein release (D). Mycoplasma removal restores cellular function to these PAMPs (P). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. n = 4 for qPCR of THP-1 treated with LPS and n = 8 for all other samples.
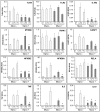
Figure 3. Gene expression in mycoplasma negative and positive THP-1 cells stimulated with LPS or F. novicida.
Mycoplasma negative (Myco −) and positive (Myco +) THP-1 cells were stimulated either with E. coli LPS or F. novicida (F.n.) for 15 hours in antibiotic-free media. Gene expression was measured in relative copy numbers (RCN). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. n = 6. Asterisk (*) represents a p value<0.05 in comparison between two groups, to show significance of mycoplasma contamination.
Similar articles
- Differential expression of immunoregulatory genes in monocytes in response to Porphyromonas gingivalis and Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide.
Barksby HE, Nile CJ, Jaedicke KM, Taylor JJ, Preshaw PM. Barksby HE, et al. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009 Jun;156(3):479-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2009.03920.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19438601 Free PMC article. - Detection and antibiotic treatment of Mycoplasma arginini contamination in a mouse epithelial cell line restore normal cell physiology.
Boslett B, Nag S, Resnick A. Boslett B, et al. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:532105. doi: 10.1155/2014/532105. Epub 2014 Mar 20. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24772428 Free PMC article. - Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) of Porphyromonas gingivalis induces IL-1beta, TNF-alpha and IL-6 production by THP-1 cells in a way different from that of Escherichia coli LPS.
Diya Zhang, Lili Chen, Shenglai Li, Zhiyuan Gu, Jie Yan. Diya Zhang, et al. Innate Immun. 2008 Apr;14(2):99-107. doi: 10.1177/1753425907088244. Innate Immun. 2008. PMID: 18713726 - Counteracting interactions between lipopolysaccharide molecules with differential activation of toll-like receptors.
Hajishengallis G, Martin M, Schifferle RE, Genco RJ. Hajishengallis G, et al. Infect Immun. 2002 Dec;70(12):6658-64. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.12.6658-6664.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 12438339 Free PMC article. - Overview of the Maintenance of Authentic Cancer Cell Lines.
Christian SL. Christian SL. Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2508:1-7. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2376-3_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35737228 Review.
Cited by
- Alpha 1-antitrypsin does not inhibit human monocyte caspase-1.
Rahman MA, Mitra S, Sarkar A, Wewers MD. Rahman MA, et al. PLoS One. 2015 Feb 6;10(2):e0117330. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117330. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25658455 Free PMC article. - Maternal microbe-specific modulation of inflammatory response in extremely low-gestational-age newborns.
Fichorova RN, Onderdonk AB, Yamamoto H, Delaney ML, DuBois AM, Allred E, Leviton A; Extremely Low Gestation Age Newborns (ELGAN) Study Investigators. Fichorova RN, et al. mBio. 2011 Jan 18;2(1):e00280-10. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00280-10. mBio. 2011. PMID: 21264056 Free PMC article. - Hyperthermia increases interleukin-6 in mouse skeletal muscle.
Welc SS, Phillips NA, Oca-Cossio J, Wallet SM, Chen DL, Clanton TL. Welc SS, et al. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012 Aug 15;303(4):C455-66. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00028.2012. Epub 2012 Jun 6. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22673618 Free PMC article. - Natural Mycoplasma Infection Reduces Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in Response to Ovine Footrot Pathogens.
Blanchard AM, Baumbach CM, Michler JK, Pickwell ND, Staley CE, Franklin JM, Wattegedera SR, Entrican G, Tötemeyer S. Blanchard AM, et al. Animals (Basel). 2022 Nov 22;12(23):3235. doi: 10.3390/ani12233235. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36496756 Free PMC article. - A human monocytic NF-κB fluorescent reporter cell line for detection of microbial contaminants in biological samples.
Battin C, Hennig A, Mayrhofer P, Kunert R, Zlabinger GJ, Steinberger P, Paster W. Battin C, et al. PLoS One. 2017 May 24;12(5):e0178220. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178220. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28542462 Free PMC article.
References
- Demczuk S, Baumberger C, Mach B, Dayer JM. Differential effects of in vitro mycoplasma infection on interleukin-1 alpha and beta mRNA expression in U937 and A431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:13039–13045. - PubMed
- Kopp EB, Medzhitov R. The Toll-receptor family and control of innate immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 1999;11:13–18. - PubMed
- Medzhitov R, Horng T. Transcriptional control of the inflammatory response. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9:692–703. - PubMed
- Seshadri S, Duncan MD, Hart JM, Gavrilin MA, Wewers MD. Pyrin levels in human monocytes and monocyte-derived macrophages regulate IL-1beta processing and release. J Immunol. 2007;179:1274–1281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL076278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5-U54-AI-057153/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL089440/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AI057153/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL076278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 - HL089440/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical