Evidence for polygenic susceptibility to multiple sclerosis--the shape of things to come - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Evidence for polygenic susceptibility to multiple sclerosis--the shape of things to come
International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Consortium (IMSGC) et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2010.
Abstract
It is well established that the risk of developing multiple sclerosis is substantially increased in the relatives of affected individuals and that most of this increase is genetically determined. The observed pattern of familial recurrence risk has long suggested that multiple variants are involved, but it has proven difficult to identify individual risk variants and little has been established about the genetic architecture underlying susceptibility. By using data from two independent genome-wide association studies (GWAS), we demonstrate that a substantial proportion of the thousands of variants that individually fail to show statistically significant evidence of association have allele frequencies in cases that are skewed away from the null distribution through the effects of multiple as-yet-unidentified risk loci. The collective effect of 12,627 SNPs with Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test (p < 0.2) in our discovery GWAS set optimally explains approximately 3% of the variance in MS risk in our independent target GWAS set, estimated by Nagelkerke's pseudo-R(2). This model has a highly significant fit (p = 9.90E-19). These results statistically demonstrate a polygenic component to MS susceptibility and suggest that the risk alleles identified to date represent just the tip of an iceberg of risk variants likely to include hundreds of modest effects and possibly thousands of very small effects.
(c) 2010 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
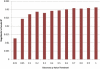
Figure 1
Nagelkerke's Pseudo-R2 for Each Scoring SNP Set Variance explained in the target set, measured by Nagelkerke's pseudo-R2, is shown for each of the seven scoring SNP sets as defined by arbitrary discovery GWAS p value thresholds.
Similar articles
- Genome-wide association study reveals greater polygenic loading for schizophrenia in cases with a family history of illness.
Bigdeli TB, Ripke S, Bacanu SA, Lee SH, Wray NR, Gejman PV, Rietschel M, Cichon S, St Clair D, Corvin A, Kirov G, McQuillin A, Gurling H, Rujescu D, Andreassen OA, Werge T, Blackwood DH, Pato CN, Pato MT, Malhotra AK, O'Donovan MC, Kendler KS, Fanous AH; Schizophrenia Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. Bigdeli TB, et al. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2016 Mar;171B(2):276-89. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32402. Epub 2015 Dec 11. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2016. PMID: 26663532 Free PMC article. - [Genome-wide association study as a method for genetic architecture analysis in polygenic diseases (by the example of multiple sclerosis)].
Favorova OO, Bashinskaia VV, Kulakova OG, Favorov AV, Boĭko AN. Favorova OO, et al. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2014 Jul-Aug;48(4):573-86. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2014. PMID: 25842843 Review. Russian. - Gene-Environment Interactions in Multiple Sclerosis: A UK Biobank Study.
Jacobs BM, Noyce AJ, Bestwick J, Belete D, Giovannoni G, Dobson R. Jacobs BM, et al. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2021 May 28;8(4):e1007. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000001007. Print 2021 Jul. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2021. PMID: 34049995 Free PMC article. - Estimating the proportion of variation in susceptibility to multiple sclerosis captured by common SNPs.
Watson CT, Disanto G, Breden F, Giovannoni G, Ramagopalan SV. Watson CT, et al. Sci Rep. 2012;2:770. doi: 10.1038/srep00770. Epub 2012 Oct 25. Sci Rep. 2012. PMID: 23105968 Free PMC article. - [The genetic profile of multiple sclerosis: risk genes and the "dark matter"].
Lill CM, Zipp F. Lill CM, et al. Nervenarzt. 2012 Jun;83(6):705-13. doi: 10.1007/s00115-011-3438-9. Nervenarzt. 2012. PMID: 22430841 Review. German.
Cited by
- Laboratory Diagnosis of Intrathecal Synthesis of Immunoglobulins: A Review about the Contribution of OCBs and K-index.
Morello M, Mastrogiovanni S, Falcione F, Rossi V, Bernardini S, Casciani S, Viola A, Reali M, Pieri M. Morello M, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 9;25(10):5170. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105170. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791208 Free PMC article. Review. - Potential application of elastic nets for shared polygenicity detection with adapted threshold selection.
John M, Lencz T. John M, et al. Int J Biostat. 2022 Nov 3;19(2):417-438. doi: 10.1515/ijb-2020-0108. eCollection 2023 Nov 1. Int J Biostat. 2022. PMID: 36327464 Free PMC article. - Multi-context genetic modeling of transcriptional regulation resolves novel disease loci.
Thompson M, Gordon MG, Lu A, Tandon A, Halperin E, Gusev A, Ye CJ, Balliu B, Zaitlen N. Thompson M, et al. Nat Commun. 2022 Sep 28;13(1):5704. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33212-0. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36171194 Free PMC article. - Genetic variants associated with sepsis.
Engoren M, Jewell ES, Douville N, Moser S, Maile MD, Bauer ME. Engoren M, et al. PLoS One. 2022 Mar 11;17(3):e0265052. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265052. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35275946 Free PMC article. - Polygenic risk score association with multiple sclerosis susceptibility and phenotype in Europeans.
Shams H, Shao X, Santaniello A, Kirkish G, Harroud A, Ma Q, Isobe N; University of California San Francisco MS-EPIC Team; Schaefer CA, McCauley JL, Cree BAC, Didonna A, Baranzini SE, Patsopoulos NA, Hauser SL, Barcellos LF, Henry RG, Oksenberg JR. Shams H, et al. Brain. 2023 Feb 13;146(2):645-656. doi: 10.1093/brain/awac092. Brain. 2023. PMID: 35253861 Free PMC article.
References
- Kenealy S.J., Pericak-Vance M.A., Haines J.L. The genetic epidemiology of multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2003;143:7–12. - PubMed
- Mumford C.J., Wood N.W., Kellar-Wood H., Thorpe J.W., Miller D.H., Compston D.A. The British Isles survey of multiple sclerosis in twins. Neurology. 1994;44:11–15. - PubMed
- Robertson N.P., Fraser M., Deans J., Clayton D., Walker N., Compston D.A. Age-adjusted recurrence risks for relatives of patients with multiple sclerosis. Brain. 1996;119:449–455. - PubMed
- Sadovnick A.D., Ebers G.C. Genetics of multiple sclerosis. Neurol. Clin. 1995;13:99–118. - PubMed
- Barcellos L.F., Sawcer S., Ramsay P.P., Baranzini S.E., Thomson G., Briggs F., Cree B.C., Begovich A.B., Villoslada P., Montalban X., International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Consortium Heterogeneity at the HLA-DRB1 locus and risk for multiple sclerosis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006;15:2813–2824. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 NS049477/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 084702/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MH065215/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- NS049477/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 084702/Z/08/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- T32 MH065215/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- NS032830/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS032830/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical