Intensity normalization improves color calling in SOLiD sequencing - PubMed (original) (raw)
Intensity normalization improves color calling in SOLiD sequencing
Hao Wu et al. Nat Methods. 2010 May.
Abstract
ABI’s SOLiD system is a commonly used massively parallel DNA sequencing platform for applications including genotyping and structural variation analysis to transcriptome quantification and reconstruction. Like other sequencing technologies, it measures fluorescence intensities from dye-labeled molecules to determine the sequence of DNA fragments. Ultimately, sequences are determined by complicated statistical manipulations of noisy intensity measurements but systematic biases may mislead downstream analysis. A number of proposed methods improve base-calling and quality metrics for other sequencing technologies- and we now present Rsolid, software implementing an intensity normalization strategy for the SOLiD platform that substantially improves yield and accuracy at small computational costs (7% increase in total matches, 13% in perfect matches, 5% reduced error rate, and substantial reduction in false-positive SNP calls).
Figures
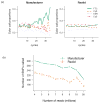
Figure 1. Effect of normalization on color proportions and SNP calling
(a) Color proportions in sample of E. coli genomic DNA on each sequencing cycle. Color calls as reported by the SOLiD 2 system (left panel), and after normalization by Rsolid (right panel), (b) Number of false-positive SNPs called in E. coli as coverage increases. Observe that after normalization fewer SNPs are called even at high coverage (30 M reads corresponds to ~100x coverage).
Similar articles
- ComB: SNP calling and mapping analysis for color and nucleotide space platforms.
Souaiaia T, Frazier Z, Chen T. Souaiaia T, et al. J Comput Biol. 2011 Jun;18(6):795-807. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2011.0027. Epub 2011 May 12. J Comput Biol. 2011. PMID: 21563978 Free PMC article. - Quake: quality-aware detection and correction of sequencing errors.
Kelley DR, Schatz MC, Salzberg SL. Kelley DR, et al. Genome Biol. 2010;11(11):R116. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-11-r116. Epub 2010 Nov 29. Genome Biol. 2010. PMID: 21114842 Free PMC article. - Automated fluorescent DNA sequencing on the ABI PRISM 377.
MacBeath JR, Harvey SS, Oldroyd NJ. MacBeath JR, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2001;167:119-52. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-113-2:119. Methods Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11265312 Review. No abstract available. - Color-coding reveals tandem repeats in the Escherichia coli genome.
Yoshida T, Obata N, Oosawa K. Yoshida T, et al. J Mol Biol. 2000 May 5;298(3):343-9. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.3667. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10772854 - A beginners guide to SNP calling from high-throughput DNA-sequencing data.
Altmann A, Weber P, Bader D, Preuss M, Binder EB, Müller-Myhsok B. Altmann A, et al. Hum Genet. 2012 Oct;131(10):1541-54. doi: 10.1007/s00439-012-1213-z. Epub 2012 Aug 11. Hum Genet. 2012. PMID: 22886560 Review.
Cited by
- Next-generation sequencing in the clinic: promises and challenges.
Xuan J, Yu Y, Qing T, Guo L, Shi L. Xuan J, et al. Cancer Lett. 2013 Nov 1;340(2):284-95. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.11.025. Epub 2012 Nov 19. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 23174106 Free PMC article. Review. - Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Chinary, Assamica and Cambod tea (Camellia sinensis) Types during Development and Seasonal Variation using RNA-seq Technology.
Kumar A, Chawla V, Sharma E, Mahajan P, Shankar R, Yadav SK. Kumar A, et al. Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 17;6:37244. doi: 10.1038/srep37244. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27853259 Free PMC article. - 16S rRNA Gene Amplicon Sequencing Data of Tailing and Nontailing Rhizosphere Soils of Mimosa pudica from a Heavy Metal-Contaminated Ex-Tin Mining Area.
Abdullahi S, Haris H, Zarkasi KZ, Amir HG. Abdullahi S, et al. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2020 Oct 15;9(42):e00761-20. doi: 10.1128/MRA.00761-20. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2020. PMID: 33060266 Free PMC article. - Genotype and SNP calling from next-generation sequencing data.
Nielsen R, Paul JS, Albrechtsen A, Song YS. Nielsen R, et al. Nat Rev Genet. 2011 Jun;12(6):443-51. doi: 10.1038/nrg2986. Nat Rev Genet. 2011. PMID: 21587300 Free PMC article. Review. - Overcoming bias and systematic errors in next generation sequencing data.
Taub MA, Corrada Bravo H, Irizarry RA. Taub MA, et al. Genome Med. 2010 Dec 10;2(12):87. doi: 10.1186/gm208. Genome Med. 2010. PMID: 21144010 Free PMC article.
References
- Tang F, et al. Nat Methods. 2009;6(5):377–382. - PubMed
- Quinlan AR, Stewart DA, Stromberg MP, Marth G. Nat Methods. 2008;5(2):179–181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources