Pretreatment levels of soluble cellular receptors and interleukin-6 are associated with HIV disease progression in subjects treated with highly active antiretroviral therapy - PubMed (original) (raw)
Pretreatment levels of soluble cellular receptors and interleukin-6 are associated with HIV disease progression in subjects treated with highly active antiretroviral therapy
Robert C Kalayjian et al. J Infect Dis. 2010.
Abstract
Background: To identify inflammatory pathways that may contribute to the pathogenesis of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) disease, we explored associations between AIDS or death and different inflammatory markers, including selected soluble tumor necrosis factor superfamily receptors (sTNFRs) and ligands, interleukin (IL)-6, and CD8 T cell activation, in individuals treated with highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART).
Methods: A case-control study of subjects in AIDS Clinical Trials Group (ACTG) protocols 384 and 5015, who were matched according to the CD4 cell count and plasma viral load at baseline, was performed using conditional logistic regression.
Results: Higher pretreatment concentrations of sTNFR-1, sCD27, sCD40L, and plasma IL-6 were associated with a new AIDS-defining illness or death in separate models adjusted for age, sex, hemoglobin, and the latest CD4 cell counts. In additional models that excluded case patients with opportunistic infections, sTNFR-1, sCD27, and sCD40L were each associated with a new AIDS-defining malignancy or death that developed at a median of 51 weeks after initiation of HAART, by which time the majority of subjects had a CD4 cell count of >200 cells/cm(3) and had achieved a plasma viral load of <50 copies/mL.
Conclusion: These data are compatible with a model in which these soluble inflammatory markers identify pathways that may contribute to the pathogenesis of HIV disease progression, pathways that might not be a direct consequence of ongoing HIV type 1 replication.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest:
R.T.G. received grant funding from Tibotec and Gilead and an honorarium from GlaxoSmith Kline.
R.B.P. is on the Speaker’s bureau for Bristol Meyers Squibb and Gilead.
G.K.R. received grant funding from Gilead, Schering-Plough, and consulting fees from Abbott Laboratories, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals and Tibotec.
A.L. received honoraria from Abbott Laboratories and Bristol-Myers Squibb.
Figures
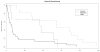
Figure 1
Kaplan-Meier plot depicting the onset of a CDC Category C clinical event or death among cases, by week after HAART-initiation.
Figure 2
Scatter/box plots of baseline immune activation markers among cases of opportunistic infection, and AIDS-associated malignancy or death, and their corresponding matched controls. The boxes encompass the upper and lower quartiles of the distribution of each variable, where the median value is represented by the line within each box. To facilitate comparisons between these markers, values of each variable were subtracted by their mean then divided by their standard deviation (z score). Trends and significant differences between cases and controls that were identified by multivariable models are indicated by the P-value for these differences.
Comment in
- Inflammation and complications of HIV disease.
Dubé MP, Sattler FR. Dubé MP, et al. J Infect Dis. 2010 Jun 15;201(12):1783-5. doi: 10.1086/652751. J Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20446849 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Soluble markers of inflammation and coagulation but not T-cell activation predict non-AIDS-defining morbid events during suppressive antiretroviral treatment.
Tenorio AR, Zheng Y, Bosch RJ, Krishnan S, Rodriguez B, Hunt PW, Plants J, Seth A, Wilson CC, Deeks SG, Lederman MM, Landay AL. Tenorio AR, et al. J Infect Dis. 2014 Oct 15;210(8):1248-59. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiu254. Epub 2014 May 1. J Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24795473 Free PMC article. - Residual viraemia in HIV-1-infected patients with plasma viral load <or=20 copies/ml is associated with increased blood levels of soluble immune activation markers.
Ostrowski SR, Katzenstein TL, Pedersen BK, Gerstoft J, Ullum H. Ostrowski SR, et al. Scand J Immunol. 2008 Dec;68(6):652-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2008.02184.x. Scand J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 19055701 - Determinants of clinical progression in antiretroviral-naive HIV-infected patients starting highly active antiretroviral therapy. Aquitaine Cohort, France, 1996-2002.
Bonnet F, Thiébaut R, Chêne G, Neau D, Pellegrin JL, Mercié P, Beylot J, Dabis F, Salamon R, Morlat P; Groupe d'Epidemiologie Clinique du SIDA en Aquitaine (GECSA). Bonnet F, et al. HIV Med. 2005 May;6(3):198-205. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-1293.2005.00290.x. HIV Med. 2005. PMID: 15876287 - [Recommendations from the GESIDA/Spanish AIDS Plan regarding antiretroviral treatment in adults with human immunodeficiency virus infection (update February 2009)].
Panel de expertos de Gesida y Plan Nacional sobre el Sida. Panel de expertos de Gesida y Plan Nacional sobre el Sida. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2009 Apr;27(4):222-35. doi: 10.1016/j.eimc.2008.11.002. Epub 2009 Feb 26. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2009. PMID: 19246124 Spanish. - [National consensus document by GESIDA/National Aids Plan on antiretroviral treatment in adults infected by the human immunodeficiency virus (January 2011 update)].
Panel de expertos de GESIDA y Plan Nacional sobre el Sida. Panel de expertos de GESIDA y Plan Nacional sobre el Sida. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2011 Mar;29(3):209.e1-103. doi: 10.1016/j.eimc.2010.12.004. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2011. PMID: 21388714 Spanish.
Cited by
- Spatiotemporal trafficking of HIV in human plasmacytoid dendritic cells defines a persistently IFN-α-producing and partially matured phenotype.
O'Brien M, Manches O, Sabado RL, Baranda SJ, Wang Y, Marie I, Rolnitzky L, Markowitz M, Margolis DM, Levy D, Bhardwaj N. O'Brien M, et al. J Clin Invest. 2011 Mar;121(3):1088-101. doi: 10.1172/JCI44960. Epub 2011 Feb 21. J Clin Invest. 2011. PMID: 21339641 Free PMC article. - HIV and the Gut Microbiota: Composition, Consequences, and Avenues for Amelioration.
Vujkovic-Cvijin I, Somsouk M. Vujkovic-Cvijin I, et al. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2019 Jun;16(3):204-213. doi: 10.1007/s11904-019-00441-w. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2019. PMID: 31037552 Free PMC article. Review. - Prediabetes among HIV-infected individuals receiving antiretroviral therapy: prevalence, diagnostic tests, and associated factors.
Phuphuakrat A, Nimitphong H, Reutrakul S, Sungkanuparph S. Phuphuakrat A, et al. AIDS Res Ther. 2020 May 24;17(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s12981-020-00284-1. AIDS Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32448349 Free PMC article. - HIV-Associated Interactions Between Oral Microbiota and Mucosal Immune Cells: Knowledge Gaps and Future Directions.
Coker MO, Cairo C, Garzino-Demo A. Coker MO, et al. Front Immunol. 2021 Sep 20;12:676669. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.676669. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34616391 Free PMC article. Review. - Inflammation investigated as a source of pharmacokinetic variability of atazanavir in AIDS Clinical Trials Group protocol A5224s.
Venuto CS, Lim J, Messing S, Hunt PW, McComsey GA, Morse GD. Venuto CS, et al. Antivir Ther. 2018;23(4):345-351. doi: 10.3851/IMP3209. Antivir Ther. 2018. PMID: 29171837 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
- Appay V, Sauce D. Immune activation and inflammation in HIV-1 infection: causes and consequences. J Pathol. 2008;214:231–41. - PubMed
- Eggena MP, Barugahare B, Okello M, et al. T cell activation in HIV-seropositive Ugandans: differential associations with viral load, CD4+ T cell depletion, and coinfection. J Infect Dis. 2005;191:694–701. - PubMed
- Erikstrup C, Kallestrup P, Zinyama-Gutsire RB, et al. Reduced mortality and CD4 cell loss among carriers of the interleukin-10 −1082G allele in a Zimbabwean cohort of HIV-1-infected adults. Aids. 2007;21:2283–91. - PubMed
- Giorgi JV, Lyles RH, Matud JL, et al. Predictive value of immunologic and virologic markers after long or short duration of HIV-1 infection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2002;29:346–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- M01 RR000080-411056/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AI69501/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AI062435/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI066992/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 36219/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI062435/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000080/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI036219/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069472/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5 RO1 AI066992-04/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069501/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI U01 68635/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069501/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI069472/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 68636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069472/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials