Genome-wide association study meta-analysis identifies seven new rheumatoid arthritis risk loci - PubMed (original) (raw)
Meta-Analysis
doi: 10.1038/ng.582. Epub 2010 May 9.
Soumya Raychaudhuri, Elaine F Remmers, Gang Xie, Stephen Eyre, Brian P Thomson, Yonghong Li, Fina A S Kurreeman, Alexandra Zhernakova, Anne Hinks, Candace Guiducci, Robert Chen, Lars Alfredsson, Christopher I Amos, Kristin G Ardlie; BIRAC Consortium; Anne Barton, John Bowes, Elisabeth Brouwer, Noel P Burtt, Joseph J Catanese, Jonathan Coblyn, Marieke J H Coenen, Karen H Costenbader, Lindsey A Criswell, J Bart A Crusius, Jing Cui, Paul I W de Bakker, Philip L De Jager, Bo Ding, Paul Emery, Edward Flynn, Pille Harrison, Lynne J Hocking, Tom W J Huizinga, Daniel L Kastner, Xiayi Ke, Annette T Lee, Xiangdong Liu, Paul Martin, Ann W Morgan, Leonid Padyukov, Marcel D Posthumus, Timothy R D J Radstake, David M Reid, Mark Seielstad, Michael F Seldin, Nancy A Shadick, Sophia Steer, Paul P Tak, Wendy Thomson, Annette H M van der Helm-van Mil, Irene E van der Horst-Bruinsma, C Ellen van der Schoot, Piet L C M van Riel, Michael E Weinblatt, Anthony G Wilson, Gert Jan Wolbink, B Paul Wordsworth; YEAR Consortium; Cisca Wijmenga, Elizabeth W Karlson, Rene E M Toes, Niek de Vries, Ann B Begovich, Jane Worthington, Katherine A Siminovitch, Peter K Gregersen, Lars Klareskog, Robert M Plenge
Affiliations
- PMID: 20453842
- PMCID: PMC4243840
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.582
Meta-Analysis
Genome-wide association study meta-analysis identifies seven new rheumatoid arthritis risk loci
Eli A Stahl et al. Nat Genet. 2010 Jun.
Abstract
To identify new genetic risk factors for rheumatoid arthritis, we conducted a genome-wide association study meta-analysis of 5,539 autoantibody-positive individuals with rheumatoid arthritis (cases) and 20,169 controls of European descent, followed by replication in an independent set of 6,768 rheumatoid arthritis cases and 8,806 controls. Of 34 SNPs selected for replication, 7 new rheumatoid arthritis risk alleles were identified at genome-wide significance (P < 5 x 10(-8)) in an analysis of all 41,282 samples. The associated SNPs are near genes of known immune function, including IL6ST, SPRED2, RBPJ, CCR6, IRF5 and PXK. We also refined associations at two established rheumatoid arthritis risk loci (IL2RA and CCL21) and confirmed the association at AFF3. These new associations bring the total number of confirmed rheumatoid arthritis risk loci to 31 among individuals of European ancestry. An additional 11 SNPs replicated at P < 0.05, many of which are validated autoimmune risk alleles, suggesting that most represent genuine rheumatoid arthritis risk alleles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that we have no competing financial interest.
Figures
Figure 1. Association with RA risk across 4 loci
Regional association plots show strength of association (-Log(_P_-value)) versus chromosomal position (kilobases, kb) for all SNPs across 1 Megabase (Mb) regions centered on the newly validated SNPs (labeled). PGWAS values are plotted with red/white diamonds for all SNPs, shaded by the degree of LD (r2, see legend) with the validated SNP (larger red diamond). Poverall in combined analysis of GWAS and replication collections is plotted with the blue diamond. Local recombination rates estimated from HapMap CEU (centi-Morgans per Mb, blue line) are plotted against the secondary y-axis, showing recombination hotspots across the region. Labeled green arrows below the plots indicate genes and their orientations. (a) 2p14, SPRED2 locus. (b) 5q11, _IL6ST_-ANKRD55 locus. (c) 5q21, C5orf13 locus. (d) 10p15, IL2RA locus.
Figure 1. Association with RA risk across 4 loci
Regional association plots show strength of association (-Log(_P_-value)) versus chromosomal position (kilobases, kb) for all SNPs across 1 Megabase (Mb) regions centered on the newly validated SNPs (labeled). PGWAS values are plotted with red/white diamonds for all SNPs, shaded by the degree of LD (r2, see legend) with the validated SNP (larger red diamond). Poverall in combined analysis of GWAS and replication collections is plotted with the blue diamond. Local recombination rates estimated from HapMap CEU (centi-Morgans per Mb, blue line) are plotted against the secondary y-axis, showing recombination hotspots across the region. Labeled green arrows below the plots indicate genes and their orientations. (a) 2p14, SPRED2 locus. (b) 5q11, _IL6ST_-ANKRD55 locus. (c) 5q21, C5orf13 locus. (d) 10p15, IL2RA locus.
Figure 1. Association with RA risk across 4 loci
Regional association plots show strength of association (-Log(_P_-value)) versus chromosomal position (kilobases, kb) for all SNPs across 1 Megabase (Mb) regions centered on the newly validated SNPs (labeled). PGWAS values are plotted with red/white diamonds for all SNPs, shaded by the degree of LD (r2, see legend) with the validated SNP (larger red diamond). Poverall in combined analysis of GWAS and replication collections is plotted with the blue diamond. Local recombination rates estimated from HapMap CEU (centi-Morgans per Mb, blue line) are plotted against the secondary y-axis, showing recombination hotspots across the region. Labeled green arrows below the plots indicate genes and their orientations. (a) 2p14, SPRED2 locus. (b) 5q11, _IL6ST_-ANKRD55 locus. (c) 5q21, C5orf13 locus. (d) 10p15, IL2RA locus.
Figure 1. Association with RA risk across 4 loci
Regional association plots show strength of association (-Log(_P_-value)) versus chromosomal position (kilobases, kb) for all SNPs across 1 Megabase (Mb) regions centered on the newly validated SNPs (labeled). PGWAS values are plotted with red/white diamonds for all SNPs, shaded by the degree of LD (r2, see legend) with the validated SNP (larger red diamond). Poverall in combined analysis of GWAS and replication collections is plotted with the blue diamond. Local recombination rates estimated from HapMap CEU (centi-Morgans per Mb, blue line) are plotted against the secondary y-axis, showing recombination hotspots across the region. Labeled green arrows below the plots indicate genes and their orientations. (a) 2p14, SPRED2 locus. (b) 5q11, _IL6ST_-ANKRD55 locus. (c) 5q21, C5orf13 locus. (d) 10p15, IL2RA locus.
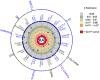
Figure 2. Previously validated autoimmune SNPs tested in our replication study
Eighteen SNPs tested in our replication samples were in LD (defined as r2 > 0.3) with a validated autoimmune risk allele. Of these, 5 were validated as RA risk alleles in our study (Poverall < 5×10−8, inner most circle), 6 were suggestive associations (_Preplication_ <0.05 but _Poverall_ > 5×10−8), and 6 demonstrated no evidence of association in our replication samples (Preplication ≥0.05). For the 12 SNPs with suggestive or no evidence of association, each SNP is plotted by the strength of association with RA risk in the replication samples; those closer to the inner circle have more significant Preplication. All of the RA risk alleles confer risk in the same direction as the validated autoimmune risk alleles (when the same allele or a near perfect proxy was tested). We include the following as “autoimmune” diseases in our study, listed on the outside of the circle, although these reflect diseases along the autoimmuneinflammatory spectrum: systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, multiple sclerosis (MS), psoriasis, and type 1 diabetes (T1D); other autoimmune diseases are not included (e.g., autoimmune thyroiditis). The haplotype tagged by the IL2RA SNP, rs706778, is associated with T1D and MS,; the SH2B3 SNP is associated with both T1D and Celiac disease,. The CCR6 SNP rs3093023 is in partial LD with a SNP associated with Crohn’s disease (rs2301436, r2 = 0.48). The AFF3 SNP has an equivocal association with T1D (where the associated SNP is rs9653442). The IL2-IL21 SNP tested in our study, rs13119723, is in LD (r2=0.67) with a SNP previously implicated in both Celiac disease and RA (rs6822844),, but only in partial LD (r2=0.09) with a T1D SNP (rs4505848). The CD19-NFATC2IP SNP tested in our study, rs8045689, was selected because of GRAIL; it is in partial LD (r2=0.38) with a SNP associated with T1D (rs4788084). The TNIP1 SNP in our study, rs6889239, is in strong LD with an SLE SNP (rs7708392, r2=0.91), but not in LD with another TNIP1 SNP associated with psoriasis (rs17728338, r2<0.01). The ZEB1 SNP (rs2793108) was from the May 2009 release of T1D base, although this SNP did not appear in a subsequent publication. The PXK SLE SNP was tested in this study but not shown, as it is in weak LD with the RA risk SNP (r2 = 0.15 between rs6445975 and rs13315591); the RA SNP was selected because of _P_GWAS<10−6, not because of its association with another autoimmune disease. Note that there are SNPs associated with RA and other autoimmune diseases not shown; we only include those SNPs tested as part of the current study.
Similar articles
- Caucasian and Asian specific rheumatoid arthritis risk loci reveal limited replication and apparent allelic heterogeneity in north Indians.
Prasad P, Kumar A, Gupta R, Juyal RC, Thelma BK. Prasad P, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31584. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031584. Epub 2012 Feb 15. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22355377 Free PMC article. - High-density genotyping of immune loci in Koreans and Europeans identifies eight new rheumatoid arthritis risk loci.
Kim K, Bang SY, Lee HS, Cho SK, Choi CB, Sung YK, Kim TH, Jun JB, Yoo DH, Kang YM, Kim SK, Suh CH, Shim SC, Lee SS, Lee J, Chung WT, Choe JY, Shin HD, Lee JY, Han BG, Nath SK, Eyre S, Bowes J, Pappas DA, Kremer JM, Gonzalez-Gay MA, Rodriguez-Rodriguez L, Ärlestig L, Okada Y, Diogo D, Liao KP, Karlson EW, Raychaudhuri S, Rantapää-Dahlqvist S, Martin J, Klareskog L, Padyukov L, Gregersen PK, Worthington J, Greenberg JD, Plenge RM, Bae SC. Kim K, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015 Mar;74(3):e13. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204749. Epub 2014 Feb 14. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015. PMID: 24532676 Free PMC article. - Meta-analysis identifies nine new loci associated with rheumatoid arthritis in the Japanese population.
Okada Y, Terao C, Ikari K, Kochi Y, Ohmura K, Suzuki A, Kawaguchi T, Stahl EA, Kurreeman FA, Nishida N, Ohmiya H, Myouzen K, Takahashi M, Sawada T, Nishioka Y, Yukioka M, Matsubara T, Wakitani S, Teshima R, Tohma S, Takasugi K, Shimada K, Murasawa A, Honjo S, Matsuo K, Tanaka H, Tajima K, Suzuki T, Iwamoto T, Kawamura Y, Tanii H, Okazaki Y, Sasaki T, Gregersen PK, Padyukov L, Worthington J, Siminovitch KA, Lathrop M, Taniguchi A, Takahashi A, Tokunaga K, Kubo M, Nakamura Y, Kamatani N, Mimori T, Plenge RM, Yamanaka H, Momohara S, Yamada R, Matsuda F, Yamamoto K. Okada Y, et al. Nat Genet. 2012 Mar 25;44(5):511-6. doi: 10.1038/ng.2231. Nat Genet. 2012. PMID: 22446963 - Anti-citrullinated peptide/protein antibody (ACPA)-negative RA shares a large proportion of susceptibility loci with ACPA-positive RA: a meta-analysis of genome-wide association study in a Japanese population.
Terao C, Ohmura K, Kochi Y, Ikari K, Okada Y, Shimizu M, Nishina N, Suzuki A, Myouzen K, Kawaguchi T, Takahashi M, Takasugi K, Murasawa A, Mizuki S, Iwahashi M, Funahashi K, Natsumeda M, Furu M, Hashimoto M, Ito H, Fujii T, Ezawa K, Matsubara T, Takeuchi T, Kubo M, Yamada R, Taniguchi A, Yamanaka H, Momohara S, Yamamoto K, Mimori T, Matsuda F. Terao C, et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015 Apr 18;17(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0623-4. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 25927497 Free PMC article. Review. - The Functional Impact of Alternative Splicing and Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Aravilli RK, Vikram SL, Kohila V. Aravilli RK, et al. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2021;22(8):1014-1029. doi: 10.2174/1389201021666201001142416. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33001009 Review.
Cited by
- Identification of the Single Immunodominant Region of the Native Human CC Chemokine Receptor 6 Recognized by Mouse Monoclonal Antibodies.
Dorgham K, Dejou C, Piesse C, Gorochov G, Pène J, Yssel H. Dorgham K, et al. PLoS One. 2016 Jun 23;11(6):e0157740. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157740. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27336468 Free PMC article. - Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the FAM167A-BLK gene are associated with polymyositis/dermatomyositis in the Han Chinese population.
Chen S, Wu W, Li J, Wang Q, Li Y, Wu Z, Zheng W, Wu Q, Wu C, Zhang F, Li Y. Chen S, et al. Immunol Res. 2015 Jun;62(2):153-62. doi: 10.1007/s12026-015-8646-0. Immunol Res. 2015. PMID: 25846585 Free PMC article. - Genome-wide association study identifies TH1 pathway genes associated with lung function in asthmatic patients.
Li X, Hawkins GA, Ampleford EJ, Moore WC, Li H, Hastie AT, Howard TD, Boushey HA, Busse WW, Calhoun WJ, Castro M, Erzurum SC, Israel E, Lemanske RF Jr, Szefler SJ, Wasserman SI, Wenzel SE, Peters SP, Meyers DA, Bleecker ER. Li X, et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013 Aug;132(2):313-20.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.01.051. Epub 2013 Mar 28. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23541324 Free PMC article. - Epistatic interaction between BANK1 and BLK in rheumatoid arthritis: results from a large trans-ethnic meta-analysis.
Génin E, Coustet B, Allanore Y, Ito I, Teruel M, Constantin A, Schaeverbeke T, Ruyssen-Witrand A, Tohma S, Cantagrel A, Vittecoq O, Barnetche T, Le Loët X, Fardellone P, Furukawa H, Meyer O, Fernández-Gutiérrez B, Balsa A, González-Gay MA, Chiocchia G, Tsuchiya N, Martin J, Dieudé P. Génin E, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Apr 30;8(4):e61044. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061044. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23646104 Free PMC article. - Association of AFF3 Gene Polymorphism rs10865035 with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Population-Based Case-Control Study on a Pakistani Cohort.
Ali Y, Khan S, Chen Y, Farooqi N, Islam ZU, Akhtar M, Aamir, Aman A, Shah AA, Jamal M, Jalil F. Ali Y, et al. Genet Res (Camb). 2021 May 15;2021:5544198. doi: 10.1155/2021/5544198. eCollection 2021. Genet Res (Camb). 2021. PMID: 34104118 Free PMC article.
References
- Klareskog L, Catrina AI, Paget S. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2009;373:659–72. - PubMed
- Suzuki A, et al. Functional haplotypes of PADI4, encoding citrullinating enzyme peptidylarginine deiminase 4, are associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Genet. 2003;34:395–402. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- M01 RR000079/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- MOP79321/CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- P01 CA087969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1K08AR055688-01A1/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR049880-06/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA67262/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AR47782/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01-AR-2-2263/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR056768/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 RR020278/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR057108/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA050385/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR044422/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA067262/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087676/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5-M01-RR-00079/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR059648/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI065841/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- CA49449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 19356/ARC_/Arthritis Research UK/United Kingdom
- U01 CA067262/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AR047782/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- 18475/ARC_/Arthritis Research UK/United Kingdom
- IIN-84042/CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- R01 AR057108/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL087676/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA87969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR44422/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR056768/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR049880/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA049449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA50385/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AR055688/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA049449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical