Mining the mind research network: a novel framework for exploring large scale, heterogeneous translational neuroscience research data sources - PubMed (original) (raw)
doi: 10.3389/neuro.11.036.2009. eCollection 2010.
Mark Scully, William Courtney, Srinivas Rachakonda, Adam Scott, Arvind Caprihan, Jill Fries, Ravi Kalyanam, Judith M Segall, Raul de la Garza, Susan Lane, Vince D Calhoun
Affiliations
- PMID: 20461147
- PMCID: PMC2866565
- DOI: 10.3389/neuro.11.036.2009
Mining the mind research network: a novel framework for exploring large scale, heterogeneous translational neuroscience research data sources
Henry J Bockholt et al. Front Neuroinform. 2010.
Abstract
A neuroinformatics (NI) system is critical to brain imaging research in order to shorten the time between study conception and results. Such a NI system is required to scale well when large numbers of subjects are studied. Further, when multiple sites participate in research projects organizational issues become increasingly difficult. Optimized NI applications mitigate these problems. Additionally, NI software enables coordination across multiple studies, leveraging advantages potentially leading to exponential research discoveries. The web-based, Mind Research Network (MRN), database system has been designed and improved through our experience with 200 research studies and 250 researchers from seven different institutions. The MRN tools permit the collection, management, reporting and efficient use of large scale, heterogeneous data sources, e.g., multiple institutions, multiple principal investigators, multiple research programs and studies, and multimodal acquisitions. We have collected and analyzed data sets on thousands of research participants and have set up a framework to automatically analyze the data, thereby making efficient, practical data mining of this vast resource possible. This paper presents a comprehensive framework for capturing and analyzing heterogeneous neuroscience research data sources that has been fully optimized for end-users to perform novel data mining.
Keywords: Mind Clinical Imaging Consortium; XCEDE; XML; data mining; magnetic resonance imaging.
Figures
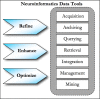
Figure 1
Neuroinformatics data tools.
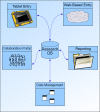
Figure 2
Overview of MRN Neuroinformatics System.
Figure 3
Real-time annotation tool.
Figure 4
Data querying application tool.
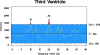
Figure 5
Quality control chart example.
Figure 6
First level analysis planning.
Figure 7
One sample _t_-test calculated on 12 images (six healthy and six schizophrenics) with a T-threshold of 1. 5 applied to the _t_-map.
Figure 8
Class mean run on five healthy, five schizophrenics and two images unknowns. Image shown is the mean image of group 1 thresholded at 1.0.
Similar articles
- The future of Cochrane Neonatal.
Soll RF, Ovelman C, McGuire W. Soll RF, et al. Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834 - Automated collection of imaging and phenotypic data to centralized and distributed data repositories.
King MD, Wood D, Miller B, Kelly R, Landis D, Courtney W, Wang R, Turner JA, Calhoun VD. King MD, et al. Front Neuroinform. 2014 Jun 5;8:60. doi: 10.3389/fninf.2014.00060. eCollection 2014. Front Neuroinform. 2014. PMID: 24926252 Free PMC article. - COINS: An Innovative Informatics and Neuroimaging Tool Suite Built for Large Heterogeneous Datasets.
Scott A, Courtney W, Wood D, de la Garza R, Lane S, King M, Wang R, Roberts J, Turner JA, Calhoun VD. Scott A, et al. Front Neuroinform. 2011 Dec 23;5:33. doi: 10.3389/fninf.2011.00033. eCollection 2011. Front Neuroinform. 2011. PMID: 22275896 Free PMC article. - Translational Metabolomics of Head Injury: Exploring Dysfunctional Cerebral Metabolism with Ex Vivo NMR Spectroscopy-Based Metabolite Quantification.
Wolahan SM, Hirt D, Glenn TC. Wolahan SM, et al. In: Kobeissy FH, editor. Brain Neurotrauma: Molecular, Neuropsychological, and Rehabilitation Aspects. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2015. Chapter 25. In: Kobeissy FH, editor. Brain Neurotrauma: Molecular, Neuropsychological, and Rehabilitation Aspects. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2015. Chapter 25. PMID: 26269925 Free Books & Documents. Review. - An Experimental Approach to Genome Annotation: This report is based on a colloquium sponsored by the American Academy of Microbiology held July 19-20, 2004, in Washington, DC.
[No authors listed] [No authors listed] Washington (DC): American Society for Microbiology; 2004. Washington (DC): American Society for Microbiology; 2004. PMID: 33001599 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
- Associations Between Age and Resting State Connectivity Are Partially Dependent Upon Cardiovascular Fitness.
Gust CJ, Moe EN, Seals DR, Banich MT, Andrews-Hanna JR, Hutchison KE, Bryan AD. Gust CJ, et al. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Apr 20;14:858405. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.858405. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35527739 Free PMC article. - The LORIS MyeliNeuroGene rare disease database for natural history studies and clinical trial readiness.
Spahr A, Rosli Z, Legault M, Tran LT, Fournier S, Toutounchi H, Darbelli L, Madjar C, Lucia C, St-Jean ML, Das S, Evans AC, Bernard G. Spahr A, et al. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2021 Jul 23;16(1):328. doi: 10.1186/s13023-021-01953-8. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2021. PMID: 34301277 Free PMC article. - Evolution of universal review and disclosure of MRI reports to research participants.
Shoemaker JM, Cole C, Petree LE, Helitzer DL, Holdsworth MT, Gluck JP, Phillips JP. Shoemaker JM, et al. Brain Behav. 2016 Feb 8;6(3):e00428. doi: 10.1002/brb3.428. eCollection 2016 Mar. Brain Behav. 2016. PMID: 26893955 Free PMC article. Review. - Multimodal Classification of Schizophrenia Patients with MEG and fMRI Data Using Static and Dynamic Connectivity Measures.
Cetin MS, Houck JM, Rashid B, Agacoglu O, Stephen JM, Sui J, Canive J, Mayer A, Aine C, Bustillo JR, Calhoun VD. Cetin MS, et al. Front Neurosci. 2016 Oct 19;10:466. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2016.00466. eCollection 2016. Front Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27807403 Free PMC article. - Northwestern University Schizophrenia Data and Software Tool (NUSDAST).
Wang L, Kogan A, Cobia D, Alpert K, Kolasny A, Miller MI, Marcus D. Wang L, et al. Front Neuroinform. 2013 Nov 7;7:25. doi: 10.3389/fninf.2013.00025. eCollection 2013. Front Neuroinform. 2013. PMID: 24223551 Free PMC article.
References
- Amari S.-I., Beltrame F., Bjaalie J. G., Dalkara T., De Schutter E., Egan G. F., Goddard N. H., Gonzalez C., Grillner S., Herz A., Hoffmann K. P., Jaaskelainen I., Koslow S. H., Lee S. Y., Matthiessen L., Miller P. L., Da Silva F. M., Novak M., Ravindranath V., Ritz R., Ruotsalainen U., Sebestra V., Subramaniam S., Tang Y., Toga A. W., Usui S., Van Pelt J., Verschure P., Willshaw D., Wrobel A. (2002). Neuroinformatics: the integration of shared databases and tools towards integrative neuroscience. J. Integr. Neurosci. 1, 117–12810.1142/S0219635202000128 - DOI - PubMed
- Andreasen N. C., Arndt S., Alliger R., Miller D., Flaum M. (1995). Symptoms of schizophrenia: methods, meanings, and mechanisms. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 52, 341–351 - PubMed
- Aroian L. A., Levene H. (1950). The effectiveness of quality control charts. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 45, 520–529 Available at: http://www.jstor.org/stable/228072010.2307/2280720 - DOI
- Bockholt H. J., Ling J., Scully M., Magnotta V. A., Gollub R. L., White T., Schulz S. C., Lauriello J., Andreasen N. C. (2007). MIND Clinical Imaging Consortium as a Case Study of Novel Multi-Center Neuroinformatics Software Colorado Springs: International Congress on Schizophrenia Research
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources