Integrated Intensity and Point-Feature Nonrigid Registration - PubMed (original) (raw)
Integrated Intensity and Point-Feature Nonrigid Registration
Xenophon Papademetris et al. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2001.
Abstract
In this work, we present a method for the integration of feature and intensity information for non rigid registration. Our method is based on a free-form deformation model, and uses a normalized mutual information intensity similarity metric to match intensities and the robust point matching framework to estimate feature (point) correspondences. The intensity and feature components of the registration are posed in a single energy functional with associated weights. We compare our method to both point-based and intensity-based registrations. In particular, we evaluate registration accuracy as measured by point landmark distances and image intensity similarity on a set of seventeen normal subjects. These results suggest that the integration of intensity and point-based registration is highly effective in yielding more accurate registrations.
Figures
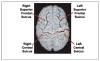
Fig. 1
Sulci used in the evaluation of the registration methods. Note that these are major sulci, hence the matching error of the intensity based method is smaller that what is reported by Hellier et al. [10]
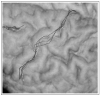
Fig. 2
Example registration result. In this close-up of the central sulcus overlaid on a volume rendered stripped brain, the target surface is shown in white. The warped template is shown for three different registrations RPM − red, Integrated λ = 0.1) − blue and NMI − green.
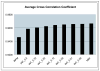
Fig. 3
Average intensity similarity for the point-based registration method (RPM), the new integrated algorithm (INT-λ) with seven different values of the weight of adherence to the point correspondences λ and the intensity only similarity algorithm (NMI) as computed from N = 17 normal controls.
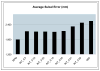
Fig. 4
Average sulcal matching error for the point-based registration method (RPM), the new integrated algorithm (INT-λ) as above and the intensity only similarity algorithm (NMI) as computed from N = 17 normal controls.
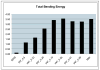
Fig. 5
Average bending energy for the registrations computed by the point-based registration method (RPM), the new integrated algorithm (INT-λ) and the intensity only similarity algorithm (NMI) as computed from N = 17 normal controls.
Similar articles
- Accurate CT∕MR vessel-guided nonrigid registration of largely deformed livers.
Vasquez Osorio EM, Hoogeman MS, Mendez Romero A, Wielopolski P, Zolnay A, Heijmen BJ. Vasquez Osorio EM, et al. Med Phys. 2012 May;39(5):2463-77. doi: 10.1118/1.3701779. Med Phys. 2012. PMID: 22559617 - Inverse consistent non-rigid image registration based on robust point set matching.
Yang X, Pei J, Shi J. Yang X, et al. Biomed Eng Online. 2014;13 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S2. doi: 10.1186/1475-925X-13-S2-S2. Epub 2014 Dec 11. Biomed Eng Online. 2014. PMID: 25559889 Free PMC article. - Self-similarity weighted mutual information: a new nonrigid image registration metric.
Rivaz H, Karimaghaloo Z, Collins DL. Rivaz H, et al. Med Image Anal. 2014 Feb;18(2):343-58. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2013.12.003. Epub 2013 Dec 21. Med Image Anal. 2014. PMID: 24412710 - Assessment of image registration accuracy in three-dimensional transrectal ultrasound guided prostate biopsy.
Karnik VV, Fenster A, Bax J, Cool DW, Gardi L, Gyacskov I, Romagnoli C, Ward AD. Karnik VV, et al. Med Phys. 2010 Feb;37(2):802-13. doi: 10.1118/1.3298010. Med Phys. 2010. PMID: 20229890 - A Robust Nonrigid Point Set Registration Method Based on Collaborative Correspondences.
Feng XW, Feng DZ. Feng XW, et al. Sensors (Basel). 2020 Jun 7;20(11):3248. doi: 10.3390/s20113248. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32517316 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Neural aspects of sentence comprehension: syntactic complexity, reversibility, and reanalysis.
Meltzer JA, McArdle JJ, Schafer RJ, Braun AR. Meltzer JA, et al. Cereb Cortex. 2010 Aug;20(8):1853-64. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhp249. Epub 2009 Nov 17. Cereb Cortex. 2010. PMID: 19920058 Free PMC article. - A 3D point matching algorithm for affine registration.
Qu J, Gong L, Yang L. Qu J, et al. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2011 Mar;6(2):229-36. doi: 10.1007/s11548-010-0503-y. Epub 2010 Jul 16. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2011. PMID: 20635158 - Effects of fructose vs glucose on regional cerebral blood flow in brain regions involved with appetite and reward pathways.
Page KA, Chan O, Arora J, Belfort-Deaguiar R, Dzuira J, Roehmholdt B, Cline GW, Naik S, Sinha R, Constable RT, Sherwin RS. Page KA, et al. JAMA. 2013 Jan 2;309(1):63-70. doi: 10.1001/jama.2012.116975. JAMA. 2013. PMID: 23280226 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - New open-source ictal SPECT analysis method implemented in BioImage Suite.
Scheinost D, Teisseyre TZ, Distasio M, DeSalvo MN, Papademetris X, Blumenfeld H. Scheinost D, et al. Epilepsia. 2010 Apr;51(4):703-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2009.02425.x. Epub 2010 Jan 13. Epilepsia. 2010. PMID: 20074234 Free PMC article. - Small decrements in systemic glucose provoke increases in hypothalamic blood flow prior to the release of counterregulatory hormones.
Page KA, Arora J, Qiu M, Relwani R, Constable RT, Sherwin RS. Page KA, et al. Diabetes. 2009 Feb;58(2):448-52. doi: 10.2337/db08-1224. Epub 2008 Nov 18. Diabetes. 2009. PMID: 19017765 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
- Cachier P, Bardinet E, Dormont D, Pennec X, Ayache N. Iconic feature based nonrigid registration: the PASHA algorithm. Computer Vision and Image Understanding. 2003;89:272–298.
- Christensen GE, Miller MI, Vannier MW. Individualizing neuroanatomical atlases using a massively parallel computer. Computer
- Chui H, Win L, Schultz RT, Duncan JS, Rangarajan A. A unified non-rigid feature registration method for brain mapping. Medical Image Analysis. 2003;7(2):113–130. - PubMed
- Collins DL, Le Goualher G, Evans AC. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention. Springer; Berlin: 1998. Non-linear cerebral registration with sulcal constraints; pp. 974–984.
- Corouge I, Barillot C, Hellier P, Toulouse P, Gibaud B. Non-linear local registration of functional data. In: Viergever MA, Dohi T, Vannier M, editors. Medical Image Computing and Computer Aided Intervention (MICCAI) 2001. pp. 948–956.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources