ConSurf 2010: calculating evolutionary conservation in sequence and structure of proteins and nucleic acids - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2010 Jul;38(Web Server issue):W529-33.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq399. Epub 2010 May 16.
Affiliations
- PMID: 20478830
- PMCID: PMC2896094
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq399
ConSurf 2010: calculating evolutionary conservation in sequence and structure of proteins and nucleic acids
Haim Ashkenazy et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Jul.
Abstract
It is informative to detect highly conserved positions in proteins and nucleic acid sequence/structure since they are often indicative of structural and/or functional importance. ConSurf (http://consurf.tau.ac.il) and ConSeq (http://conseq.tau.ac.il) are two well-established web servers for calculating the evolutionary conservation of amino acid positions in proteins using an empirical Bayesian inference, starting from protein structure and sequence, respectively. Here, we present the new version of the ConSurf web server that combines the two independent servers, providing an easier and more intuitive step-by-step interface, while offering the user more flexibility during the process. In addition, the new version of ConSurf calculates the evolutionary rates for nucleic acid sequences. The new version is freely available at: http://consurf.tau.ac.il/.
Figures
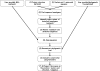
Figure 1.
A flowchart of ConSurf protocol.
Figure 2.
A ConSurf analysis for the GAL4 transcription factor and its DNA binding site. The 3D structure of the N-terminal region of the GAL4 transcription factor in yeast bound to the DNA is presented using a space-filled model. The amino-acids and the nucleotides are colored by their conservation grades using the color-coding bar, with turquoise-through-maroon indicating variable-through-conserved. Positions, for which the inferred conservation level was assigned with low confidence, are marked with light yellow. The figure reveals that the functionally important regions on both the DNA and the protein are highly conserved. The run was carried out using PDB code 3COQ and the figure was generated using the PyMol (10) script output by ConSurf.
Similar articles
- ConSurf 2016: an improved methodology to estimate and visualize evolutionary conservation in macromolecules.
Ashkenazy H, Abadi S, Martz E, Chay O, Mayrose I, Pupko T, Ben-Tal N. Ashkenazy H, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jul 8;44(W1):W344-50. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw408. Epub 2016 May 10. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27166375 Free PMC article. - ConSurf 2005: the projection of evolutionary conservation scores of residues on protein structures.
Landau M, Mayrose I, Rosenberg Y, Glaser F, Martz E, Pupko T, Ben-Tal N. Landau M, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Jul 1;33(Web Server issue):W299-302. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki370. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15980475 Free PMC article. - The ConSurf-DB: pre-calculated evolutionary conservation profiles of protein structures.
Goldenberg O, Erez E, Nimrod G, Ben-Tal N. Goldenberg O, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Jan;37(Database issue):D323-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn822. Epub 2008 Oct 29. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 18971256 Free PMC article. - The ConSurf-HSSP database: the mapping of evolutionary conservation among homologs onto PDB structures.
Glaser F, Rosenberg Y, Kessel A, Pupko T, Ben-Tal N. Glaser F, et al. Proteins. 2005 Feb 15;58(3):610-7. doi: 10.1002/prot.20305. Proteins. 2005. PMID: 15614759 - Wenxiang 3.0: Evolutionary Visualization of α, π, and 3/10 Helices.
Jungck JR, Cebeci M. Jungck JR, et al. Evol Bioinform Online. 2022 May 31;18:11769343221101014. doi: 10.1177/11769343221101014. eCollection 2022. Evol Bioinform Online. 2022. PMID: 35668741 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- First description of novel compound heterozygous mutations in HYCC1: clinical evaluations and molecular analysis in patient with hypomyelinating leukodystrophy-5 with retrospective view.
Ben Issa A, Kamoun F, Khabou B, Bouchaala W, Fakhfakh F, Triki C. Ben Issa A, et al. J Hum Genet. 2025 Feb;70(2):75-85. doi: 10.1038/s10038-024-01300-2. Epub 2024 Oct 28. J Hum Genet. 2025. PMID: 39468300 - Genome Protection by the 9-1-1 Complex Subunit HUS1 Requires Clamp Formation, DNA Contacts, and ATR Signaling-independent Effector Functions.
Lim PX, Patel DR, Poisson KE, Basuita M, Tsai C, Lyndaker AM, Hwang BJ, Lu AL, Weiss RS. Lim PX, et al. J Biol Chem. 2015 Jun 12;290(24):14826-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.630640. Epub 2015 Apr 24. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25911100 Free PMC article. - Cloning, identification and expression analysis of ACC oxidase gene involved in ethylene production pathway.
Jafari Z, Haddad R, Hosseini R, Garoosi G. Jafari Z, et al. Mol Biol Rep. 2013 Feb;40(2):1341-50. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-2178-7. Epub 2012 Oct 18. Mol Biol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23076530 - Structure of the TPR domain of AIP: lack of client protein interaction with the C-terminal α-7 helix of the TPR domain of AIP is sufficient for pituitary adenoma predisposition.
Morgan RM, Hernández-Ramírez LC, Trivellin G, Zhou L, Roe SM, Korbonits M, Prodromou C. Morgan RM, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e53339. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053339. Epub 2012 Dec 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23300914 Free PMC article. - BamA POTRA Domain Interacts with a Native Lipid Membrane Surface.
Fleming PJ, Patel DS, Wu EL, Qi Y, Yeom MS, Sousa MC, Fleming KG, Im W. Fleming PJ, et al. Biophys J. 2016 Jun 21;110(12):2698-2709. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.05.010. Biophys J. 2016. PMID: 27332128 Free PMC article.
References
- Glaser F, Pupko T, Paz I, Bell RE, Bechor-Shental D, Martz E, Ben-Tal N. ConSurf: identification of functional regions in proteins by surface-mapping of phylogenetic information. Bioinformatics. 2003;19:163–164. - PubMed
- Berezin C, Glaser F, Rosenberg J, Paz I, Pupko T, Fariselli P, Casadio R, Ben-Tal N. ConSeq: the identification of functionally and structurally important residues in protein sequences. Bioinformatics. 2004;20:1322–1324. - PubMed
- Mayrose I, Graur D, Ben-Tal N, Pupko T. Comparison of site-specific rate-inference methods for protein sequences: empirical Bayesian methods are superior. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004;21:1781–1791. - PubMed
- Pupko T, Bell RE, Mayrose I, Glaser F, Ben-Tal N. Rate4Site: an algorithmic tool for the identification of functional regions in proteins by surface mapping of evolutionary determinants within their homologues. Bioinformatics. 2002;18(Suppl 1):S71–S77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources