Phase I and pharmacologic study of SNS-032, a potent and selective Cdk2, 7, and 9 inhibitor, in patients with advanced chronic lymphocytic leukemia and multiple myeloma - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical Trial
. 2010 Jun 20;28(18):3015-22.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.26.1347. Epub 2010 May 17.
Rong Chen, William Plunkett, David Siegel, Rajni Sinha, R Donald Harvey, Ashraf Z Badros, Leslie Popplewell, Steven Coutre, Judith A Fox, Kristi Mahadocon, Tianling Chen, Peggy Kegley, Ute Hoch, William G Wierda
Affiliations
- PMID: 20479412
- PMCID: PMC4979218
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2009.26.1347
Clinical Trial
Phase I and pharmacologic study of SNS-032, a potent and selective Cdk2, 7, and 9 inhibitor, in patients with advanced chronic lymphocytic leukemia and multiple myeloma
Wei-Gang Tong et al. J Clin Oncol. 2010.
Abstract
Purpose: SNS-032 is a highly selective and potent inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) 2, 7, and 9, with in vitro growth inhibitory effects and ability to induce apoptosis in malignant B cells. A phase I dose-escalation study of SNS-032 was conducted to evaluate safety, pharmacokinetics, biomarkers of mechanism-based pharmacodynamic (PD) activity, and clinical efficacy.
Patients and methods: Parallel cohorts of previously treated patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and multiple myeloma (MM) received SNS-032 as a loading dose followed by 6-hour infusion weekly for 3 weeks of each 4-week course.
Results: There were 19 patients with CLL and 18 with MM treated. Tumor lysis syndrome was the dose-limiting toxicity (DLT) for CLL, the maximum-tolerated dose (MTD) was 75 mg/m(2), and the most frequent grade 3 to 4 toxicity was myelosuppression. One patient with CLL had more than 50% reduction in measurable disease without improvement in hematologic parameters. Another patient with low tumor burden had stable disease for four courses. For patients with MM, no DLT was observed and MTD was not identified at up to 75 mg/m(2), owing to early study closure. Two patients with MM had stable disease and one had normalization of spleen size with treatment. Biomarker analyses demonstrated mechanism-based PD activity with inhibition of Cdk7 and Cdk9, decreases in Mcl-1 and XIAP expression level, and associated CLL cell apoptosis.
Conclusion: SNS-032 demonstrated mechanism-based target modulation and limited clinical activity in heavily pretreated patients with CLL and MM. Further single-agent, PD-based, dose and schedule modification is warranted to maximize clinical efficacy.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
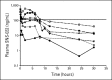
Fig 1.
SNS-032 plasma concentration-time profiles. Mean pharmacokinetic profiles for all dose cohorts from patients with multiple myeloma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia are shown. Filled circles, 15 mg/m2, n = 3; open circles, 22 mg/m2, n = 2; filled inverted triangles, 33 mg/m2, n = 8; open triangles, 50 mg/m2, n = 7; filled squares, 75 mg/m2, n = 10; open squares, 100 mg/m2, n = 2; solid line, concentration that inhibits 90%.
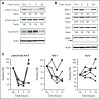
Fig 2.
Target modulation after SNS-032 infusion in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. (A) Representative immunoblots from a patient treated with 75 mg/m2 of SNS-032. The ratio indicates the densitometry analysis between pPol II-Ser2 or pPol II-Ser5 and total Pol II, normalized to predose controls. (B) Representative immunoblots showing the protein levels of Mcl-1, XIAP, and Bcl-2 after SNS-032 infusion. The ratio indicates the densitometry analysis between Mcl-1, XIAP or Bcl-2, and actin, normalized to predose controls. Cleavage of poly (adenosine diphosphate–ribose) polymerase (PARP; arrow) was used as an indicator of apoptosis. (C) The summarized quantitations of phosphorylation of Ser2 at the C-terminal domain of RNA Pol II and protein levels of Mcl-1 and Bcl-2 for two patients treated with 75 mg/m2 (closed symbols) and two patients treated with 100 mg/m2 (open symbols) of SNS-032.
Similar articles
- SNS-032 is a potent and selective CDK 2, 7 and 9 inhibitor that drives target modulation in patient samples.
Conroy A, Stockett DE, Walker D, Arkin MR, Hoch U, Fox JA, Hawtin RE. Conroy A, et al. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2009 Sep;64(4):723-32. doi: 10.1007/s00280-008-0921-5. Epub 2009 Jan 24. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19169685 Clinical Trial. - Mechanism of action of SNS-032, a novel cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Chen R, Wierda WG, Chubb S, Hawtin RE, Fox JA, Keating MJ, Gandhi V, Plunkett W. Chen R, et al. Blood. 2009 May 7;113(19):4637-45. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-12-190256. Epub 2009 Feb 20. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19234140 Free PMC article. - Phase I study of samalizumab in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and multiple myeloma: blockade of the immune checkpoint CD200.
Mahadevan D, Lanasa MC, Farber C, Pandey M, Whelden M, Faas SJ, Ulery T, Kukreja A, Li L, Bedrosian CL, Zhang X, Heffner LT. Mahadevan D, et al. J Immunother Cancer. 2019 Aug 23;7(1):227. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0710-1. J Immunother Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31443741 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Rituximab: a review of its use in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.
Plosker GL, Figgitt DP. Plosker GL, et al. Drugs. 2003;63(8):803-43. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363080-00005. Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12662126 Review. - Alvocidib (flavopiridol) for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Wiernik PH. Wiernik PH. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2016 Jun;25(6):729-34. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2016.1169273. Epub 2016 Apr 7. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2016. PMID: 26998706 Review.
Cited by
- Emerging drug profile: cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors.
Blachly JS, Byrd JC. Blachly JS, et al. Leuk Lymphoma. 2013 Oct;54(10):2133-43. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2013.783911. Epub 2013 Jul 29. Leuk Lymphoma. 2013. PMID: 23488658 Free PMC article. Review. - Characterization of cyclin E expression in multiple myeloma and its functional role in seliciclib-induced apoptotic cell death.
Josefsberg Ben-Yehoshua L, Beider K, Shimoni A, Ostrovsky O, Samookh M, Peled A, Nagler A. Josefsberg Ben-Yehoshua L, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e33856. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033856. Epub 2012 Apr 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22558078 Free PMC article. - Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases: from biology to tumorigenesis and therapeutic opportunities.
Zabihi M, Lotfi R, Yousefi AM, Bashash D. Zabihi M, et al. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Apr;149(4):1585-1606. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04135-6. Epub 2022 Jul 4. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 35781526 Review. - Synthesis, Biological Assessment, and Structure Activity Relationship Studies of New Flavanones Embodying Chromene Moieties.
Assirey E, Alsaggaf A, Naqvi A, Moussa Z, Okasha RM, Afifi TH, Abd-El-Aziz AS. Assirey E, et al. Molecules. 2020 Jan 27;25(3):544. doi: 10.3390/molecules25030544. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32012737 Free PMC article. - CDK9 inhibitors in multiple myeloma: a review of progress and perspectives.
Borowczak J, Szczerbowski K, Ahmadi N, Szylberg Ł. Borowczak J, et al. Med Oncol. 2022 Jan 29;39(4):39. doi: 10.1007/s12032-021-01636-1. Med Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35092513 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Soundararajan S, Chen W, Spicer EK, et al. The nucleolin targeting aptamer AS1411 destabilizes Bcl-2 messenger RNA in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2008;68:2358–2365. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous