Stabilization of an E3 ligase-E2-ubiquitin complex increases cell surface MHC class I expression - PubMed (original) (raw)
Stabilization of an E3 ligase-E2-ubiquitin complex increases cell surface MHC class I expression
Lidia M Duncan et al. J Immunol. 2010.
Abstract
The Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded ubiquitin E3 ligase K3 ubiquitinates cell-surface MHC class I molecules (MHC I), causing the internalization and degradation of MHC I via the endolysosomal pathway. K3 recruits the cellular E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme Ubc13 to generate lysine-63-linked polyubiquitin chains on MHC I, leading to the clathrin-mediated endocytosis and lysosomal degradation of MHC I. In this study, we identify a ubiquitin isoleucine-44-alanine mutant (I44A) that inhibits K3-mediated downregulation of MHC I by preventing MHC I polyubiqitination. This E3-specific inhibition by I44A prevents dissociation of the MHC I-K3-Ubc13-ubiquitin complex, allows the in vivo visualization of a transient substrate-E3-E2-ubiquitin complex interaction, and highlights a potential substrate hierarchy between the different MHC I alleles downregulated by K3. The I44A mutant also increases cell-surface MHC I expression in control cells in the absence of K3, predicting the presence of an endogenous E3 ubiquitin ligase required for cell-surface MHC I regulation.
Figures
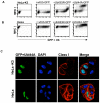
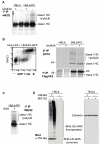
Figure 1. The 144A ubiquitin mutant increases cell surface MHC I in HeLa-K3 and HeLa cells
(A-B) Cytofluorometric analysis of MHC class I expression in HeLa-K3 or HeLa cells following transient transfection with GFP-tagged wildtype-ubiquitin (wtUb), Lys-63Arg-ubiquitin (UbK63R) or Ile44Ala-ubiquitin (UbI44A). Cells were stained with mAb. W6/32 (C) Wildtype HeLa and HeLa-K3 cells were transfected with His-UbI44A-GFP (green) and stained with w6/32 mAb. for MHC I (red), and DAPI as a nuclear stain (blue).
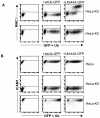
Figure 2. The I44A ubiquitin mutant is K3 and MHC I specific
(A) I44A expression does not affect cell surface MHC I in HeLa-K5 cells. Cytofluorometric analysis of MHC class I expression in HeLa-K3 or HeLa-K5 cells following transient transfection with GFP-tagged UbI44A, or wildtype ubiquitin as control. Cells were labelled as for Fig 1A. (B) I44A expression does not effect cell surface ICAM1 levels. Cytofluorometric analysis of ICAM1 expression in HeLa, HeLa-K5 and HeLa-K3 cells following transient transfection with GFP-tagged UbI44A, or wildtype ubiquitin as control. Cells were labelled with APC-conjugated anti-ICAM1 mAb.
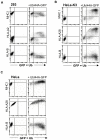
Figure 3. The I44A ubiquitin mutant is MHC I allotype specific
(A - C) I44A expression leads to upregulation of the cell surface HLA-A allotype and decreased expression of the HLA-B allotype. Cytofluorometric analysis of MHC class I expression in (A) 293, (B) HeLa-K3, or (C) HeLa cells following transient transfection with GFP-tagged UbI44A. Cells were labelled with w6/32 Ab (total MHC I), anti-HLA-A2 mAb., anti-HLA-A28 mAb, or with anti-HLA-B mAb. as indicated.
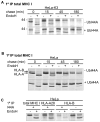
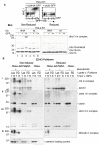
Figure 4. The I44A ubiquitin mutant prevents K3-mediated degradation of MHC I and promotes HLA-A at the expense of HLA-B expression
(A) K3 induced degradation of MHC I is inhibited by the I44A ubiquitin mutant. Cell sorted HeLa-K3 cells (+/− I44A) were pulsed for 10 min with [35S]methionine and [35S]cysteine and chased for the times indicated. TritonX-100 lysates were immunoprecipitated with the anti-MHC I w6/32 mAb and protein A sepharose beads for 2hrs, and treated with Endo H to follow maturation of MHC I. Samples were analysed by 10% SDS–PAGE and autoradiography. (B) The I44A mutant delays MHC I maturation and promotes expression of HLA-A28 at the expense of HLA-B. Cell sorted HeLa cells (+/− I44A) were pulse labelled, immunoprecipitated with the anti-MHC I w6/32 mAb as in (A) and analysed by 12% SDS–PAGE. (C) In the presence of I44A, expression of the HLA-B allele is dramatically reduced. To compare expression levels of the HLA-A and -B allele in the presence of I44A, HeLa cells (+/− I44A) were pulse chased for 15 min, immunoprecipitated with the anti-MHC I w6/32 mAb, the anti-HLA-A28 mAb and the anti-HLA-B mAb 4E and analysed as in (A).
Figure 5. The I44A ubiquitin mutant prevents the K3 but not K5-mediated polyubiquitination of MHC I
(A) HeLa and HeLa-K3 cells (+/− transiently transfected I44A) were pulsed for 15 min and chased for 45 min. TritonX-100 lysates were immunoprecipitated with the anti-MHC I w6/32 mAb and protein A sepharose beads for 2hrs and treated as in Fig 4A (B) HeLa-K3 cells transfected with I44A were cell sorted for high and low expressing GFP (I44A ubiquitin) populations, pulsed for 20 min. in [35S]methionine and [35S]cysteine and chased for 30 minutes. Tx-100 lysates were immunoprecipitated with the anti-FLAG M2 mAb, the resulting complex was dissociated (1% SDS) and reprecipitated with the HC10 (class I heavy chain (HC)) specific mAb. and analysed by SDS–PAGE and autoradiography. (C) The I44A ubiquitin mutant does not affect K5-mediated polyubiquitination of MHC I. HeLa-K5 cells transiently transfected with I44A were immunoprecipitated as in (A). (D) Polyubiquitination and proteasomal degradation is normal in the presence of I44A. HeLa cell lysates (+/− I44A) were were immunoblotted for 6His-I44A-Ub in the presence or absence of the MG132 inhibitor. Calnexin was used as loading control.
Figure 6. The I44A ubiquitin mutant stabilises the MHC I-E3-E2-Ub ligase complex
(A) The Ubc13 E2 conjugating enzyme is detected in a 120KDa reducible complex in the presence of the I44A ubiquitin mutant. I44A-transfected HeLa-K3 cells were labelled for surface MHC I with the w6/32 Ab and cells were sorted into three populations representing untransfected GFP-negative (I44A negative) cells (−); GFP intermediate, (I44A intermediate) MHC I low cells (+); and GFP high, (I44A high), MHC I high cells (++), prior to immunoblotting equivalent amounts of total lysates for Ubc13 under non-reducing and reducing conditions (lower panels). (B) Ubc13, K3, MHC I and I44A-Ub are components of the 120kDa complex. HeLa-ZZ-Flag-K3 cells +/−I44A were lysed in 1%Tx-100/TBS or RIPA buffers and total cell lysates (Lys) were either directly immunoblotted for K3 (anti-Flag M2 Ab), MHC I (HC10 Ab), Ubc13 and 6HisI44A (anti-His Ab), or pulldowns performed with ZZ-FLAG-K3 (PD), and the resulting complex separated by SDS-PAGE and then probed for the same components. Calnexin was used as loading control.
Figure 7. Schematic model to show trapping of the MHC I-E3-E2-UbI44A complex
(A) In the presence of wildtype ubiquitin, K3 recruits Ub-charged Ubc13 for transfer of the charged donor ubiquitin from Ubc13 to the acceptor ubiquitin. (B) In the presence of the I44A mutant ubiquitin, Uev1a is unable to bind the I44 patch on the acceptor ubiquitin and orient its K63 for conjugation by Ubc13. Uev1a dissociates and in the absence of polyubiquitination the monoubiquitin on MHC I is likely removed by a deubiquinating enzyme. As Ubc13 is unable to transfer the donor ubiquitin to an acceptor ubiquitin it cannot dissociate from K3 stabilising the otherwise transient MHC I-E3-E2-I44A complex.
Similar articles
- Lysine-63-linked ubiquitination is required for endolysosomal degradation of class I molecules.
Duncan LM, Piper S, Dodd RB, Saville MK, Sanderson CM, Luzio JP, Lehner PJ. Duncan LM, et al. EMBO J. 2006 Apr 19;25(8):1635-45. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601056. Epub 2006 Apr 6. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16601694 Free PMC article. - Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus K3 and K5 ubiquitin E3 ligases have stage-specific immune evasion roles during lytic replication.
Brulois K, Toth Z, Wong LY, Feng P, Gao SJ, Ensser A, Jung JU. Brulois K, et al. J Virol. 2014 Aug;88(16):9335-49. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00873-14. Epub 2014 Jun 4. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24899205 Free PMC article. - A non-canonical ESCRT pathway, including histidine domain phosphotyrosine phosphatase (HD-PTP), is used for down-regulation of virally ubiquitinated MHC class I.
Parkinson MD, Piper SC, Bright NA, Evans JL, Boname JM, Bowers K, Lehner PJ, Luzio JP. Parkinson MD, et al. Biochem J. 2015 Oct 1;471(1):79-88. doi: 10.1042/BJ20150336. Epub 2015 Jul 28. Biochem J. 2015. PMID: 26221024 Free PMC article. - Identifying the ERAD ubiquitin E3 ligases for viral and cellular targeting of MHC class I.
van den Boomen DJ, Lehner PJ. van den Boomen DJ, et al. Mol Immunol. 2015 Dec;68(2 Pt A):106-11. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2015.07.005. Epub 2015 Jul 22. Mol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26210183 Free PMC article. Review. - Downregulation of cell surface receptors by the K3 family of viral and cellular ubiquitin E3 ligases.
Lehner PJ, Hoer S, Dodd R, Duncan LM. Lehner PJ, et al. Immunol Rev. 2005 Oct;207:112-25. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2005.00314.x. Immunol Rev. 2005. PMID: 16181331 Review.
Cited by
- Molecular mechanisms of ubiquitin-dependent membrane traffic.
Hurley JH, Stenmark H. Hurley JH, et al. Annu Rev Biophys. 2011;40:119-42. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-042910-155404. Annu Rev Biophys. 2011. PMID: 21332354 Free PMC article. - Trim-Away ubiquitinates and degrades lysine-less and N-terminally acetylated substrates.
Kiss L, Rhinesmith T, Luptak J, Dickson CF, Weidenhausen J, Smyly S, Yang JC, Maslen SL, Sinning I, Neuhaus D, Clift D, James LC. Kiss L, et al. Nat Commun. 2023 Apr 15;14(1):2160. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37504-x. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37061529 Free PMC article. - Modulation of Ubiquitin Signaling in Innate Immune Response by Herpesviruses.
Soh SM, Kim YJ, Kim HH, Lee HR. Soh SM, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 1;23(1):492. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010492. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35008917 Free PMC article. Review. - The RNA-binding E3 ubiquitin ligase MEX-3C links ubiquitination with MHC-I mRNA degradation.
Cano F, Bye H, Duncan LM, Buchet-Poyau K, Billaud M, Wills MR, Lehner PJ. Cano F, et al. EMBO J. 2012 Aug 29;31(17):3596-606. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.218. Epub 2012 Aug 3. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22863774 Free PMC article. - Multiple E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes regulate human cytomegalovirus US2-mediated immunoreceptor downregulation.
van de Weijer ML, Schuren ABC, van den Boomen DJH, Mulder A, Claas FHJ, Lehner PJ, Lebbink RJ, Wiertz EJHJ. van de Weijer ML, et al. J Cell Sci. 2017 Sep 1;130(17):2883-2892. doi: 10.1242/jcs.206839. Epub 2017 Jul 25. J Cell Sci. 2017. PMID: 28743740 Free PMC article.
References
- Peaper DR, Cresswell P. Regulation of MHC class I assembly and peptide binding. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2008;24:343–368. - PubMed
- Lehner PJ, Hoer S, Dodd R, Duncan LM. Downregulation of cell surface receptors by the K3 family of viral and cellular ubiquitin E3 ligases. Immunol Rev. 2005;207:112–125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 085733/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G9800943/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0600823/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 084957/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials