On safari to Random Jungle: a fast implementation of Random Forests for high-dimensional data - PubMed (original) (raw)
On safari to Random Jungle: a fast implementation of Random Forests for high-dimensional data
Daniel F Schwarz et al. Bioinformatics. 2010.
Erratum in
- Bioinformatics. 2011 Feb 1;27(3):439
Abstract
Motivation: Genome-wide association (GWA) studies have proven to be a successful approach for helping unravel the genetic basis of complex genetic diseases. However, the identified associations are not well suited for disease prediction, and only a modest portion of the heritability can be explained for most diseases, such as Type 2 diabetes or Crohn's disease. This may partly be due to the low power of standard statistical approaches to detect gene-gene and gene-environment interactions when small marginal effects are present. A promising alternative is Random Forests, which have already been successfully applied in candidate gene analyses. Important single nucleotide polymorphisms are detected by permutation importance measures. To this day, the application to GWA data was highly cumbersome with existing implementations because of the high computational burden.
Results: Here, we present the new freely available software package Random Jungle (RJ), which facilitates the rapid analysis of GWA data. The program yields valid results and computes up to 159 times faster than the fastest alternative implementation, while still maintaining all options of other programs. Specifically, it offers the different permutation importance measures available. It includes new options such as the backward elimination method. We illustrate the application of RJ to a GWA of Crohn's disease. The most important single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) validate recent findings in the literature and reveal potential interactions.
Availability: The RJ software package is freely available at http://www.randomjungle.org
Figures
Fig. 1.
Comparison of computing time and memory usage of several RF implementations. Each program analyzed a simulated dataset comprising 1006 samples genotyped at 275 153 SNPs. A short bar indicates a fast implementation of RF in comparison to other programs: (a) Comparison of computing time of five implementations. The figure reads for example: For analyzing data, RJ calculations took 0.53 h. (b) Comparison of memory usage of five programs. Memory was sparsely used by Willows and RJ in comparison to randomForest and RF in Fortran. (Asterisk indicates memory usage of each computer node.)
Fig. 2.
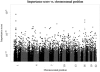
CVI scores of SNPs and their chromosomal position. The axis of CVI scores was log transformed. Small and negative CVI values were omitted.
Fig. 3.
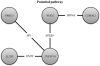
Six of the 10 most important genes can be combined to a potential pathway. TNFSF10 potentially interacts with IL23R, NOD2 and PRKG1. The NOD2 conceivably interacts with CDKAL1.
Similar articles
- Uncovering networks from genome-wide association studies via circular genomic permutation.
Cabrera CP, Navarro P, Huffman JE, Wright AF, Hayward C, Campbell H, Wilson JF, Rudan I, Hastie ND, Vitart V, Haley CS. Cabrera CP, et al. G3 (Bethesda). 2012 Sep;2(9):1067-75. doi: 10.1534/g3.112.002618. Epub 2012 Sep 1. G3 (Bethesda). 2012. PMID: 22973544 Free PMC article. - SNPHarvester: a filtering-based approach for detecting epistatic interactions in genome-wide association studies.
Yang C, He Z, Wan X, Yang Q, Xue H, Yu W. Yang C, et al. Bioinformatics. 2009 Feb 15;25(4):504-11. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn652. Epub 2008 Dec 19. Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19098029 - Genome-wide association data classification and SNPs selection using two-stage quality-based Random Forests.
Nguyen TT, Huang J, Wu Q, Nguyen T, Li M. Nguyen TT, et al. BMC Genomics. 2015;16 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S5. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-16-S2-S5. Epub 2015 Jan 21. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25708662 Free PMC article. - Classification of genetic profiles of Crohn's disease: a focus on the ATG16L1 gene.
Grant SF, Baldassano RN, Hakonarson H. Grant SF, et al. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2008 Mar;8(2):199-207. doi: 10.1586/14737159.8.2.199. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2008. PMID: 18366306 Review. - Genome simulation approaches for synthesizing in silico datasets for human genomics.
Ritchie MD, Bush WS. Ritchie MD, et al. Adv Genet. 2010;72:1-24. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-380862-2.00001-1. Adv Genet. 2010. PMID: 21029846 Review.
Cited by
- BOOST: A fast approach to detecting gene-gene interactions in genome-wide case-control studies.
Wan X, Yang C, Yang Q, Xue H, Fan X, Tang NL, Yu W. Wan X, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2010 Sep 10;87(3):325-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.07.021. Am J Hum Genet. 2010. PMID: 20817139 Free PMC article. - Random forests on Hadoop for genome-wide association studies of multivariate neuroimaging phenotypes.
Wang Y, Goh W, Wong L, Montana G; Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Wang Y, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013;14 Suppl 16(Suppl 16):S6. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-S16-S6. Epub 2013 Oct 22. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 24564704 Free PMC article. - The boon and bane of boldness: movement syndrome as saviour and sink for population genetic diversity.
Premier J, Fickel J, Heurich M, Kramer-Schadt S. Premier J, et al. Mov Ecol. 2020 Apr 21;8:16. doi: 10.1186/s40462-020-00204-y. eCollection 2020. Mov Ecol. 2020. PMID: 32337047 Free PMC article. - Mind the dbGAP: the application of data mining to identify biological mechanisms.
Wooten EC, Huggins GS. Wooten EC, et al. Mol Interv. 2011 Apr;11(2):95-102. doi: 10.1124/mi.11.2.6. Mol Interv. 2011. PMID: 21540468 Free PMC article. - GWGGI: software for genome-wide gene-gene interaction analysis.
Wei C, Lu Q. Wei C, et al. BMC Genet. 2014 Oct 16;15:101. doi: 10.1186/s12863-014-0101-z. BMC Genet. 2014. PMID: 25318532 Free PMC article.
References
- Archer KJ, Kimes RV. Empirical characterization of random forest variable importance measures. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2008;52:2249–2260.
- Baader E, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated proliferation of tumor cells with receptor-proximal apoptosis defects. Cancer Res. 2005;65:7888–7895. - PubMed
- Baetu TM, et al. Disruption of NF-kappaB signaling reveals a novel role for NF-kappaB in the regulation of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand expression. J. Immunol. 2001;167:3164–3173. - PubMed
- Breiman L. Bagging predictors. Mach. Learn. 1996;24:123–140.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01-GM031575/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG021917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01-HL049609-14/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM031575/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01-AG021917-01A1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL049609/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States