SATB1 dictates expression of multiple genes including IL-5 involved in human T helper cell differentiation - PubMed (original) (raw)
SATB1 dictates expression of multiple genes including IL-5 involved in human T helper cell differentiation
Helena Ahlfors et al. Blood. 2010.
Abstract
Special AT-rich binding protein 1 (SATB1) is a global chromatin organizer and a transcription factor regulated by interleukin-4 (IL-4) during the early T helper 2 (Th2) cell differentiation. Here we show that SATB1 controls multiple IL-4 target genes involved in human Th cell polarization or function. Among the genes regulated by SATB1 is that encoding the cytokine IL-5, which is predominantly produced by Th2 cells and plays a key role in the development of eosinophilia in asthma. We demonstrate that, during the early Th2 cell differentiation, IL-5 expression is repressed through direct binding of SATB1 to the IL-5 promoter. Furthermore, SATB1 knockdown-induced up-regulation of IL-5 is partly counteracted by down-regulating GATA3 expression using RNAi in polarizing Th2 cells. Our results suggest that a competitive mechanism involving SATB1 and GATA3 regulates IL-5 transcription, and provide new mechanistic insights into the stringent regulation of IL-5 expression during human Th2 cell differentiation.
Figures
Figure 1
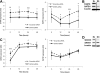
SATB1 expression is down-regulated by knockdown of STAT6 but not by knockdown of GATA3. (A) Cord blood and buffy coat CD4+ T cells were nucleofected with STAT6-siRNA or scrambled control siRNA, and cells were cultured in Th2-polarizing conditions. Cells from 3 to 7 independent experiments were harvested at indicated time points and analyzed using quantitative RT-PCR. The normalized expression (dCt) of STAT6 (left panel) and SATB1 (right panel) mRNA of STAT6-siRNA (solid line) and control siRNA (dashed line) nucleofected cells is presented. (B) Effect of STAT6 knockdown on SATB1 expression at 3-day time point in Th2 condition analyzed with Western blotting. Sc indicates scrambled control siRNA; and S6, STAT6-siRNA. Representative value of 3 independent experiments. Vertical lines have been inserted to indicate a repositioned gel lane. (C) Cord blood CD4+ T cells were nucleofected with GATA3-siRNA or scrambled control siRNA, and cells were cultured in Th2-polarizing conditions. Cells from 3 independent experiments were harvested at indicated time points and analyzed using quantitative RT-PCR. The normalized expression (dCt) of GATA3 (left panel) and SATB1 (right panel) mRNA of GATA3-siRNA (solid line) and control siRNA (dashed line) nucleofected cells is presented. (D) Effect of GATA3 knockdown on SATB1 expression at 1-day time point in Th2 condition analyzed with Western blotting. Sc indicates scrambled control siRNA; and G3, GATA3-siRNA. Representative value of 3 independent experiments. Vertical lines have been inserted to indicate a repositioned gel lane. *P < .05. **P < .01. ***P < .005.
Figure 2
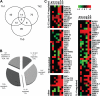
SATB1 target genes during Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation. (A) Expression profiles of SATB1-siRNA/shRNA and scrambled control siRNA/shRNA-treated cells were studied using Illumina bead arrays. Venn diagram shows the number of genes of which the expression was altered on SATB1 knockdown in each Th subtype. (B) The regulation of SATB1 RNAi target genes by cytokines (IL-12 and/or IL-4) and TCR was determined as described in “SATB1 regulates more than 300 genes in developing Th1 and Th2 cells.” (C) Direct SATB1 target genes are common hits of 2 independent approaches: (1) gene expression profiling of SATB1-siRNA/shRNA-treated cells analyzed using Illumina bead arrays and (2) ChIP-on-chip analysis using SATB1-enriched chromatin from cord blood CD4+ T cells polarized to Th1 and Th2 directions for 24 hours. Heat map visualization of direct SATB1 target genes grouped according to their regulation by IL-4, IL-12, and IL-4, T-cell activation (TCR), or none of the above (other). Green represents decreased; and red, increased gene expression (fold change) on SATB1 down-regulation in indicated Th subtypes (Thp, Th0, Th1, or Th2) or across all Th subtypes (Any). *The 2 last columns indicated represent the Th1 or Th2 specific binding of SATB1 detected with ChIP-on-chip approach.
Figure 3
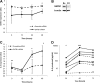
Knockdown of SATB1 greatly induces IL-5 expression in polarizing Th2 cells. Cord blood CD4+ T cells were nucleofected with SATB1-siRNA or scrambled control siRNA and cultured in Th2-polarizing conditions. The cells and the culture media were collected at indicated time points. (A) Samples from 3 independent experiments were analyzed using quantitative RT-PCR. The normalized expression (dCt) of SATB1 mRNA of SATB1-siRNA (solid line) and control siRNA (dashed line) nucleofected cells is presented. (B) Effect of SATB1-siRNA on SATB1 expression at the 24-hour time point in the Th2 condition analyzed with Western blotting. Sc indicates scrambled control siRNA; and S1, SATB1-siRNA. Representative value of 3 independent experiments. Vertical lines have been inserted to indicate a repositioned gel lane. (C) Samples from 3 independent experiments were analyzed using quantitative RT-PCR. The normalized expression (dCt) of IL-5 mRNA of SATB1-siRNA (solid line) and control siRNA (dashed line) nucleofected cells is presented. (D) The culture media of 4 independent experiments was measured for secreted IL-5 using Bio-Plex assay and is expressed as picograms per milliliter. Each symbol type represents an independent experiment. Solid and dashed lines indicate SATB1-siRNA and scrambled control-treated cells, respectively. *P < .05. *P < .01. ***P < .005.
Figure 4
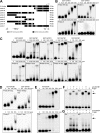
Human IL-5 promoter harbors several SBSs. (A) A schematic of IL-5 promoter sequence and its truncations used in EMSAs as well as location of identified SBSs and previously published GATA3-binding sites. (B) Increasing concentrations of recombinant SATB1 was incubated with the full-length (615-bp) IL-5 probe and probes A, B, and C. (C) Increasing concentrations of recombinant SATB1 were incubated with probes D, E, F, G, H, and I or with the mutated (without SBSs) probes F, G, H, and I. (D) Increasing concentrations of recombinant SATB1 were incubated with the full-length IL-5 probe and probe C as well as with the corresponding mutated (without SBSs) probes. (E) Increasing concentrations of nuclear lysates from cord blood CD4+ T cells polarized to Th1 and Th2 directions for 24 hours were incubated with probe A. (F) Probe A was incubated with 4.0 μg Th1 or Th2 nuclear extract and additionally with anti-SATB1 or normal rabbit IgG. (G) Probe A was incubated with 16.0 μg nuclear extract from cord blood CD4+ T cells nucleofected with scrambled (Scr) control or SATB1-siRNA (siR) and cultured in Th2-polarizing conditions for 24 hours and additionally with anti-SATB1 or normal rabbit IgG. The arrow indicates the lysate-probe complex. *Band shift of the complex. The protein concentrations used with each probe are marked in the figure. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments.
Figure 5
Differential role of SBSs on IL-5 expression. (A) A schematic of IL-5 promoter constructs with different combinations of SBSs deleted used in the reporter assay. (B) Buffy coat CD4+ T cells were nucleofected with pSUPER-H-2Kk-Scramble2-shRNA construct and WT IL-5 luciferase reporter vector or its SBS deleted version. Data represent mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments.
Figure 6
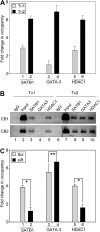
Differential occupancy of SATB1, GATA3, and HDAC1 on IL-5 proximal promoter in Th1 and Th2 cells during T-cell differentiation. (A) Naive CD4+ cells were polarized for 24 hours and subjected to ChIP assay. Occupancy of IL-5 promoter by SATB1, GATA3, and HDAC1 during Th1 ( ) and Th2 (▬) differentiation was monitored by quantitative RT-PCR using primers corresponding to fragment A of the IL-5 promoter. Data represent fold change in occupancy of indicated proteins compared with their corresponding IgG controls, after normalizing for the input chromatin. Each error bar represents SD calculated from triplicates. (B) ChIP-PCR analysis for occupancy of SATB1, GATA3, and HDAC1 on proximal IL-5 promoter in Th1 and Th2 cells was performed as described in “ChIP and ChIP-on-chip.” ChIP-PCR products (∼ 200 bp) from 2 representative cord blood (CB) samples are depicted. Vertical lines have been inserted to indicate a repositioned gel lane. (C) Naive CD4+ T cells nucleofected with scrambled (Scr) control or SATB1-siRNA (siR) were cultured in Th2-polarizing conditions for 24 hours and subjected to ChIP assay. Occupancy of IL-5 promoter by SATB1, GATA3, and HDAC1 during Th2 differentiation in the presence of Scr (
) and Th2 (▬) differentiation was monitored by quantitative RT-PCR using primers corresponding to fragment A of the IL-5 promoter. Data represent fold change in occupancy of indicated proteins compared with their corresponding IgG controls, after normalizing for the input chromatin. Each error bar represents SD calculated from triplicates. (B) ChIP-PCR analysis for occupancy of SATB1, GATA3, and HDAC1 on proximal IL-5 promoter in Th1 and Th2 cells was performed as described in “ChIP and ChIP-on-chip.” ChIP-PCR products (∼ 200 bp) from 2 representative cord blood (CB) samples are depicted. Vertical lines have been inserted to indicate a repositioned gel lane. (C) Naive CD4+ T cells nucleofected with scrambled (Scr) control or SATB1-siRNA (siR) were cultured in Th2-polarizing conditions for 24 hours and subjected to ChIP assay. Occupancy of IL-5 promoter by SATB1, GATA3, and HDAC1 during Th2 differentiation in the presence of Scr ( ) or siR (▬) was monitored by quantitative RT-PCR using primers corresponding to fragment A of IL-5 promoter as described in “Quantitative RT-PCR analyses.” Error bar represents SD calculated from triplicates. *P < .005. **P < .01.
) or siR (▬) was monitored by quantitative RT-PCR using primers corresponding to fragment A of IL-5 promoter as described in “Quantitative RT-PCR analyses.” Error bar represents SD calculated from triplicates. *P < .005. **P < .01.
Figure 7
Induction of IL-5 in SATB1-silenced Th2-polarizing cells is GATA3-dependent. Cord blood CD4+ T cells were nucleofected with siRNA oligonucleotides targeting SATB1 or GATA3 (1.5 μg specific siRNA and 1.5 μg scrambled control siRNA) or both (1.5 μg each siRNA) or only scrambled control siRNA (3 μg) and cells were cultured in Th2-polarizing conditions. (A-C) Samples of the 24-hour time point from 6 independent experiments were analyzed using quantitative RT-PCR. The normalized expression (dCt) of SATB1 (A), GATA3 (B), and IL-5 (C) mRNA of specific siRNA-treated and scrambled control siRNA nucleofected cells is presented. (D) The culture media of the 48-hour time point was measured for secreted IL-5 using Bio-Plex assay and is expressed in picograms per milliliter. Data are mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments. *P < .05. **P < .01. ***P < .005.
Similar articles
- Global regulator SATB1 recruits beta-catenin and regulates T(H)2 differentiation in Wnt-dependent manner.
Notani D, Gottimukkala KP, Jayani RS, Limaye AS, Damle MV, Mehta S, Purbey PK, Joseph J, Galande S. Notani D, et al. PLoS Biol. 2010 Jan 26;8(1):e1000296. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000296. PLoS Biol. 2010. PMID: 20126258 Free PMC article. - Methylation of Gata3 protein at Arg-261 regulates transactivation of the Il5 gene in T helper 2 cells.
Hosokawa H, Kato M, Tohyama H, Tamaki Y, Endo Y, Kimura MY, Tumes DJ, Motohashi S, Matsumoto M, Nakayama KI, Tanaka T, Nakayama T. Hosokawa H, et al. J Biol Chem. 2015 May 22;290(21):13095-103. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.621524. Epub 2015 Apr 10. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25861992 Free PMC article. - c-Myb, Menin, GATA-3, and MLL form a dynamic transcription complex that plays a pivotal role in human T helper type 2 cell development.
Nakata Y, Brignier AC, Jin S, Shen Y, Rudnick SI, Sugita M, Gewirtz AM. Nakata Y, et al. Blood. 2010 Aug 26;116(8):1280-90. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-05-223255. Epub 2010 May 18. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20484083 Free PMC article. - Chromatin remodeling and T helper subset differentiation.
Miyatake S, Arai N, Arai K. Miyatake S, et al. IUBMB Life. 2000 Jun;49(6):473-8. doi: 10.1080/15216540050166990. IUBMB Life. 2000. PMID: 11032239 Review. - 'All things considered': transcriptional regulation of T helper type 2 cell differentiation from precursor to effector activation.
Zeng WP. Zeng WP. Immunology. 2013 Sep;140(1):31-8. doi: 10.1111/imm.12121. Immunology. 2013. PMID: 23668241 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- The Bcl6 target gene microRNA-21 promotes Th2 differentiation by a T cell intrinsic pathway.
Sawant DV, Wu H, Kaplan MH, Dent AL. Sawant DV, et al. Mol Immunol. 2013 Jul;54(3-4):435-42. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2013.01.006. Epub 2013 Feb 13. Mol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23416424 Free PMC article. - An anti-silencer- and SATB1-dependent chromatin hub regulates Rag1 and Rag2 gene expression during thymocyte development.
Hao B, Naik AK, Watanabe A, Tanaka H, Chen L, Richards HW, Kondo M, Taniuchi I, Kohwi Y, Kohwi-Shigematsu T, Krangel MS. Hao B, et al. J Exp Med. 2015 May 4;212(5):809-24. doi: 10.1084/jem.20142207. Epub 2015 Apr 6. J Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 25847946 Free PMC article. - Independent Prognostic Value of Intratumoral Heterogeneity and Immune Response Features by Automated Digital Immunohistochemistry Analysis in Early Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Carcinoma.
Zilenaite D, Rasmusson A, Augulis R, Besusparis J, Laurinaviciene A, Plancoulaine B, Ostapenko V, Laurinavicius A. Zilenaite D, et al. Front Oncol. 2020 Jun 16;10:950. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00950. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32612954 Free PMC article. - Identification of the novel FOXP3-dependent Treg cell transcription factor MEOX1 by high-dimensional analysis of human CD4+ T cells.
Baßler K, Schmidleithner L, Shakiba MH, Elmzzahi T, Köhne M, Floess S, Scholz R, Ohkura N, Sadlon T, Klee K, Neubauer A, Sakaguchi S, Barry SC, Huehn J, Bonaguro L, Ulas T, Beyer M. Baßler K, et al. Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 25;14:1107397. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1107397. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37559728 Free PMC article. - NF-κB Signaling and IL-4 Signaling Regulate SATB1 Expression via Alternative Promoter Usage During Th2 Differentiation.
Khare SP, Shetty A, Biradar R, Patta I, Chen ZJ, Sathe AV, Reddy PC, Lahesmaa R, Galande S. Khare SP, et al. Front Immunol. 2019 Apr 2;10:667. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00667. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31001272 Free PMC article.
References
- Cai S, Han HJ, Kohwi-Shigematsu T. Tissue-specific nuclear architecture and gene expression regulated by SATB1. Nat Genet. 2003;34(1):42–51. - PubMed
- Yasui D, Miyano M, Cai S, Varga-Weisz P, Kohwi-Shigematsu T. SATB1 targets chromatin remodelling to regulate genes over long distances. Nature. 2002;419(6907):641–645. - PubMed
- Pavan Kumar P, Purbey PK, Sinha CK, et al. Phosphorylation of SATB1, a global gene regulator, acts as a molecular switch regulating its transcriptional activity in vivo. Mol Cell. 2006;22(2):231–243. - PubMed
- Lund R, Aittokallio T, Nevalainen O, Lahesmaa R. Identification of novel genes regulated by IL-12, IL-4, or TGF-beta during the early polarization of CD4+ lymphocytes. J Immunol. 2003;171(10):5328–5336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials