Clinical relevance and diversity of two homologous genes encoding glycosyltransferases in Helicobacter pylori - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical relevance and diversity of two homologous genes encoding glycosyltransferases in Helicobacter pylori
Mónica Oleastro et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2010 Aug.
Abstract
Helicobacter pylori is known to be a major cause of peptic ulceration. The jhp0562 gene, encoding a glycosyltransferase involved in the synthesis of the lipopolysaccharide, was associated with peptic ulcer disease (PUD) in children. The beta-(1,3)-galactosyltransferase [beta-(1,3)GalT] gene (jhp0563), involved in Lewis (Le) antigen expression, is highly similar to jhp0562. The clinical significance and diversity of both genes were examined by PCR and sequencing of clinical strains (n = 117) isolated from children with PUD (n = 57) and nonulcer dyspepsia (NUD; n = 60). The prevalence of the jhp0562 gene was significantly higher in strains with a more-virulent profile (strains positive for the cag pathogenicity island [PAI], vacA sl allele, babA, homB, phase-variable gene oipA "on" [i.e., functional], and hopQ I allele). The distribution of genotypes according to clinical outcome showed that the presence of jhp0562 represented one of the greatest risks for the development of PUD. Moreover, the triple-positive genotype for the cag PAI, jhp0562, and homB provided the best discriminatory model for distinguishing PUD and NUD outcomes in children. Sequence and in vitro expression analyses of jhp0562 showed the presence of a complete open reading frame, while the beta-(1,3)GalT gene was shown to be a phase-variable gene. The regular presence of jhp0562 in strains with a truncated beta-(1,3)GalT gene suggests that jhp0562 may also be implicated in the regulation of Le antigen expression. Overall, the results of this study suggest that the jhp0562 gene is of great clinical relevance, being a useful comarker for severe H. pylori-related disease and contributing to host adaptation.
Figures
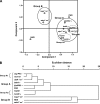
FIG. 1.
Analysis of the association of Helicobacter pylori virulence factors between themselves and according to clinical outcome. Complete data (for the cag PAI, vacA s1 allele, babA, homB, oipA and sabA status, and hopQ and hopZ alleles) were available for 83 H. pylori strains isolated from children with peptic ulcer disease (n = 41) and nonulcer dyspepsia (n = 42). (A) Principal-component analysis plot. (B) Dendrogram constructed using the average aggregation method and Euclidian distance.
FIG. 2.
jhp0562 and β-(1,3)GalT gene profiles observed in Helicobacter pylori strains. The gene profiles were determined by PCR performed on 117 Helicobacter pylori strains and amplicons were separated on a 1.5% agarose gel. MW, molecular weight marker X174 RF DNA/HaeIII fragments (72 to 1,353 bp).
Similar articles
- Prevalence of two homologous genes encoding glycosyltransferases of Helicobacter pylori in the United States and Japan.
Matsuda M, Shiota S, Matsunari O, Watada M, Murakami K, Fujioka T, Yamaoka Y. Matsuda M, et al. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011 Sep;26(9):1451-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2011.06779.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 21592227 Free PMC article. - Novel functions for glycosyltransferases Jhp0562 and GalT in Lewis antigen synthesis and variation in Helicobacter pylori.
Pohl MA, Kienesberger S, Blaser MJ. Pohl MA, et al. Infect Immun. 2012 Apr;80(4):1593-605. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00032-12. Epub 2012 Jan 30. Infect Immun. 2012. PMID: 22290141 Free PMC article. - Investigation of the association between clinical outcome and the cag pathogenicity-island and other virulence genes of Helicobacter pylori isolates from patients with dyspepsia in Eastern Turkey.
Ozbey G, Demirel U, Aygun C, Ertas HB. Ozbey G, et al. Braz J Microbiol. 2014 Mar 10;44(4):1267-74. doi: 10.1590/s1517-83822013000400034. eCollection 2013 Dec. Braz J Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24688521 Free PMC article. - Intact cag pathogenicity island of Helicobacter pylori without disease association in Kolkata, India.
Patra R, Chattopadhyay S, De R, Datta S, Chowdhury A, Ramamurthy T, Nair GB, Berg DE, Mukhopadhyay AK. Patra R, et al. Int J Med Microbiol. 2011 Apr;301(4):293-302. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2010.10.003. Epub 2010 Dec 30. Int J Med Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21195664 Free PMC article. - Helicobacter pylori oipA genetic diversity and its associations with both disease and cagA, vacA s, m, and i alleles among Bulgarian patients.
Markovska R, Boyanova L, Yordanov D, Gergova G, Mitov I. Markovska R, et al. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011 Dec;71(4):335-40. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2011.08.008. Epub 2011 Sep 19. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21937185
Cited by
- In Vivo Genome and Methylome Adaptation of _cag_-Negative Helicobacter pylori during Experimental Human Infection.
Estibariz I, Ailloud F, Woltemate S, Bunk B, Spröer C, Overmann J, Aebischer T, Meyer TF, Josenhans C, Suerbaum S. Estibariz I, et al. mBio. 2020 Aug 25;11(4):e01803-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01803-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32843556 Free PMC article. - Association of presence/absence and on/off patterns of Helicobacter pylori oipA gene with peptic ulcer disease and gastric cancer risks: a meta-analysis.
Liu J, He C, Chen M, Wang Z, Xing C, Yuan Y. Liu J, et al. BMC Infect Dis. 2013 Nov 20;13:555. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-555. BMC Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 24256489 Free PMC article. - Ulcerogenic Helicobacter pylori strains isolated from children: a contribution to get insight into the virulence of the bacteria.
Vitoriano I, Saraiva-Pava KD, Rocha-Gonçalves A, Santos A, Lopes AI, Oleastro M, Roxo-Rosa M. Vitoriano I, et al. PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e26265. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026265. Epub 2011 Oct 19. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22039453 Free PMC article. - The Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori Virulence Factors in Bhutan, Vietnam, and Myanmar Is Related to Gastric Cancer Incidence.
Trang TT, Shiota S, Matsuda M, Binh TT, Suzuki R, Vilaichone RK, Mahachai V, Tshering L, Dung HD, Uchida T, Matsunari O, Myint T, Khien VV, Yamaoka Y. Trang TT, et al. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:830813. doi: 10.1155/2015/830813. Epub 2015 May 18. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26090448 Free PMC article. - BabA-mediated adherence of pediatric ulcerogenic H. pylori strains to gastric mucins at neutral and acidic pH.
Quintana-Hayashi MP, Rocha R, Padra M, Thorell A, Jin C, Karlsson NG, Roxo-Rosa M, Oleastro M, Lindén SK. Quintana-Hayashi MP, et al. Virulence. 2018;9(1):1699-1717. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2018.1532243. Virulence. 2018. PMID: 30298790 Free PMC article.
References
- Akopyants, N. S., S. W. Clifton, D. Kersulyte, J. E. Crabtree, B. E. Youree, C. A. Reece, N. O. Bukanov, E. S. Drazek, B. A. Roe, and D. E. Berg. 1998. Analyses of the cag pathogenicity island of Helicobacter pylori. Mol. Microbiol. 28:37-53. - PubMed
- Alm, R. A., L. S. L. Ling, D. T. Moir, B. L. King, E. D. Brown, P. C. Doig, D. R. Smith, B. Noonan, B. C. Guild, B. L. deJonge, G. Carmel, P. J. Tummino, A. Caruso, M. Uria-Nickelsen, D. M. Mills, C. Ives, R. Gibson, D. Merberg, S. D. Mills, Q. Jiang, D. E. Taylor, G. F. Vovis, and T. J. Trust. 1999. Genomic-sequence comparison of two unrelated isolates of the human gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature 397:176-180. - PubMed
- Appelmelk, B. J., M. C. Martino, E. Veenhof, M. A. Monteiro, J. J. Maaskant, R. Negrini, F. Lindh, M. Perry, G. Del Giudice, and C. M. J. E. Vandenbroucke-Grauls. 2000. Phase variation in H type I and Lewis a epitopes of Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide. Infect. Immun. 68:5928-5932. - PMC - PubMed
- Atherton, J. C., P. Cao, R. M. Peek, M. K. R. Tummuru, M. J. Blaser, and T. L. Cover. 1995. Mosaicism in vacuolating cytotoxin alleles of Helicobacter pylori—association of specific vacA types with cytotoxin production and peptic ulceration. J. Biol. Chem. 270:17771-17777. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical