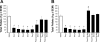Dose combinations of exendin-4 and salmon calcitonin produce additive and synergistic reductions in food intake in nonhuman primates - PubMed (original) (raw)
Dose combinations of exendin-4 and salmon calcitonin produce additive and synergistic reductions in food intake in nonhuman primates
Nicholas T Bello et al. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010 Sep.
Abstract
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and amylin mediate the feedback control of eating by seemingly separate, but overlapping mechanisms. This study examined the effects of combined doses of the GLP-1 agonist, exendin-4 (Ex-4), and the amylin analog, salmon calcitonin (sCT), on food intake and meal patterns in adult male rhesus monkeys. Monkeys received intramuscular injections of Ex-4 (0, 0.1, 0.32, or 0.56 microg/kg), sCT (0, 0.1, or 0.32 microg/kg), or combinations thereof before a 6-h daily access to food. Dose combinations produced reductions in food intake that were significantly greater than those produced by the individual doses. Surface plots of the hourly intake indicated a synergistic interaction at lower doses of Ex-4 and sCT during the first 4 h of feeding and additive effects at hours 5 and 6. Meal pattern analysis revealed the combinational doses reduced average meal size and meal frequency by additive interactions, whereas infra-additive effects were apparent at lower doses for first meal size. Combinational doses were further characterized by administration of repeated daily injections of 0.56 microg/kg Ex-4 + 0.32 microg/kg sCT for 5 days. This resulted in sustained reductions in daily food intake (>70% from saline baseline) for 5 days with residual reductions ( approximately 48% from saline baseline) persisting on day 1 following the injections. In contrast, when pair-fed an identical amount of daily food, there was a compensatory food intake increase on day 1 following the pair-feeding ( approximately 132% of saline baseline). Such data suggest Ex-4 and sCT interact in an overall additive fashion to reduce food intake and further the understanding of how GLP-1 and amylin agonist combinations influence feeding behavior.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Quadratic-fit surface plots for effects of peripheral doses of exendin-4 (Ex-4), salmon calcitonin (sCT), and Ex-4 + sCT on cumulative hourly food intake of rhesus monkeys (n = 4) consuming 1-g pellets. Data are expressed as hourly intake for the corresponding hour of the saline intake (percent saline) from Table 1. The surface plots revealed a synergistic shape for low doses of each compound for hours 1 through 4 demonstrated by the pattern of the surface partitions that are not equal in size. For hours 5 and 6, the surface plots demonstrated an additive relationship. Note the surface partitions are equal in size and size for hours 5 and 6. Daily food access was for 6 h represents the total daily intake.
Fig. 2.
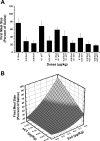
Effects of peripheral doses of Ex-4, sCT, and Ex4 + sCT on first meal size in rhesus monkeys consuming 1-g pellets. First meal sizes are expressed as a percentage of the 3-day saline average meal size (means ± SE). A: although there were overall significance differences for single and combinational doses, post hoc, there were no significant difference between single doses and the combinational doses. B: An infra-additive relationship for the 0.1 μg/kg of Ex-4 and the sCT was apparent, while a ceiling effect was evident in the flattening out of the surface plot at the higher doses of both compounds.
Fig. 3.
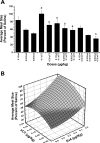
Effects of peripheral doses of Ex-4, sCT, and Ex4 + sCT on average meal size in rhesus monkeys consuming 1-g pellets. Average meal sizes are expressed as a percentage of the 3-day saline average meal size (means ± SE). a,bSimilar letters indicate significance (P < 0.05) from each other. The response surface plot has a somewhat similar additive pattern as hours 5 and 6 in Fig. 1.
Fig. 4.
Effects of repeated 5-day administration of 0.56 μg/kg Ex-4 + 0.32 μg/kg sCT on food intake in rhesus monkeys consuming 1-g pellets. A: daily intakes (means ± SE) were reduced from saline baseline on injection days 1 through 5 (*P < 0.001). Daily intakes also remained reduced from saline baseline on postinjection day 1 (*P < 0.001). B: pair-feeding for 5 days produced a similar reduction in food intake, but a significant rebound in daily food intake on post-pair-fed day 1 (#P < 0.05).
References
- Aaboe K, Krarup T, Madsbad S, Holst JJ. GLP-1: physiological effects and potential therapeutic applications. Diabetes Obes Metab 10: 994–1003, 2008 - PubMed
- Ai G, Chen Z, Shan C, Che J, Hou Y, Cheng Y. Single- and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of exendin-4 in rhesus monkeys. Int J Pharm 353: 56–64, 2008 - PubMed
- Brubaker PL, Drucker DJ. Minireview: Glucagon-like peptides regulate cell proliferation and apoptosis in the pancreas, gut, and central nervous system. Endocrinology 145: 2653–2659, 2004 - PubMed
- Chan JL, Roth JD, Weyer C. It takes two to tango: combined amylin/leptin agonism as a potential approach to obesity drug development. J Investig Med 57: 777–783, 2009 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources