Cytotoxic effect of trans-cinnamaldehyde on human leukemia K562 cells - PubMed (original) (raw)
Cytotoxic effect of trans-cinnamaldehyde on human leukemia K562 cells
Jia-hua Zhang et al. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010 Jul.
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effects of trans-cinnamaldehyde (TCA) on the human leukemia K562 cell line and the cytotoxicity of cytokine-induced killer (CIK) cells against K562 cells.
Methods: Apoptosis, Fas expression, and mitochondrial transmembrane potential in K652 cells were analyzed using flow cytometry. K562 cells were labeled with CFSE. The cytotoxic effect of expanded CIK cells on CFSE-labeled K562 cells was determined by FACS flow cytometry.
Results: Treatment with TCA 180 micromol/L for 9 h induced apoptosis in 8.9%+/-1.23% of K562 cells. Treatment with 120 or 180 micromol/L TCA for 24 h significantly increased the apoptotic cells to 18.63%+/-1.42 % and 38.98%+/-2.74%, respectively. TCA significantly upregulates Fas expression and decreases mitochondrial transmembrane potential in K562 cells. TCA treatment at 120 and 180 micromol/L for 9 h enhanced the percentage of lysis of K562 cells by expanded CIK cells from 34.84%+/-2.13% to 48.21%+/-2.22 % and 64.81%+/-3.22% at the E:F ratio of 25:1 and from 49.26%+/-3.22% to 57.81%+/-5.13% and 73.36%+/-5.98% at E:F ratio of 50:1.
Conclusion: TCA exerts cytotoxic effects on human leukemia K562 cells by inducing apoptosis and synergizing the cytotoxicity of CIK cells against K562 cells. These properties of TCA are beneficial to the treatment of leukemia, even in the patients who have received hematopoietic stem cells transplantation (HSCT).
Figures
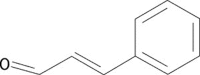
Figure 1
Chemical structure of TCA.
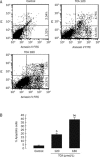
Figure 2
TCA induced significant apoptosis in K562 cells in a dose-dependent manner at 24 h. A) Original flow cytometry data. Medium supplemented with 0 μmol/L TCA (Control); Medium supplemented with 120 μmol/L TCA (TCA 120); Medium supplemented with 180 μmol/L TCA (TCA 180). B) Percentage of apoptosis in K562 cells. n_=6. Mean±SD. b_P<0.05 vs Control. e_P_<0.05 vs 120 μmol/L TCA.
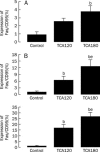
Figure 3
TCA upregulated expression of Fas/CD95 in K562 cells. A) Effect of TCA treatment for 4 h on expression of Fas/CD95 in K562 cells. B) Effect of TCA treatment for 9 h on expression of Fas/CD95 in K562 cells. C) Effect of TCA treatment for 24 h on expression of Fas/CD95 in K562 cells. n_=5. Mean±SD. b_P<0.05 vs Control. e_P_<0.05 vs 120 μmol/L TCA.
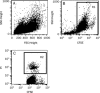
Figure 4
Lysis quantitation by the CFSE/PI assay. A) K562 cells are not distinct in the ungated FSC/SSC dot plot. B) Selection of K562 target cells (R1 gate) according to their CFSE-positivity on the SSC/CFSE dot plot. C) Quantitation of target cell lysis on the CFSE/PI dot plot. Dead K562 cells (R2 gate) are positive for both PI and CFSE.
Figure 5
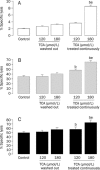
TCA synergized the cytotoxicity of CIK cells to K562 cells. A) Effect of TCA on cytotoxic activity by CIK cells to K562 cells at the indicated effector:target ratio of 0:1. B) Effect of TCA on cytotoxic activity by CIK cells to K562 cells at the indicated effector: target ratio of 25:1. C) Effect of TCA on cytotoxic activity by CIK cells to K562 at the indicated effector: target ratio of 50:1. n_=5. Mean±SD. b_P<0.05 vs Control. e_P_<0.05 vs 120 μmol/L TCA treated continuously. TCA washout group: target cells were pretreated with TCA for 4 h and then washed out in the presence of CIK cells. TCA continuously treated group: target cells were pretreated with TCA for 4 h and then for another 5 h in the presence of CIK cells.
Similar articles
- [Effects and mechanism on anti-leukemic activity of cytokine-induced killer cells with an endogenous expression of interleukin-21].
Zhao N, Zhao MF, Rajbhandary S, Lu WY, Zhu HB, Ma L, You Q, Xiao X, Deng Q, Li YM. Zhao N, et al. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2013 Jan 22;93(4):293-9. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23578511 Chinese. - [Cytokine-induced killer cells induce apoptosis of K562 cells expressed bcr-abl].
Cen XN, Zhu P, Shi YJ, Ren YL, Ma MX, Yu JR. Cen XN, et al. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2002 Jun;10(3):201-4. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2002. PMID: 12513785 Chinese. - Polytrichum commune L.ex Hedw ethyl acetate extract-triggered perturbations in intracellular Ca²⁺ homeostasis regulates mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis.
Yuan W, Cheng X, Wang P, Jia Y, Liu Q, Tang W, Wang X. Yuan W, et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Aug 22;172:410-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.07.002. Epub 2015 Jul 4. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26151243 - CIK cells from recurrent or refractory AML patients can be efficiently expanded in vitro and used for reduction of leukemic blasts in vivo.
Wang Y, Bo J, Dai HR, Lu XC, Lv HY, Yang B, Wang T, Han WD. Wang Y, et al. Exp Hematol. 2013 Mar;41(3):241-52.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2012.10.014. Epub 2012 Oct 30. Exp Hematol. 2013. PMID: 23123634 - [Thymoglobulin efficiently expands cytokine-induced killer cells in a clinical-grade culture protocol].
Chen W, Lin D, Jiang Z, Yang Z, Song S, Zhou J, Zhou L, Sun Y, Yu H, Ma D. Chen W, et al. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2014 Jul;30(7):681-5, 690. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25001928 Chinese.
Cited by
- Cinnamaldehyde: Pharmacokinetics, anticancer properties and therapeutic potential (Review).
Han R, Li X, Gao X, Lv G. Han R, et al. Mol Med Rep. 2024 Sep;30(3):163. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13287. Epub 2024 Jul 12. Mol Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 38994757 Free PMC article. Review. - Natural Compounds and Breast Cancer: Chemo-Preventive and Therapeutic Capabilities of Chlorogenic Acid and Cinnamaldehyde.
Olayiwola Y, Gollahon L. Olayiwola Y, et al. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Mar 11;17(3):361. doi: 10.3390/ph17030361. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38543147 Free PMC article. Review. - Inhibitory effect of temozolomide on apoptosis induction of cinnamaldehyde in human glioblastoma multiforme T98G cell line.
Abband H, Dabirian S, Jafari A, Nasiri M, Nasiri E. Abband H, et al. Anat Cell Biol. 2024 Mar 31;57(1):85-96. doi: 10.5115/acb.23.159. Epub 2023 Nov 22. Anat Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 37994040 Free PMC article. - In Vitro Evaluation of ALDH1A3-Affinic Compounds on Breast and Prostate Cancer Cell Lines as Single Treatments and in Combination with Doxorubicin.
Abusara OH, Ibrahim AIM, Issa H, Hammad AM, Ismail WH. Abusara OH, et al. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Mar 6;45(3):2170-2181. doi: 10.3390/cimb45030139. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36975509 Free PMC article. - Design, Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and In Silico Study of Benzyloxybenzaldehyde Derivatives as Selective ALDH1A3 Inhibitors.
Ibrahim AIM, Ikhmais B, Batlle E, AbuHarb WK, Jha V, Jaradat KT, Jiménez R, Pequerul R, Parés X, Farrés J, Pors K. Ibrahim AIM, et al. Molecules. 2021 Sep 23;26(19):5770. doi: 10.3390/molecules26195770. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34641313 Free PMC article.
References
- Ringdén O. Immunotherapy by allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Adv Cancer Res. 2007;97:25–60. - PubMed
- Nencioni A, Grünebach F, Patrone F, Ballestrero A, Brossart P. Proteasome: inhibitors antitumor effects and beyond. Leukemia. 2007;21:30–6. - PubMed
- Ka H, Park HJ, Jung HJ, Choi JW, Cho KS, Ha J, et al. Cinnamaldehyde induces apoptosis by ROS-mediated mitochondrial permeability transition in human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells. Cancer Lett. 2003;196:143–52. - PubMed
- Lee CW, Lee SH, Lee JW, Ban JO, Lee SY, Yoo HS, et al. 2-hydroxy cinnamaldehyde inhibits SW620 colon cancer cell growth through AP-1 inactivation. J Pharmacol Sci. 2007;104:19–28. - PubMed
- Koh WS, Yoon SY, Kwon BM, Jeong TC, Nam KS, Han MY. Cinnamaldehyde inhibits lymphocyte proliferation and modulates T-cell differentiation. Int J immunopharmacol. 1998;20:643–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous