Gemcitabine plus bevacizumab compared with gemcitabine plus placebo in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: phase III trial of the Cancer and Leukemia Group B (CALGB 80303) - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical Trial
. 2010 Aug 1;28(22):3617-22.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.28.1386. Epub 2010 Jul 6.
Donna Niedzwiecki, Donna Hollis, Susan Sutherland, Deborah Schrag, Herbert Hurwitz, Federico Innocenti, Mary Frances Mulcahy, Eileen O'Reilly, Timothy F Wozniak, Joel Picus, Pankaj Bhargava, Robert J Mayer, Richard L Schilsky, Richard M Goldberg
Affiliations
- PMID: 20606091
- PMCID: PMC2917317
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2010.28.1386
Clinical Trial
Gemcitabine plus bevacizumab compared with gemcitabine plus placebo in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: phase III trial of the Cancer and Leukemia Group B (CALGB 80303)
Hedy Lee Kindler et al. J Clin Oncol. 2010.
Abstract
Purpose: The combination of gemcitabine plus bevacizumab produced a 21% response rate and a median survival of 8.8 months in a multicenter phase II trial in patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer. These encouraging data led Cancer and Leukemia Group B (CALGB) to conduct a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized phase III trial of gemcitabine/bevacizumab versus gemcitabine/placebo in advanced pancreatic cancer patients.
Patients and methods: Eligible patients had no prior therapy for advanced disease, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status 0 to 2, no tumor invasion of adjacent organs, and no increased bleeding risk. The primary end point was overall survival. Patients were stratified by performance status, extent of disease, and prior radiotherapy. Patients received gemcitabine at 1,000 mg/m(2) over 30 minutes on days 1, 8, and 15 every 28 days and bevacizumab at 10 mg/kg or placebo on days 1 and 15 every 28 days.
Results: Between June 2004 and April 2006, 602 patients were enrolled onto the study and 535 were treated. Median overall survival was 5.8 months for gemcitabine/bevacizumab and 5.9 months for gemcitabine/placebo (P = .95). Median progression-free survival was 3.8 and 2.9 months, respectively (P = .07). Overall response rates were 13% and 10%, respectively. Patients with a performance status of 0, 1, and 2 survived a median of 7.9, 4.8, and 2.4 months, respectively. The only statistically significant differences in grades 3 and 4 toxicity occurred for hypertension (10% v 3%; P < .001) and proteinuria (5% v 1%; P = .002); venous thrombosis grade > or = 3 was equivalent in both arms (14% and 15%, respectively).
Conclusion: The addition of bevacizumab to gemcitabine does not improve survival in advanced pancreatic cancer patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
Fig 1.
CONSORT diagram. ITT, intent to treat; Alt, alternative; PD, progressive disease.
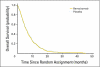
Fig 2.
Overall survival by treatment arm.
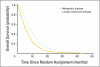
Fig 3.
Overall survival by disease extent.
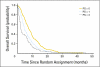
Fig 4.
Overall survival by performance status (PS).
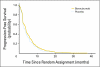
Fig 5.
Progression-free survival by treatment arm.
Similar articles
- Multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized phase II trial of gemcitabine/cisplatin plus bevacizumab or placebo in patients with malignant mesothelioma.
Kindler HL, Karrison TG, Gandara DR, Lu C, Krug LM, Stevenson JP, Jänne PA, Quinn DI, Koczywas MN, Brahmer JR, Albain KS, Taber DA, Armato SG 3rd, Vogelzang NJ, Chen HX, Stadler WM, Vokes EE. Kindler HL, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2012 Jul 10;30(20):2509-15. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.41.5869. Epub 2012 Jun 4. J Clin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22665541 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Phase II trial of bevacizumab plus gemcitabine in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer.
Kindler HL, Friberg G, Singh DA, Locker G, Nattam S, Kozloff M, Taber DA, Karrison T, Dachman A, Stadler WM, Vokes EE. Kindler HL, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2005 Nov 1;23(31):8033-40. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.01.9661. J Clin Oncol. 2005. PMID: 16258101 Clinical Trial. - Phase II study of bevacizumab with concurrent capecitabine and radiation followed by maintenance gemcitabine and bevacizumab for locally advanced pancreatic cancer: Radiation Therapy Oncology Group RTOG 0411.
Crane CH, Winter K, Regine WF, Safran H, Rich TA, Curran W, Wolff RA, Willett CG. Crane CH, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2009 Sep 1;27(25):4096-102. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.21.8529. Epub 2009 Jul 27. J Clin Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19636002 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Phase III trial of bevacizumab in combination with gemcitabine and erlotinib in patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer.
Van Cutsem E, Vervenne WL, Bennouna J, Humblet Y, Gill S, Van Laethem JL, Verslype C, Scheithauer W, Shang A, Cosaert J, Moore MJ. Van Cutsem E, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2009 May 1;27(13):2231-7. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.20.0238. Epub 2009 Mar 23. J Clin Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19307500 Clinical Trial. - Can inhibition of angiogenic pathways increase the efficacy of intravenous 5-fluorouracil-based regimens?
Kabbinavar FF, Ellis LM. Kabbinavar FF, et al. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2004 Oct;4 Suppl 2:S69-73. doi: 10.3816/ccc.2004.s.011. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2004. PMID: 15479482 Review.
Cited by
- Hypofractionated ablative radiotherapy for locally advanced pancreatic cancer.
Crane CH. Crane CH. J Radiat Res. 2016 Aug;57 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):i53-i57. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrw016. Epub 2016 Mar 29. J Radiat Res. 2016. PMID: 27029741 Free PMC article. Review. - CD44+ Circulating Tumor Endothelial Cells Indicate Poor Prognosis in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma After Radical Surgery: A Pilot Study.
Xing C, Li Y, Ding C, Wang S, Zhang H, Chen L, Li P, Dai M. Xing C, et al. Cancer Manag Res. 2021 Jun 1;13:4417-4431. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S309115. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 34103996 Free PMC article. - Increased risk of hemorrhage in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with bevacizumab: An updated meta-analysis of 12 randomized controlled trials.
Zhu X, Tian X, Yu C, Hong J, Fang J, Chen H. Zhu X, et al. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Aug;95(34):e4232. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004232. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27559943 Free PMC article. Review. - Systemic Therapy for Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer-Current Landscape and Future Directions.
Netto D, Frizziero M, Foy V, McNamara MG, Backen A, Hubner RA. Netto D, et al. Curr Oncol. 2024 Sep 4;31(9):5206-5223. doi: 10.3390/curroncol31090385. Curr Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39330013 Free PMC article. Review. - Phytochemicals in Pancreatic Cancer Treatment: A Machine Learning Study.
Genc DE, Ozbek O, Oral B, Yıldırım R, Ileri Ercan N. Genc DE, et al. ACS Omega. 2023 Dec 27;9(1):413-421. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c05861. eCollection 2024 Jan 9. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 38222639 Free PMC article.
References
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–249. - PubMed
- Burris HA, Moore MJ, Andersen J, 3rd, et al. Improvements in survival and clinical benefit with gemcitabine as first-line therapy for patients with advanced pancreas cancer: A randomized trial. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15:2403–2413. - PubMed
- Berlin JD, Catalano P, Thomas JP, et al. Phase III study of gemcitabine in combination with fluorouracil versus gemcitabine alone in patients with advanced pancreatic carcinoma: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Trial E2297. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:3270–3275. - PubMed
- Rocha Lima CM, Green MR, Rotche R, et al. Irinotecan plus gemcitabine results in no survival advantage compared with gemcitabine monotherapy in patients with locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer despite increased tumor response rate. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:3776–3783. - PubMed
- Van Cutsem E, van de Velde H, Karasek P, et al. Phase III trial of gemcitabine plus tipifarnib compared with gemcitabine plus placebo in advanced pancreatic cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:1430–1438. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA33601/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA 32291/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA47577/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA41287/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA033601/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA017145/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045418/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA077440/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA041287/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA47559/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA45418/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA21115/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA31946/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA047577/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA032291/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA021115/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA031946/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA77651/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA77440/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA17145/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA047559/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA077651/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous