Geodesic Shooting for Computational Anatomy - PubMed (original) (raw)
Geodesic Shooting for Computational Anatomy
Michael I Miller et al. J Math Imaging Vis. 2006.
Abstract
Studying large deformations with a Riemannian approach has been an efficient point of view to generate metrics between deformable objects, and to provide accurate, non ambiguous and smooth matchings between images. In this paper, we study the geodesics of such large deformation diffeomorphisms, and more precisely, introduce a fundamental property that they satisfy, namely the conservation of momentum. This property allows us to generate and store complex deformations with the help of one initial "momentum" which serves as the initial state of a differential equation in the group of diffeomorphisms. Moreover, it is shown that this momentum can be also used for describing a deformation of given visual structures, like points, contours or images, and that, it has the same dimension as the described object, as a consequence of the normal momentum constraint we introduce.
Figures
Figure 1
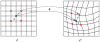
Here is represented the deformation obtained by pulling back the Eulerian frame associated with ve and represents pictorially the adjoint action.
Figure 2
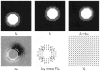
Three random deformations of an image.
Figure 3
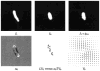
Figure shows objects under translation (column 1), scale (column 2), and mitochondria 1 and 2.
Figure 4
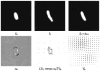
Rows 1, 2: Results from translation experiment. Panels 1, 2, and 3 show _I_0, _I_1, _I_0 ◦ _φ_10. Panels 4, 5 and 6 show _α_0, _Lv_0 versus _α_0∇_I_0, and _V_0 and _L_−1_α_∇ _I_0.
Figure 5
Rows 1, 2: Results from scale experiment. Panels 1, 2, and 3 show _I_0, _I_1, _I_0 ◦; _φ_10. Panels 4, 5 and 6 show _α_0, _Lv_0 versus _α_0∇_I_0, and _V_0 and _L_−1_α_∇ _I_0.
Figure 6
Results from mitochondria 2. Panels 1, 2, and 3 show _I_1, _I_0, _I_1 ◦ _φ_10. Panels 4, 5 and 6 show _α_0, _LV_0 versus _α_0∇ _I_0, and _V_0.
Figure 7
Results from mitochondria 1. Panels 1, 2, and 3 show _I_0, _I_1, _I_0 ◦ _φ_10. Panels 4, 5 and 6 show _α_0, _LV_0 versus _α_0∇ _I_0, and _V_0.
Similar articles
- Statistics on diffeomorphisms via tangent space representations.
Vaillant M, Miller MI, Younes L, Trouvé A. Vaillant M, et al. Neuroimage. 2004;23 Suppl 1:S161-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.07.023. Neuroimage. 2004. PMID: 15501085 - Splines for diffeomorphisms.
Singh N, Vialard FX, Niethammer M. Singh N, et al. Med Image Anal. 2015 Oct;25(1):56-71. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2015.04.012. Epub 2015 Apr 18. Med Image Anal. 2015. PMID: 25980676 - Diffeomorphometry and geodesic positioning systems for human anatomy.
Miller MI, Younes L, Trouvé A. Miller MI, et al. Technology (Singap World Sci). 2014 Mar;2(1):36. doi: 10.1142/S2339547814500010. Technology (Singap World Sci). 2014. PMID: 24904924 Free PMC article. - Soliton dynamics in computational anatomy.
Holm DD, Ratnanather JT, Trouvé A, Younes L. Holm DD, et al. Neuroimage. 2004;23 Suppl 1:S170-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.07.017. Neuroimage. 2004. PMID: 15501086 Review. - On the metrics and euler-lagrange equations of computational anatomy.
Miller MI, Trouve A, Younes L. Miller MI, et al. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2002;4:375-405. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bioeng.4.092101.125733. Epub 2002 Mar 22. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2002. PMID: 12117763 Review.
Cited by
- Parametric Surface Diffeomorphometry for Low Dimensional Embeddings of Dense Segmentations and Imagery.
Tward D, Miller M, Trouve A, Younes L. Tward D, et al. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2017 Jun;39(6):1195-1208. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2578317. Epub 2016 Jun 8. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2017. PMID: 27295651 Free PMC article. - Symmetric diffeomorphic modeling of longitudinal structural MRI.
Ashburner J, Ridgway GR. Ashburner J, et al. Front Neurosci. 2013 Feb 5;6:197. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2012.00197. eCollection 2012. Front Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23386806 Free PMC article. - Shape and diffusion tensor imaging based integrative analysis of the hippocampus and the amygdala in Alzheimer's disease.
Tang X, Qin Y, Wu J, Zhang M, Zhu W, Miller MI. Tang X, et al. Magn Reson Imaging. 2016 Oct;34(8):1087-99. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2016.05.001. Epub 2016 May 20. Magn Reson Imaging. 2016. PMID: 27211255 Free PMC article. - Fast Geodesic Regression for Population-Based Image Analysis.
Hong Y, Golland P, Zhang M. Hong Y, et al. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2017 Sep;10433:317-325. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-66182-7_37. Epub 2017 Sep 4. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2017. PMID: 29379899 Free PMC article. - Inferring brain variability from diffeomorphic deformations of currents: an integrative approach.
Durrleman S, Pennec X, Trouvé A, Thompson P, Ayache N. Durrleman S, et al. Med Image Anal. 2008 Oct;12(5):626-37. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2008.06.010. Epub 2008 Jun 21. Med Image Anal. 2008. PMID: 18658005 Free PMC article.
References
- Arnold VI. Mathematical Methods of Classical Mechanics. 1. Springer; 1978. 1989.
- Arnold V, Khesin B. Topological methods in hydrodynamics. Ann Rev Fluid Mech. 1992;24:145–166.
- Arnold VI. Sur la géometrie differentielle des groupes de Lie de dimension infinie et ses applications à l’hydrodynamique des fluides parfaits. Ann Inst Fourier (Grenoble) 1966;1:319–361.
- Beg MF, Miller MI, Trouvé A, Younes L. Computing large deformation metric mappings via geodesics flows of diffeomorphisms. Int J Comp Vis. 2005 February;61(2):139–157.
- Camion V, Younes L. Geodesic interpolating splines. In: Figueiredo MAT, Zerubia J, Jain AK, editors. EMM-CVPR 2001, Vol. 2134 of Lecture Notes in Computer Sciences. Springer-Verlag; 2001. pp. 513–527.
Grants and funding
- U24 RR021382/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR015241/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH071616/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR015241-078616/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U24 RR021382-04/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH071616-01/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources