Circulating microRNA in body fluid: a new potential biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Circulating microRNA in body fluid: a new potential biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis
Nobuyoshi Kosaka et al. Cancer Sci. 2010 Oct.
Abstract
In the past several years, the importance of microRNA (miRNA) in cancer cells has been recognized. Proper control of miRNA expression is essential for maintaining a steady state of the cellular machinery. Recently, it was discovered that extracellular miRNAs circulate in the blood of both healthy and diseased patients, although ribonuclease is present in both plasma and serum. Most of the circulating miRNAs are included in lipid or lipoprotein complexes, such as apoptotic bodies, microvesicles, or exosomes, and are, therefore, highly stable. The existence of circulating miRNAs in the blood of cancer patients has raised the possibility that miRNAs may serve as a novel diagnostic marker. However, the secretory mechanism and biological function, as well as the meaning of the existence of extracellular miRNAs, remain largely unclear. In this review, we summarize the usefulness of circulating miRNA for cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutics. Furthermore, we propose a mechanism for the secretion and incorporation of miRNA into the cells.
© 2010 Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
Figure 1
miRNAs in human body fluids are non‐invasive diagnostic markers for cancers. Many kinds of circulating miRNAs have been reported in various types of cancers. However, certain cancers cannot be diagnosed by known serum biomarkers. In such cases, circulating miRNAs in serum, saliva, and urine are good candidates for future use. AML, acute myeloid leukemia; DLBCL, diffuse large B‐cell lymphoma.
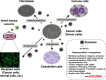
Figure 2
Secreted miRNAs contained in exosomes potentially influence microenvironmental cells, including immune cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblast cells. Soluble factors, such as cytokines and chemokines, have been shown to be intercellular communication tools between cancer and microenvironmental cells. In addition, recent observations have indicated that exosomes also function as an intercellular communication tool between them. For instance, exosomes, which are secreted by living tumor cells, contain and transfer tumor antigens to dendritic cells, and dendritic cells then induce potent CD8+ T‐cell‐dependent antitumor effects on syngenic and allogeneic established mouse tumors. In addition, this transforming activity can possibly be transferred via exosome. Furthermore, miRNA, which regulates multiple target genes, can also be transferred from tumor cells to tumor cells or tumor cells to normal cells. When purified PKH67‐labeled exosomes from donor cancer cells were incubated with recipient cancer cells, they became fluorescent, indicating that an oncogene can be propagated horizontally through exosomes. CEA, carcinoembryonic antigen; HLA, human leukocyte antigen; HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; TGF; transforming growth factor; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
Similar articles
- Clinical relevance of circulating cell-free microRNAs in ovarian cancer.
Nakamura K, Sawada K, Yoshimura A, Kinose Y, Nakatsuka E, Kimura T. Nakamura K, et al. Mol Cancer. 2016 Jun 24;15(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s12943-016-0536-0. Mol Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27343009 Free PMC article. Review. - MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers in human solid tumors.
Shen J, Stass SA, Jiang F. Shen J, et al. Cancer Lett. 2013 Feb 28;329(2):125-36. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.11.001. Epub 2012 Nov 27. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 23196059 Free PMC article. Review. - Circulating microRNAs and long non-coding RNAs in gastric cancer diagnosis: An update and review.
Huang YK, Yu JC. Huang YK, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Sep 14;21(34):9863-86. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i34.9863. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26379393 Free PMC article. Review. - The impact of extracellular vesicle-encapsulated circulating microRNAs in lung cancer research.
Fujita Y, Kuwano K, Ochiya T, Takeshita F. Fujita Y, et al. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:486413. doi: 10.1155/2014/486413. Epub 2014 Sep 11. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25295261 Free PMC article. Review. - Current State of Circulating MicroRNAs as Cancer Biomarkers.
He Y, Lin J, Kong D, Huang M, Xu C, Kim TK, Etheridge A, Luo Y, Ding Y, Wang K. He Y, et al. Clin Chem. 2015 Sep;61(9):1138-55. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2015.241190. Epub 2015 Aug 3. Clin Chem. 2015. PMID: 26319452 Review.
Cited by
- Characterization of miRNAs in Milk Small Extracellular Vesicles from Enzootic Bovine Leukosis Cattle.
Tsukada F, Takashima S, Wakihara Y, Kamatari YO, Shimizu K, Okada A, Inoshima Y. Tsukada F, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 15;23(18):10782. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810782. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142686 Free PMC article. - Identification of retinopathy of prematurity related miRNAs in hyperoxia-induced neonatal rats by deep sequencing.
Zhao R, Qian L, Jiang L. Zhao R, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Dec 31;16(1):840-56. doi: 10.3390/ijms16010840. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25561234 Free PMC article. - Detection of gastric cancer-associated microRNAs on microRNA microarray comparing pre- and post-operative plasma.
Konishi H, Ichikawa D, Komatsu S, Shiozaki A, Tsujiura M, Takeshita H, Morimura R, Nagata H, Arita T, Kawaguchi T, Hirashima S, Fujiwara H, Okamoto K, Otsuji E. Konishi H, et al. Br J Cancer. 2012 Feb 14;106(4):740-7. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2011.588. Epub 2012 Jan 19. Br J Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22262318 Free PMC article. - Macro view of microRNA function in osteoarthritis.
Miyaki S, Asahara H. Miyaki S, et al. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012 Sep;8(9):543-52. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2012.128. Epub 2012 Aug 14. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012. PMID: 22890245 Free PMC article. Review. - An Autopsy Case of an Elderly Patient with Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma Presenting with a Plethora of Clinical Symptoms and Signs.
Kobayashi H, Seki R, Ujita M, Hirayama K, Yamada S, Ohashi R, Otsuki Y, Watanabe T, Yoshino T. Kobayashi H, et al. Am J Case Rep. 2020 Oct 22;21:e926177. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.926177. Am J Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 33087692 Free PMC article.
References
- Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin‐4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin‐14. Cell 1993; 75: 843–54. - PubMed
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004; 116: 281–97. - PubMed
- Kim VN, Han J, Siomi MC. Biogenesis of small RNAs in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2009; 10: 126–39. - PubMed
- Rosenfeld N, Aharonov R, Meiri E et al. MicroRNAs accurately identify cancer tissue origin. Nat Biotechnol 2008; 26: 462–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous