Unexpected roles for core promoter recognition factors in cell-type-specific transcription and gene regulation - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Unexpected roles for core promoter recognition factors in cell-type-specific transcription and gene regulation
James A Goodrich et al. Nat Rev Genet. 2010 Aug.
Abstract
The eukaryotic core promoter recognition complex was generally thought to play an essential but passive role in the regulation of gene expression. However, recent evidence now indicates that core promoter recognition complexes together with 'non-prototypical' subunits may have a vital regulatory function in driving cell-specific programmes of transcription during development. Furthermore, new roles for components of these complexes have been identified beyond development; for example, in mediating interactions with chromatin and in maintaining active gene expression across cell divisions.
Figures
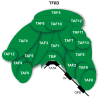
Figure 1. Core promoter recognition by TFIID
Multiple subunits of the TFIID (transcription factor IID) complex bind core promoter elements. TBP (TATA binding protein) binds TATA boxes. TAF1 (TBP associated factor 1) and TAF2 (TBP associated factor 2) bind the initiator element (Inr). TAF6 (TBP associated factor 6) and TAF9 (TBP associated factor 9) bind the downstream promoter element (DPE).
Figure 2. Roles of TRFs and TAFs in germ cell differentiation
(a) Overview of mouse spermatogenesis. TRF2 (TBP related factor 2), TAF4b (TBP associated factor 4b), and TAF7L (TBP associated factor 7L) are expressed where indicated and the effect of knocking out each of these factors is shown–,–. (b) Overview of a subset of the stages of mouse oogenesis. TRF3 and TAF4b are thought to be expressed where indicated and the effect of knocking out each of these factors is shown,,,. In the case of TAF4b, knockout could affect multiple stages; the last of these stages is indicated.
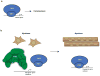
Figure 3. Roles of TRF3 and TAF3 in somatic cell differentiation
(a) TRF3 (TBP related factor 3) and TAF3 (TBP associated factor 3) function in hematopoiesis. During embryogenesis in zebrafish, TRF3 and TAF3 associate with the core promoter of the mespa gene, which encodes a transcription factor that is critical for hematopoiesis,. (b) Proposed TRF3 and TAF3 function in myogenesis. When mouse myoblasts differentiate into myotubes, levels of multiple TFIID subunits decrease,. By contrast, TAF3 levels remain constant, as do levels of TRF3. TRF3 and TAF3 form a complex in myotubes and are found together at the promoter of the myogenin gene, which encodes a transcriptional activator that is critical for myogenesis.
Figure 4. TBP bookmarks genes during mitosis
In mitotic nuclei, TBP (TATA binding protein) binds protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) and the CAP-G subunit of condensin at the core promoters of genes that were active prior to mitosis. PP2A dephosphorylates CAP-G, which inactivates condensin and keeps the core promoters from being tightly compacted in mitotic chromatin. This allows transcription of the bookmarked genes to be reactivated when cells exit mitosis and enter G1. During mitosis Pol II leaves chromatin and genes are transcriptionally inactive. Whether any general transcription factors (GTFs) other than TBP remain at bookmarked genes is unknown.
Similar articles
- Regulatory factor interactions and somatic silencing of the germ cell-specific ALF gene.
Kim M, Li D, Cui Y, Mueller K, Chears WC, DeJong J. Kim M, et al. J Biol Chem. 2006 Nov 10;281(45):34288-98. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M607168200. Epub 2006 Sep 11. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16966320 - Regulation of the initiation of eukaryotic transcription.
Gill G. Gill G. Essays Biochem. 2001;37:33-43. doi: 10.1042/bse0370033. Essays Biochem. 2001. PMID: 11758455 Review. - The DPE, a core promoter element for transcription by RNA polymerase II.
Kadonaga JT. Kadonaga JT. Exp Mol Med. 2002 Sep 30;34(4):259-64. doi: 10.1038/emm.2002.36. Exp Mol Med. 2002. PMID: 12515390 Review. - Activator-mediated disruption of sequence-specific DNA contacts by the general transcription factor TFIIB.
Evans R, Fairley JA, Roberts SG. Evans R, et al. Genes Dev. 2001 Nov 15;15(22):2945-9. doi: 10.1101/gad.206901. Genes Dev. 2001. PMID: 11711430 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Holo-TFIID controls the magnitude of a transcription burst and fine-tuning of transcription.
Pennington KL, Marr SK, Chirn GW, Marr MT 2nd. Pennington KL, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 May 7;110(19):7678-83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1221712110. Epub 2013 Apr 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23610421 Free PMC article. - Calpain induces N-terminal truncation of β-catenin in normal murine liver development: diagnostic implications in hepatoblastomas.
Lade A, Ranganathan S, Luo J, Monga SP. Lade A, et al. J Biol Chem. 2012 Jun 29;287(27):22789-98. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.378224. Epub 2012 May 21. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22613727 Free PMC article. - Context-dependent dual role of SKI8 homologs in mRNA synthesis and turnover.
Dorcey E, Rodriguez-Villalon A, Salinas P, Santuari L, Pradervand S, Harshman K, Hardtke CS. Dorcey E, et al. PLoS Genet. 2012;8(4):e1002652. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002652. Epub 2012 Apr 12. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 22511887 Free PMC article. - A Systems Biology Approach on the Regulatory Footprint of Human Endogenous Retroviruses (HERVs).
Markopoulos GS. Markopoulos GS. Diseases. 2022 Nov 2;10(4):98. doi: 10.3390/diseases10040098. Diseases. 2022. PMID: 36412592 Free PMC article. - Perspectives on the RNA polymerase II core promoter.
Kadonaga JT. Kadonaga JT. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2012 Jan-Feb;1(1):40-51. doi: 10.1002/wdev.21. Epub 2011 Dec 6. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 23801666 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Thomas MC, Chiang CM. The general transcription machinery and general cofactors. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2006;41:105–178. - PubMed
- Naar AM, Lemon BD, Tjian R. Transcriptional coactivator complexes. Annu Rev Biochem. 2001;70:475–501. - PubMed
- Conaway RC, Conaway JW. Transcription initiated by RNA polymerase II and purified transcription factors from liver: transcription factors alpha, beta gamma, and delta promote formation of intermediates in assembly of the functional preinitiation complex. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:7559–7563. - PubMed
- Biggin MD, Tjian R. Transcription Factors That Activate the Ultabithorax Promoter in Develpmentally Staged Extracts. Cell. 1988;53:699–711. - PubMed
- Wasylyk B, Kedinger C, Corden J, Brison O, Chambon P. Specific in vitro initiation of transcription on conalbumin and ovalbumin genes and comparison with adenovirus-2 early and late genes. Nature. 1980;285:367–373. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 CA025417/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 GM055235-12/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM055235/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM55235/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA25417/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases