Ribavirin as an anti-cancer therapy: acute myeloid leukemia and beyond? - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Ribavirin as an anti-cancer therapy: acute myeloid leukemia and beyond?
Katherine L B Borden et al. Leuk Lymphoma. 2010 Oct.
Abstract
Ribavirin was discovered nearly 40 years ago as a broad-spectrum antiviral drug. Recent data suggest that ribavirin may also be an effective cancer therapy. In this case, ribavirin targets an oncogene, the eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF4E, elevated in approximately 30% of cancers including many leukemias and lymphomas. Specifically, ribavirin impedes eIF4E mediated oncogenic transformation by acting as an inhibitor of eIF4E. In a phase II clinical trial, ribavirin treatment led to substantial clinical benefit in patients with poor-prognosis acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Here molecular targeting of eIF4E correlated with clinical response. Ribavirin also targets a key enzyme in the guanosine biosynthetic pathway, inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH), and also modulates immunity. Parallels with known antiviral mechanisms could be informative; however, after 40 years, these are not entirely clear. The antiviral effects of ribavirin appear cell-type specific. This variation likely arises for many reasons, including cell specific variations in ribavirin metabolism as well as virus specific factors. Thus, it seems that the mechanisms for ribavirin action in cancer therapy may also vary in terms of the cancer/tissue under study. Here we review the anticancer activities of ribavirin and discuss the possible utility of incorporating ribavirin into diverse cancer therapeutic regimens.
Figures
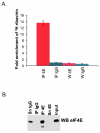
Figure 1. 3H ribavirin associates with eIF4E in living cells
A. 0.7 uM 3H ribavirin was incubated with eIF4E for 24 hours, FaDu cells were washed, crosslinked with formaldehyde (1% formaldehyde for 15 minutes), lysed and immunoprecipitated (IP) with IgG or anti-eIF4E antibody according to [66]. The ribavirin was tritiated at the 5 position of the triazole ring (Moravek Pharmaceuticals). The extent of ribavirin binding was assessed by scintillation counting. Note that IPs were washed six times prior to scintillation counting and the sixth wash (W) was also examined for 3H ribavirin content. B. Western blot analysis confirmed that eIF4E was present in the eIF4E IP but not in the IgG control. These are taken from the same cells used for scintillation counting.
Similar articles
- Targeting the oncogene eIF4E in cancer: From the bench to clinical trials.
Borden KL. Borden KL. Clin Invest Med. 2011 Dec 1;34(6):E315. doi: 10.25011/cim.v34i6.15889. Clin Invest Med. 2011. PMID: 22129918 - Molecular targeting of the oncogene eIF4E in acute myeloid leukemia (AML): a proof-of-principle clinical trial with ribavirin.
Assouline S, Culjkovic B, Cocolakis E, Rousseau C, Beslu N, Amri A, Caplan S, Leber B, Roy DC, Miller WH Jr, Borden KL. Assouline S, et al. Blood. 2009 Jul 9;114(2):257-60. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-02-205153. Epub 2009 May 11. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19433856 Clinical Trial. - Molecular targeting of the UDP-glucuronosyltransferase enzymes in high-eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E refractory/relapsed acute myeloid leukemia patients: a randomized phase II trial of vismodegib, ribavirin with or without decitabine.
Assouline S, Gasiorek J, Bergeron J, Lambert C, Culjkovic-Kraljacic B, Cocolakis E, Zakaria C, Szlachtycz D, Yee K, Borden KLB. Assouline S, et al. Haematologica. 2023 Nov 1;108(11):2946-2958. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2023.282791. Haematologica. 2023. PMID: 36951168 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - The eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF4E in the nucleus: taking the road less traveled.
Osborne MJ, Borden KL. Osborne MJ, et al. Immunol Rev. 2015 Jan;263(1):210-23. doi: 10.1111/imr.12240. Immunol Rev. 2015. PMID: 25510279 Free PMC article. Review. - Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E as a novel therapeutic target in hematological malignancies and beyond.
Pettersson F, Del Rincon SV, Miller WH Jr. Pettersson F, et al. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2014 Sep;18(9):1035-48. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2014.937426. Epub 2014 Jul 8. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2014. PMID: 25004955 Review.
Cited by
- The Impact of Post-transcriptional Control: Better Living Through RNA Regulons.
Culjkovic-Kraljacic B, Borden KLB. Culjkovic-Kraljacic B, et al. Front Genet. 2018 Nov 5;9:512. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00512. eCollection 2018. Front Genet. 2018. PMID: 30455716 Free PMC article. Review. - The biological and therapeutic relevance of mRNA translation in cancer.
Blagden SP, Willis AE. Blagden SP, et al. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2011 May;8(5):280-91. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2011.16. Epub 2011 Mar 1. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21364523 Review. - The Development of Novel Therapies for the Treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML).
Assouline S, Cocolakis E, Borden KL. Assouline S, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2012 Nov 2;4(4):1161-79. doi: 10.3390/cancers4041161. Cancers (Basel). 2012. PMID: 24213503 Free PMC article. - Cryptotanshinone induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of multidrug resistant human chronic myeloid leukemia cells by inhibiting the activity of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E.
Ge Y, Cheng R, Zhou Y, Shen J, Peng L, Xu X, Dai Q, Liu P, Wang H, Ma X, Jia J, Chen Z. Ge Y, et al. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012 Sep;368(1-2):17-25. doi: 10.1007/s11010-012-1338-3. Epub 2012 May 22. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22614784 - Ribavirin Does Not Impair the Suppressive Activity of Foxp3(+)CD4(+)CD25(+) Regulatory T Cells.
Lee J, Choi YS, Shin EC. Lee J, et al. Immune Netw. 2013 Feb;13(1):25-9. doi: 10.4110/in.2013.13.1.25. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Immune Netw. 2013. PMID: 23559897 Free PMC article.
References
- Sidwell RW, Huffman JH, Khare GP, Allen LB, Witkowski JT, Robins RK. Broad-spectrum antiviral activity of Virazole: 1-beta-D-ribofuranosyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide. Science. 1972;177:705–6. - PubMed
- Hong Z, Cameron CE. Pleiotropic mechanisms of ribavirin antiviral activities. Prog Drug Res. 2002;59:41–69. - PubMed
- Parker WB. Metabolism and antiviral activity of ribavirin. Virus Res. 2005;107:165–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources