Models for the functions of Arf GAPs - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Models for the functions of Arf GAPs
Michael P East et al. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011 Feb.
Abstract
Arf GAPs (ADP-ribosylation factor GTPase-activating proteins) are essential components of Arf (ADP-ribosylation factor) signaling pathways. Arf GAPs stimulate the hydrolysis of GTP to GDP to transition Arf from the active, GTP bound, state to the inactive, GDP bound, state. Based on this activity, Arf GAPs were initially proposed to function primarily or exclusively as terminators of Arf signaling. Further studies of Arf GAPs have revealed that they also function as effectors of Arf signaling in at least a few steps or processes in which Arfs are not directly involved. In this review we discuss the non-canonical functions of Arf GAPs and address several key questions in the field, including: whether (1) Arf GAPs are terminators or effectors of Arf signaling, (2) Arf GAPs positively or negatively regulate COPI assembly, (3) Arf GAPs are involved in vesicle fission, and (4) Arf GAPs regulate vesicle uncoating.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
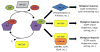
Figure 1
Model of Arf GAP functions in Arf-dependent signaling and termination. The GTP cycle of Arf depends upon Arf GEFs to facilitate the exchange of bound GDP for GTP and Arf GAPs to stimulate hydrolysis of GTP to GDP. GTP binding by Arf induces a conformational change that increases the affinity of Arf for effector proteins ultimately leading to a biological response, mediated by effectors. As discussed in the text, association with Arf GAPs or with Arf GAP/effector complexes also results in biological responses, suggesting that Arf GAPs can serve as Arf effectors. Thus, Arf GAPs have at least dual roles in regulating Arf signaling as terminators and effectors. This conclusion also points to the regulation of Arf GAP activity as a critical, yet understudied, aspect of Arf and Arf GAP signaling.
Similar articles
- The role of ADP-ribosylation factor and SAR1 in vesicular trafficking in plants.
Memon AR. Memon AR. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Jul 1;1664(1):9-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2004.04.005. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15238254 Review. - ArfGAP1 acts as a GTPase-activating protein for human ADP-ribosylation factor-like 1 protein.
Feng HP, Cheng HY, Hsiao TF, Lin TW, Hsu JW, Huang LH, Yu CJ. Feng HP, et al. FASEB J. 2021 Apr;35(4):e21337. doi: 10.1096/fj.202000818RR. FASEB J. 2021. PMID: 33715220 - Arf GAPs and membrane traffic.
Nie Z, Randazzo PA. Nie Z, et al. J Cell Sci. 2006 Apr 1;119(Pt 7):1203-11. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02924. J Cell Sci. 2006. PMID: 16554436 Review. - Arf GAPs: A family of proteins with disparate functions that converge on a common structure, the integrin adhesion complex.
Vitali T, Girald-Berlingeri S, Randazzo PA, Chen PW. Vitali T, et al. Small GTPases. 2019 Jul;10(4):280-288. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2017.1299271. Epub 2017 Mar 31. Small GTPases. 2019. PMID: 28362242 Free PMC article. Review. - Arfs at a glance.
Jackson CL, Bouvet S. Jackson CL, et al. J Cell Sci. 2014 Oct 1;127(Pt 19):4103-9. doi: 10.1242/jcs.144899. Epub 2014 Aug 21. J Cell Sci. 2014. PMID: 25146395 Review.
Cited by
- Arf GTPase-Activating proteins ADAP1 and ARAP1 regulate incorporation of CD63 in multivesicular bodies.
Suzuki K, Okawa Y, Akter S, Ito H, Shiba Y. Suzuki K, et al. Biol Open. 2024 May 15;13(5):bio060338. doi: 10.1242/bio.060338. Epub 2024 May 10. Biol Open. 2024. PMID: 38682696 Free PMC article. - Identification of Atg2 and ArfGAP1 as Candidate Genetic Modifiers of the Eye Pigmentation Phenotype of Adaptor Protein-3 (AP-3) Mutants in Drosophila melanogaster.
Rodriguez-Fernandez IA, Dell'Angelica EC. Rodriguez-Fernandez IA, et al. PLoS One. 2015 Nov 13;10(11):e0143026. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143026. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26565960 Free PMC article. - A competitive nucleotide binding inhibitor: in vitro characterization of Rab7 GTPase inhibition.
Agola JO, Hong L, Surviladze Z, Ursu O, Waller A, Strouse JJ, Simpson DS, Schroeder CE, Oprea TI, Golden JE, Aubé J, Buranda T, Sklar LA, Wandinger-Ness A. Agola JO, et al. ACS Chem Biol. 2012 Jun 15;7(6):1095-108. doi: 10.1021/cb3001099. Epub 2012 Apr 23. ACS Chem Biol. 2012. PMID: 22486388 Free PMC article. - Direct Functional Interaction of the Kinesin-13 Family Member Kinesin-like Protein 2A (Kif2A) and Arf GAP with GTP-binding Protein-like, Ankyrin Repeats and PH Domains1 (AGAP1).
Luo R, Chen PW, Wagenbach M, Jian X, Jenkins L, Wordeman L, Randazzo PA. Luo R, et al. J Biol Chem. 2016 Oct 7;291(41):21350-21362. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.732479. Epub 2016 Aug 16. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27531749 Free PMC article. - Roles for ELMOD2 and Rootletin in ciliogenesis.
Turn RE, Linnert J, Gigante ED, Wolfrum U, Caspary T, Kahn RA. Turn RE, et al. Mol Biol Cell. 2021 Apr 15;32(8):800-822. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E20-10-0635. Epub 2021 Feb 17. Mol Biol Cell. 2021. PMID: 33596093 Free PMC article.
References
- Kahn RA, Gilman AG. The protein cofactor necessary for ADP-ribosylation of Gs by cholera toxin is itself a GTP binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1986;261:7906–11. - PubMed
- Cukierman E, Huber I, Rotman M, Cassel D. The ARF1 GTPase-activating protein: zinc finger motif and Golgi complex localization. Science. 1995;270:1999–2002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 GM090158-01A1/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM067226/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM061268/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM090158/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM067226-08/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM061268/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM067226-07/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM067226/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources