Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase: is it an immune suppressor? - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase: is it an immune suppressor?
Hatem Soliman et al. Cancer J. 2010 Jul-Aug.
Abstract
This article covers what is currently known about the role of the enzyme indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) in cancer-related immunosuppression and the clinical research on IDO inhibitors. A PUBMED search was performed using the terms IDO, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, 1-MT. IDO is an inducible enzyme that catalyzes the rate-limiting first step in tryptophan catabolism. This enzyme is overexpressed in response to IFNgamma in a variety of different malignancies. IDO causes immunosuppression through breakdown of tryptophan in the tumor microenvironment and tumor-draining lymph nodes. The depletion of tryptophan and toxic catabolites renders effector T cells inactive and dendritic cells immunosuppressive. Preclinical data suggest that IDO inhibition can delay tumor growth, enhance dendritic cell vaccines, and synergize with chemotherapy through immune-mediated mechanisms. The lead IDO inhibitor, d-1-methyl-tryptophan (d-1-MT), was selected for phase I trials and seems to have immune modulating activity. Subsequently, another isoform of IDO, IDO2, was discovered and found to be the target of d-1-MT. Multiple single-nucleotide polymorphisms in IDO2 affecting its catalytic activity may serve as a pharmacogenetic predictive biomarker for d-1-MT. The IDO pathway is an important mechanism of tumor-related immunosuppression and blocking it could improve cancer immunotherapy outcomes. Clinical development of d-1-MT and other IDO inhibitors as systemic immunomodulators to be combined with other immune modulators, vaccines, and chemotherapy are ongoing.
Figures
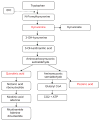
FIGURE 1
Metabolism of tryptophan. The catabolites in red are directly toxic to T lymphocytes.
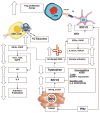
FIGURE 2
The mechanism of action of IDO. IDO causes decreased cytotoxic T-cell activity and systemic anergy via tryptophan depletion and toxic tryptophan catabolites. Treg indicates T regulatory cell; Trp, tryptophan; pDCs, plasmacytoid dendritic cells.
Similar articles
- Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in T-cell tolerance and tumoral immune escape.
Katz JB, Muller AJ, Prendergast GC. Katz JB, et al. Immunol Rev. 2008 Apr;222:206-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00610.x. Immunol Rev. 2008. PMID: 18364004 Review. - Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO): Biology and Target in Cancer Immunotherapies.
Selvan SR, Dowling JP, Kelly WK, Lin J. Selvan SR, et al. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2016;16(9):755-764. doi: 10.2174/1568009615666151030102250. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2016. PMID: 26517538 Review. - Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in immune suppression and cancer.
Muller AJ, Prendergast GC. Muller AJ, et al. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2007 Feb;7(1):31-40. doi: 10.2174/156800907780006896. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2007. PMID: 17305476 Review. - Influence of tryptophan contained in 1-Methyl-Tryptophan on antimicrobial and immunoregulatory functions of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase.
Schmidt SK, Siepmann S, Kuhlmann K, Meyer HE, Metzger S, Pudelko S, Leineweber M, Däubener W. Schmidt SK, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44797. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044797. Epub 2012 Sep 13. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23028625 Free PMC article. - Novel tryptophan catabolic enzyme IDO2 is the preferred biochemical target of the antitumor indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibitory compound D-1-methyl-tryptophan.
Metz R, Duhadaway JB, Kamasani U, Laury-Kleintop L, Muller AJ, Prendergast GC. Metz R, et al. Cancer Res. 2007 Aug 1;67(15):7082-7. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1872. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17671174
Cited by
- Necrostatin-1 analogues: critical issues on the specificity, activity and in vivo use in experimental disease models.
Takahashi N, Duprez L, Grootjans S, Cauwels A, Nerinckx W, DuHadaway JB, Goossens V, Roelandt R, Van Hauwermeiren F, Libert C, Declercq W, Callewaert N, Prendergast GC, Degterev A, Yuan J, Vandenabeele P. Takahashi N, et al. Cell Death Dis. 2012 Nov 29;3(11):e437. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2012.176. Cell Death Dis. 2012. PMID: 23190609 Free PMC article. - Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-1 (IDO1) enhances survival and invasiveness of endometrial stromal cells via the activation of JNK signaling pathway.
Mei J, Li MQ, Ding D, Li DJ, Jin LP, Hu WG, Zhu XY. Mei J, et al. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013;6(3):431-44. Epub 2013 Feb 15. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23411497 Free PMC article. - Stable triangle: nanomedicine-based synergistic application of phototherapy and immunotherapy for tumor treatment.
Cai W, Sun T, Qiu C, Sheng H, Chen R, Xie C, Kou L, Yao Q. Cai W, et al. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Oct 18;22(1):635. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02925-3. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39420366 Free PMC article. Review. - Intra-articular delivery of an indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase galectin-3 fusion protein for osteoarthritis treatment in male Lewis rats.
Partain BD, Bracho-Sanchez E, Farhadi SA, Yarmola EG, Keselowsky BG, Hudalla GA, Allen KD. Partain BD, et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023 Sep 18;25(1):173. doi: 10.1186/s13075-023-03153-0. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37723593 Free PMC article. - Immune response and immunopathology during toxoplasmosis.
Dupont CD, Christian DA, Hunter CA. Dupont CD, et al. Semin Immunopathol. 2012 Nov;34(6):793-813. doi: 10.1007/s00281-012-0339-3. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Semin Immunopathol. 2012. PMID: 22955326 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Bickels J, Kollender Y, Merinsky O, et al. Coley’s toxin: historical perspective. Isr Med Assoc J. 2002;4:471– 472. - PubMed
- Hoption Cann SA, van Netten JP, van Netten C, et al. Spontaneous regression: a hidden treasure buried in time. Med Hypotheses. 2002;58:115–119. - PubMed
- Higuchi K, Hayaishi O. Enzymic formation of D-kynurenine from D-tryptophan. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967;120:397– 403. - PubMed
- Yamamoto S, Hayaishi O. Tryptophan pyrrolase of rabbit intestine. D- and L-tryptophan-cleaving enzyme or enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1967;242:5260–5266. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials